Hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, producing water as a byproduct. This technology provides a clean energy alternative, particularly in the transportation and industrial sectors.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells Overview
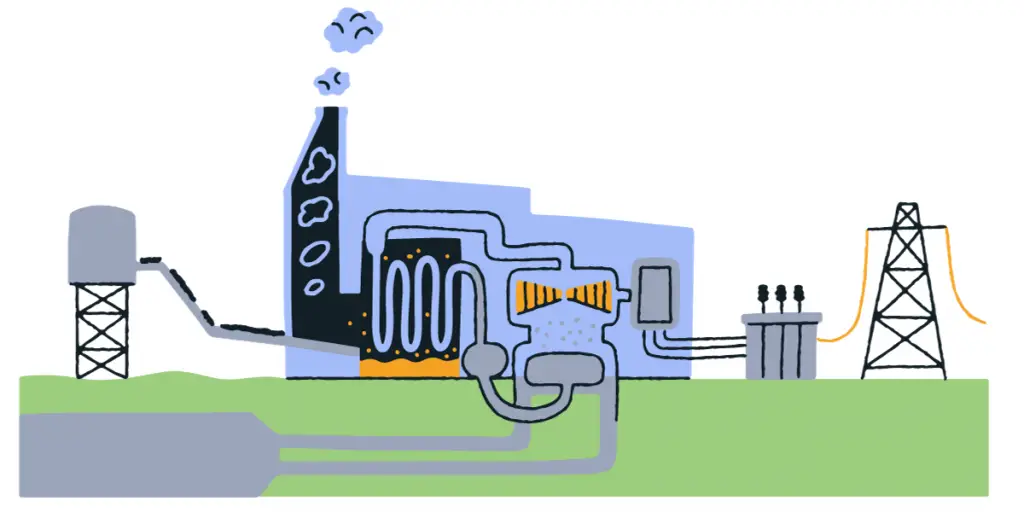
Hydrogen fuel cells are electrochemical devices that convert hydrogen fuel directly into electricity, with water and heat as byproducts. Hydrogen Fuel Cells consist of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte, typically made of proton-conducting material.
When hydrogen is supplied to the anode and oxygen to the cathode, a chemical reaction occurs, releasing electrons and creating an electric current. This is one of the most powerful technologies to reduce carbon emissions in the present world.
Work Process of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
- Hydrogen supply
- Hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode of the fuel cell.
- Electrochemical reaction
- At the anode, hydrogen molecules undergo an electrochemical reaction, splitting into protons and electrons.
- Ion Exchange
- Protons move through the electrolyte, while electrons flow through an external circuit, creating an electric current.
- Combination with Oxygen
- At the cathode, oxygen from the air combines with protons and electrons, producing water and heat as byproducts.
- Electricity generation
- The electric current generated powers electrical devices or is stored for later use.
Applications in Different Industries
Fuel cell vehicles use hydrogen fuel cells to power electric motors, providing an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional combustion engines.
Hydrogen fuel cells can be employed to generate on-site power for commercial buildings, ensuring energy resiliency and reducing dependence on the grid.
Fuel cell buses utilize hydrogen fuel cells to provide efficient and clean public transportation options.
The Fuel Cell Technologies Office (FCTO) focuses on research and development to advance hydrogen and fuel cell technologies. This includes innovations for transportation and various applications to enhance energy security and support a robust domestic economy.
By promoting the use of hydrogen and fuel cells, the FCTO contributes to energy security by diversifying energy sources and reducing dependence on traditional fuels.
Fuel cells offer a resilient energy solution, particularly in critical infrastructure, ensuring continuous power supply even in the face of disruptions.
Study
The global demand for hydrogen has been historically met through methods that result in significant carbon emissions, mainly from fossil fuels.
In 2020, hydrogen demand reached 90 million tonnes (Mt), primarily utilized in refining and industrial applications, contributing to approximately 900 Mt of CO2 emissions. However, there is optimism surrounding the transition to cleaner hydrogen production methods.
Over the past five years, electrolyzer capacity doubled, reaching just over 300 megawatts (MW) by mid-2021. The promising trend continues, with approximately 350 projects in various stages of development, aiming to elevate global electrolyzer capacity to an impressive 54 gigawatts (GW) by 2030.
An additional 40 projects, accounting for over 35 GW, are in the early stages of development. If these initiatives come to fruition, the global supply of hydrogen from electrolyzers could surpass 8 million tonnes by 2030.
Recent updates
Europe leads the charge in deploying Electrolyzer capacity, boasting 40% of the global installed capacity.
With ambitious hydrogen strategies in place, particularly from the European Union and the United Kingdom, Europe is expected to maintain its dominance in the near term.
Australia is poised to catch up with Europe in the coming years, driven by its ambitious plans.
Latin America and the Middle East are also anticipated to contribute significantly to electrolyzer capacity, especially for hydrogen export.
Despite a slower start, China is rapidly expanding its hydrogen projects, and the United States is intensifying its efforts with the recently announced Hydrogen Earthshot initiative.
Worldwide development in Hydrogen fuel cells
| Country | Notable Hydrogen Initiatives |
| China | Active participant in developing hydrogen solutions. Rapidly expanding hydrogen projects and initiatives |
| Republic of Korea | Issued a hydrogen economy roadmap in 2020, envisioning the production of 6.2 million hydrogen and fuel cell-based vehicles and 1,200 refueling stations by 2040 |
| Japan | Leading the way in hydrogen solutions development |
| Germany | Recognized for significant efforts in hydrogen technology and solutions |
| Australia | Actively involved in hydrogen initiatives, with a focus on green hydrogen production |
| France | Actively participating in the development of hydrogen solutions |
| United States | Engaged in various hydrogen projects and initiatives |
| United Kingdom | Actively involved in hydrogen-related activities |
| Canada | Active participant in the development of hydrogen solutions |
| Europe | Highest number of hydrogen projects, particularly on a large industrial scale. Ambitious hydrogen strategy and roadmap up to 2050 |
| India | Planning a public auction for green hydrogen production in 2021 |