Smart grids are advanced electrical grid systems that utilize digital technology to monitor and manage the transport of electricity from all generation sources to meet the varying electricity demands of end users.
They are equipped with smart meters, sensors, and controls, which enable two-way communication between the utility and its customers.
This technology enhances the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity distribution.
Our blog post explores how Smart Grids and Green Building Technologies innovations are revolutionizing sustainability practices in three distinct ways: enhancing energy efficiency, promoting eco-friendly structures, and reshaping the future of green technology.
Smart Grids and Green Building Technologies
Smart Grids and Green Building Technologies are at the forefront of sustainable innovation, revolutionizing how we manage energy and construct eco-friendly spaces.
Let’s delve into each of these transformative technologies separately to understand their significant impact on fostering sustainability.
How Does Smart Grids Work?
Renewable Integration
Smart grid technology efficiently integrates renewable energy sources at scale, allowing for increased reliance on clean and sustainable power generation.
Electric Transportation Support
Facilitates the growth of the electric transportation market by providing a robust infrastructure for charging stations and managing the increased demand for electricity.
Enhanced Sustainability
Enables a new era of sustainability by leveraging advanced technologies to optimize energy use, reduce wastage, and enhance overall grid efficiency.
Data-Driven Efficiency
Utilizes real-time data from sensors throughout the grid to optimize the transmission and distribution of electricity, ensuring more efficient and reliable energy delivery.
Consumer Interaction
Transforms the traditional producer-controlled grid into a more consumer-interactive model, empowering users to actively engage in energy management and conservation.
Environmental Responsiveness
Promotes a less centralized and more environmentally responsive grid model, aligning with the global push for eco-friendly energy systems.
Transactive Intelligence
Enables transactive intelligence by leveraging computing power to make data actionable, fostering a dynamic and responsive electric grid.
Internet-Inspired Transformation
Draws inspiration from Internet technologies to transform the utility and electric grid, utilizing tools and techniques that proved successful in the digital realm.
Carbon Emission Reduction
Contributes significantly to carbon emission reduction by optimizing energy distribution, promoting the use of renewables, and fostering energy-efficient practices
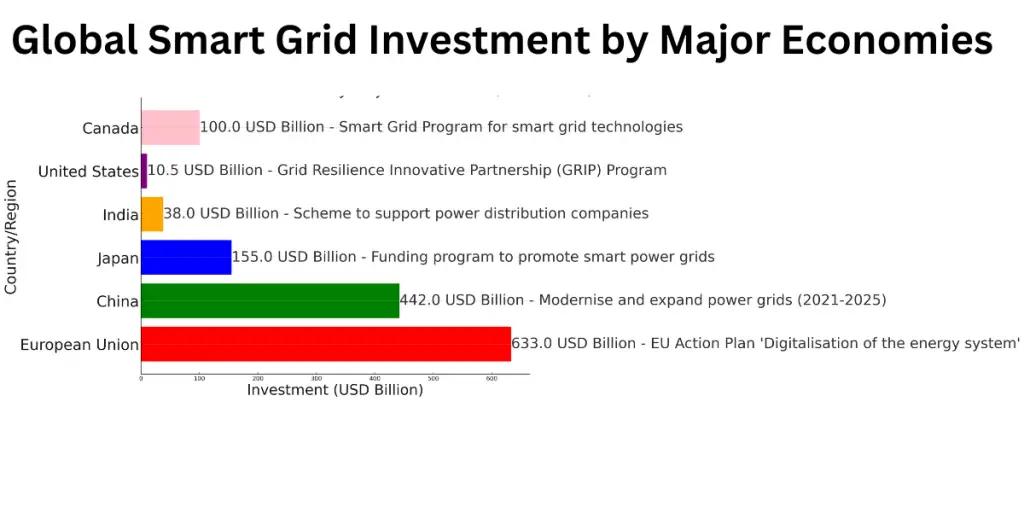
Case Studies on Smart Grid Implementation in Turkey and Colombia
Turkey’s Smart Grid Development
Government Investment and Policy
- Turkey’s government and stakeholders have been actively investing in smart energy technologies. Approximately $25.2 million has been invested, focusing on eliminating power outages and reducing transmission and distribution losses.
- Turkey aims to generate 30% of its energy from renewable sources by 2023, with ongoing projects in solar and wind energy.
Smart Meter Systems
Following the EU directive, Turkey has exceeded its target by installing 4.6 million smart meters by 2016, surpassing the annual target of 3.6 million meters.
Private Sector Involvement
Enerjisa, Turkey’s largest energy distribution service company, invested $28.6 million in smart energy infrastructure, contributing to Turkey’s first digital power plant.
Strategic Focus Areas
Turkey’s roadmap for smart grid includes advanced network monitoring, IT infrastructure, distributed energy integration, and smart grid strategy.
Colombia’s Smart Grid Initiatives
National Strategy and Roadmap
“Smart Grid Colombia Vision 2030” is a comprehensive plan, focusing on improving electrical system efficiency, integrating renewable energy standards, and enhancing electricity system reliability.
Pilot Projects in Major Cities
Pilot projects involving smart meter systems have been conducted in cities like Bogotá, Medellín, and Cali.
These projects are crucial for the phased implementation of smart grid systems across Colombia by 2030.
Energy Diversity and Renewable Integration
Colombia is focusing on Distributed Energy Resource (DER) architecture to manage operations and contribute to the system optimally. Regions like the Caribbean and La Guajira are seeing significant investments in wind and solar power.
Infrastructure Development
The development and strengthening of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) are prioritized, with an emphasis on creating a flexible and sustainable energy supply.
Green Building Technologies
Energy-efficient building designs, green construction materials, and smart building technologies play an important role in reducing carbon emissions from the construction and operation of buildings.
Green building meaning
Green building practices encompass a variety of strategies, such as the utilization of sustainable materials like wood and bamboo, integration of natural lighting, and reliance on renewable energy sources, among others.
These approaches contribute to reduced carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, enhanced indoor air quality, and decreased operational expenses.
How does it work?
Material Efficiency
By prioritizing recycled content and using reclaimed materials, green building practices effectively cut down on the need for new materials, minimizing resource consumption and lowering associated CO2 levels.

Energy Efficiency
Green buildings excel in energy efficiency, outperforming traditional construction methods.
They achieve this through high-insulation value materials, and energy-efficient systems like windows and heating/cooling, resulting in reduced energy consumption and subsequent CO2 emissions.
Renewable Energy Integration
Utilizing renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, green buildings further diminish their reliance on conventional power sources.
This not only reduces carbon emissions but also aligns with sustainable energy practices.

Indoor Air Quality Improvement
Green buildings enhance indoor air quality by efficiently maintaining comfortable temperatures.
This is achieved through careful material selection, insulation, and advanced systems, reducing the need for excessive energy use and subsequently lowering CO2 emissions.
Proper Material Disposal
Green building practices prioritize responsible disposal methods, including recycling and reusing solid waste and ensuring proper handling of hazardous materials.
This approach minimizes the generation of waste and, consequently, lowers associated CO2 levels.

This table summarizes the principles, offering a structured approach for organizations aiming for sustainable and carbon-neutral building practices.
| Principle | Description |
| Calculate Carbon Footprint | Assess the carbon footprint of your portfolio for a recent representative year. |
| Set Net-Zero Target | Aim for net-zero carbon by 2050, with an interim goal of reducing 50% emissions by 2030. |
| Measure Embodied Carbon | Record embodied carbon in new developments and major refurbishments. |
| Maximize Emissions Reductions | Ensure new developments and refurbishments align with net-zero carbon goals. |
| Drive Energy Optimization | Optimize energy use across existing assets and new developments. |
| Maximize On-site Renewable Energy | Increase the supply of on-site renewable energy. |
| Procure Renewable Off-site Energy | Ensure off-site energy is from renewable sources. |
| Reduce Scope 3 Emissions | Engage stakeholders to reduce Scope 3 emissions in your value chain. |
| Procure Carbon Offsets | Use high-quality carbon offsets for residual emissions. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Collaborate with stakeholders for joint projects and cost-benefit sharing. |
Annual Global EV Growth
Here is a graph illustrating the annual growth in global EV sales based on the statistics from the “Annual update on the global transition to electric vehicles: 2022” document.
The graph shows a significant increase in EV sales from 2021 to 2022, highlighting the rapid growth and adoption of EVs globally. In 2022, the annual EV sales reached 10 million, which is a 54% increase from the previous year.
Cumulative global EV sales: This “milestone” graph depicts the growth in cumulative EV sales from 2010 to 2022, with the significant achievement of 29 million sales by the end of 2022 highlighted.
Conclusion
Smart Grids and Green Building Technologies work together effectively to address Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions. Smart Grids use advanced digital tools to manage electricity distribution efficiently, incorporating renewable energy sources and maximizing energy efficiency.
Meanwhile, Green Building Technologies concentrates on eco-friendly construction and operational practices, cutting down energy needs and lessening environmental consequences.