The Greenhouse Gas Protocol or GHG Protocol is the most widely used international standard for calculating and reporting greenhouse gas emissions.
The GHG Protocol helps organizations measure, manage, and report their greenhouse gas emissions. It provides a framework that any organization, of any size, from any sector can use.
This post will explain the GHG Protocol and how it can help organizations reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Calculate fuel emissions effortlessly with our Emissions From Fuel Consumption Calculator
Evaluate carbon emission calculation using our Carbon Emission Calculator
Assess emissions resulting from fuel consumption with our Vehicle Emission Calculator
What is GHG Protocol?
The GHG Protocol is a set of standards and guidelines used to measure, report, and verify greenhouse gas emissions. It was established in 1998, and its first corporate standard was published in 2001.
It is developed by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) in collaboration with the World Resource Institute. It helps companies and organizations understand their greenhouse gas emissions and take steps to reduce them.
It covers scope emissions such as scopes 1, 2, and 3 and standards for different use cases. The standards keep updating periodically, and GHG protocol established training and tools to calculate carbon emissions.
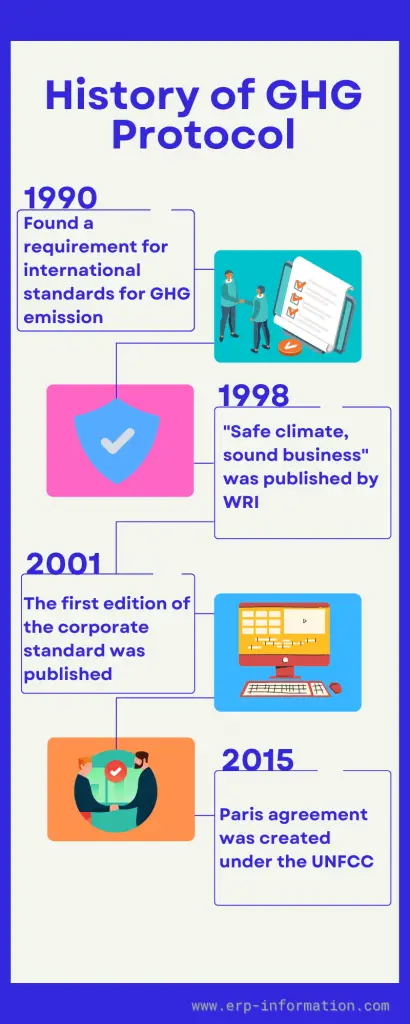
History of GHG Protocol
In the late 1990s
The world resource institute and world business council for sustainable development found a requirement for international standards for greenhouse gas emission accounting and reporting.
In 1998
A report named “Safe Climate, Sound Business” was published by WRI. That report determined the actions to be taken to reduce GHG emissions, including the requirement of standardized measurement of GHG emissions.
WBCSD ALSO thought similarly and met the WRI higher officials and agreed with some standard methods for GHG accounting.
In 2001
The first edition of the corporate standard was published with standard guidance on how organizations can measure emissions.
In 2015
The Paris Agreement was created under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCC), which wants countries to do their best to slow global temperature rise. That means adapting to changes that are already occurring and making a continuous effort over time.
Who Uses the GHG Protocol?
Governments, companies, organizations, cities, and countries use the GHG Protocol to measure, report, and verify greenhouse gas emissions.
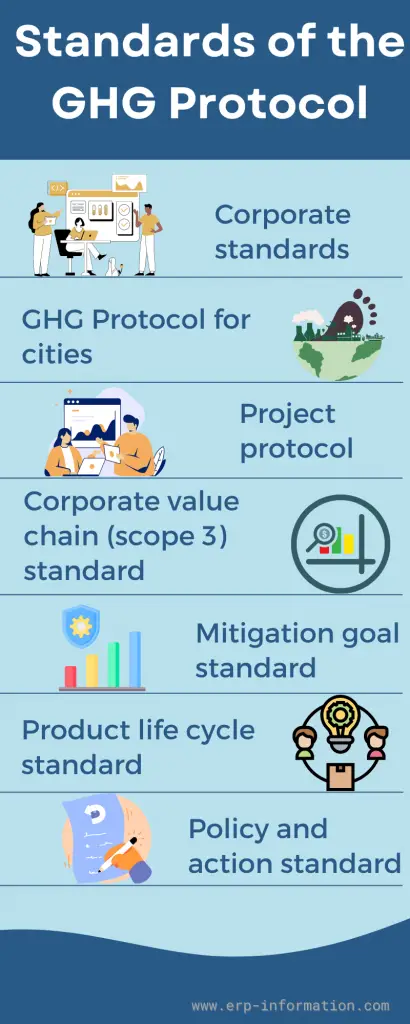
Standards of the Greenhouse Gas Protocol
Corporate standards
Organizations, NGOs, universities, and government agencies use this standard. The corporate accounting and reporting standard guides organizations to prepare GHG emission INVENTORY.
This standard contains tracking and monitoring seven greenhouse gas emissions that include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PCFs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3).
Benefits
- It allows organizations to have a GHG inventory of accurate accounts of emissions.
- It reduces the costs of compiling a GHG inventory.
- It informs organizations to construct an effective strategy to control and monitor GHG emissions.
- It increases transparency and consistency in GHG accounting and reporting among organizations.
GHG protocol for cities
The protocol for cities tells the importance of GHG emissions throughout the world. It is an accounting and reporting standard for cities.
We know, Cities are the greatest source of carbon dioxide emissions. Around 75% of the carbon emissions come from cities. So it is necessary to determine where the emissions come from and measure them.
This protocol provides standards and necessary tools to measure emissions, build emission strategies, and set goals to reduce emissions.
GHG Protocol standard for cities is created by the GHG protocol community – Scale Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventories (GPC). In addition, organizations such as The World Resources Institute, C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group, and ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability (ICLEI) are involved in this community.
Benefits
- The standard allows cities to construct a complete GHG inventory to reach climate action planning.
- It helps cities achieve the real goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and monitoring their performance.
- Cities can ensure that they follow the principles of internationally recognized greenhouse gas accounting and reporting.
Project protocol
Project protocol is a project accounting tool to qualify the greenhouse gas reduction benefits for climate change mitigation projects.
This standard offers particular features, methods, and concepts to reduce GHG Emissions and increase emission removals from climate change mitigation projects.
It allows project creators such as organizations, cities, and countries to include GHG accounting in mitigation projects like reforestation, renewable energy, decreasing ocean acidification, etc.
Corporate value chain (scope 3) standard
The Corporate value chain accounting and reporting standard helps organizations to analyze their scope three emissions and reduce them.
We know scope 3 emissions are indirect. Production, transportation of products, and overall organization’s upstream and downstream activities are the main sources of Scope 3 or value chain emissions.
Tracking and monitoring it is a daunting task for organizations. So to help organizations to come out of these difficulties, GHG protocol introduced this corporate value chain standard in 2011. This is the only internationally accepted standard for organizations to account for and report scope 3 emissions.
Value chain standard allows companies to assess 15 categories of value chain emissions.
Mitigation goal standard
This standard is all about guidelines on how to reduce GHG emissions. The above four standards are about measuring and reporting GHG emissions. But mitigation goal standard provides guidelines to cities and countries on achieving their GHG emissions reduction targets.
It helps to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement and allows them to analyze and report their performance in reducing emissions.
Product life cycle standard
Product life cycle accounting and reporting standards analyze the environmental impact of products in their manufacturing process and find a way to reduce them.
2300 people from 55 countries are involved in developing this standard. The standard helps to produce more sustainable products as it helps to measure greenhouse gas emissions associated with the product life cycle, including purchasing raw materials, production, transportation, storage, and disposal.
Policy and action standard
This standard estimate the greenhouse gas effect of policies and actions. By analyzing the GHG impact of various policies, analysts can improve the efficacy of these policy choices and learn where it would be most practical to allocate resources—the national, state, provincial, and municipal policymakers use this standard.
Benefits
- It provides a standardized method to estimate and report the change in greenhouse gas emissions and removals.
- Users can assess the accurate, transparent, and consistent GHG effects of policies and actions.
- It allows policymakers to build efficient strategies to manage and reduce GHG emissions.
- It creates consistent and transparent public reporting of emissions impacts and policy effectiveness.
GHG Protocol Scopes
It is increasingly important for organizations to understand and reduce their carbon footprints to meet environmental goals. A key element of carbon footprinting is understanding the difference between Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions.
Scope 1
These emissions are directly created by the organization from sources owned or controlled by the organization. That includes emissions from factory operations, a fleet of vehicles, business travel, boilers for space heating and cooling, and on-site electricity generation (such as fuel cells or renewables).
Scope 2
These emissions refer to indirect energy-related activities such as purchased electricity and steam.
Scope 3
At the same time, Scope 3 incorporates all other indirect sources, such as waste production, water use, supply chain activities, air travel, product transportation, and customer use.
In summary, understanding the distinction between scope 1 and beyond is essential to any business’s plan for reducing its overall carbon footprint. With a clear understanding of these distinctions, it becomes much easier for organizations to pinpoint areas of emissions reduction focus and develop effective strategies to reduce their impact on the environment.
FAQ
Why is greenhouse gas protocol useful for companies?
The greenhouse gas protocol is useful for companies because it provides a framework for understanding, measuring, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It also helps companies to track and report their emissions and to compare their performance with other companies.
The survey found 92% of companies responding to the CDP were generating emissions measured using a standard for emissions of greenhouse gases in 2016.
GHG corporate standards and value chain standards have been widely used for corporate use. Corporate standards assist companies in measuring and maintaining their emissions and greenhouse gases in their operations. In contrast, the value chain standard enables them to audit carbon over their whole value chain.
Value chains in most industries generate almost 90% of global greenhouse gas emissions. The value chain standards of the GHG Protocol help reduce their corresponding emission levels.
What are the 6 greenhouse gases Kyoto Protocol?
Six greenhouse gases regulated by the Kyoto Protocol are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
Conclusion
Greenhouse gas protocol, also known as GHG protocol, is a set of internationally accepted guidelines for organizations to measure and report their greenhouse gas emissions. Since its inception, it has been adopted by public and private sector organizations worldwide.
Ultimately, It provides organizations with a clear pathway to measure and report their impact on global climate change. As more organizations recognize this need to account for their emissions, GHG protocols will become even more important in helping support sustainability efforts.
This post has discussed the basics of GHG protocol, its importance in understanding and managing greenhouse gas emissions, and its standards.
Reference