You’ve probably heard the term “Shadow IT,” but you may be unaware of it in detail.
It is when employees use unauthorized applications and services to get their work done. That can be a significant security risk for your company.
Implement a shadow IT policy to ensure all employees use authorized applications and services. It protects your company from data breaches and other security risks.
The article will explain the meaning of Shadow IT and its associated risks, give some examples and tell you how to create a policy to protect your company.
What is Shadow IT?
It is the term used for unauthorized and unregulated software, devices, and services within an organization without its approval. Because of the adoption of cloud-based applications, It has become a growing problem for enterprises.
Aspects
It consists of IT-related things such as hardware and software.
- Hardware includes routers, PCs, servers, smartphones, switches,
- The software consists of applications, operating systems, and cloud services (SaaS, IaaS, PaaS).
- Off-the-shelf software packages
Why do employees use Shadow IT?
- To get around restrictions or policies put in place by their organization
- To find faster or more efficient ways of completing tasks
- To access tools or applications that their organization does not approve
The rapid growth of cloud-based applications allows them to do this.
Shadow IT Risks
Security
Since Shadow IT is often done outside formal IT channels, securing and protecting sensitive data can be difficult.
It is not sanctioned by the organization. As a result, it may not undergo the same security testing and review as approved applications. That can leave sensitive data vulnerable to attack.
Compliance
Organizations may not comply with regulations if they are unaware of all the tools and applications used by their employees.
Support
If something goes wrong with this application, the organization may not be able to provide support since they are unfamiliar with it.
Costs
Unapproved applications may not be covered by the organization’s licensing agreement, leading to unexpected expenses.
Decreased productivity
Employees using unofficial applications can reduce productivity as they may not know how to use the application or may not have access to the necessary support.
Benefits
- Employee satisfaction: If employees can use the tools they are familiar with, they will be more satisfied with their work.
- Increased productivity: Allowing employees to use their familiar applications can increase productivity.
- Improved collaboration: It can improve collaboration among employees as they can share information and work on projects together more efficiently.
- Decreasing IT workload: Allowing employees to use their applications can help decrease the IT department’s workload.
- Enhanced employee time: If employees can use their time more efficiently, they will be able to focus on other tasks.
How do you control Shadow IT?
It can be controlled by developing and enforcing a shadow IT policy. It can also be detected and managed through discovery tools, which can provide visibility into the systems and applications used within the organization.
Finally, it can be mitigated through cloud-based security services, which can help secure unsanctioned cloud applications and platforms.
Steps to control Shadow IT
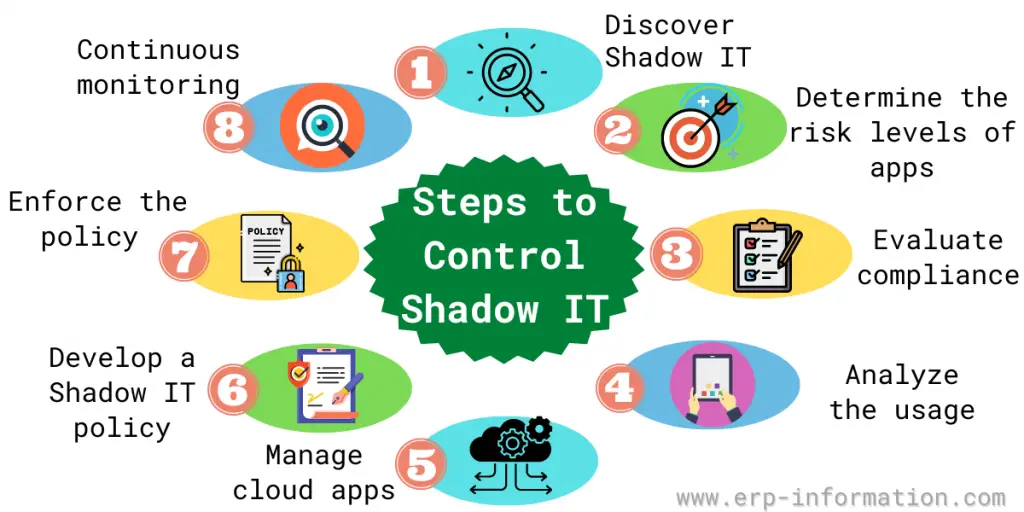
Discover
The first step to controlling Shadow IT is to gain visibility into the systems and applications being used within your organization. This can be done through discovery tools, which provide information on the devices, users, and applications.
Determine the risk levels of apps
Once you have a list of these apps being used, you can begin to assess the risks associated with each one. To do this, consider the data shared through the app, the security controls in place, and the compliance requirements that must be met.
Evaluate compliance
Another important consideration when assessing the risks is compliance. A number of compliance requirements need to be considered, such as those related to data privacy, data security, and industry-specific regulations.
Analyze the usage
In addition to the risks and compliance considerations, it is also essential to analyze the usage of these apps.
That can help you to understand how the app is being used and whether or not it is meeting the needs of the business. And also determine the high-risk volume of users.
Manage cloud apps
Manage cloud apps through a central platform and leverage governance actions like sanctioned and unsanctioned, mark them for review or mark them for the block.
Develop a shadow IT policy
Once you have assessed the risks and evaluated the compliance requirements, you can develop this policy. This policy should outline its acceptable use within the organization and the consequences for violating the policy.
Enforce the policy
Train employees on the policy, issue warnings for violations, and take disciplinary action for repeated violations.
Continuous monitoring
It will always be a risk, even with the best controls. As such, it is vital to have a continuous monitoring program to identify new threats and mitigate them quickly.
How to create a Shadow IT policy?
A good policy should accomplish the following:
- Define what is considered shadow IT within the organization
- Outline the risks associated with it
- Describe the consequences of violating the policy
- Include a process for employees to request approval for using unauthorized applications or services
A well-defined policy will help ensure that all applications and services are properly vetted and approved before use.
Shadow IT Examples
- Software applications like Dropbox, Google Docs, Skype, and Microsoft Office
- Hardware like smartphones, tablets, PC, and USB thumb drives
FAQs
What is Shadow IT policy?
It is a document that outlines what employees can and cannot do when using unauthorized applications and services. The policy should be created with the input of both IT and business managers.
What is the difference between Shadow IT and BYOD?
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) is when employees use their own devices for work purposes. In addition, this is when employees use unauthorized applications or services for work purposes. Both can pose risks to the organization if not adequately managed.
Conclusion
Shadow IT is a term used in organizations to describe the unofficial use of technology within an organization. For example, it can refer to the use of unauthorized software, hardware or cloud services.
It can present several business risks, including data security breaches and compliance issues. Therefore, organizations must develop this policy and conduct regular Shadow IT assessments to mitigate these risks.
The article provided a great deal of background information on Shadow IT, its risks, and how to control it.

