We all know that data is essential, but what do we need to ensure accurate and reliable data?
Most people think of data accuracy and integrity as similar, but they are pretty different. Maintaining data quality is essential for businesses, but it can be hard to keep track of everything and ensure data is accurate across various departments and data sets.
This blog post will explore data accuracy vs data integrity and provide more information about data integrity, including its types, examples, metrics, data integrity risks, and benefits.
Data Accuracy vs Data Integrity
What is Data Accuracy?
Data accuracy is the most vital aspect of data quality. It guarantees that your company’s business operations are based on reliable and proper data, leading to more profitable decision-making capabilities in all areas, including planning, forecasting, budgeting intelligence & more!
Data Integrity Definition
Data integrity meaning is the quality of data entered into a system. That means that data is complete, consistent, and accurate.
In technical terms, data integrity is “The measure of how well data is preserved during its life cycle.”
Data integrity is the accuracy and completeness of data. It ensures that data is not corrupted and can be trusted for further use. That involves ensuring data is protected from unauthorized access, alteration, or destruction.
Example of Data Accuracy
Let’s say you’re a retailer and want to track inventory levels. If you have an accurate data set, you’ll be able to ensure you always have enough stock on hand to meet customer demand. You can also use data accuracy to predict trends to order stock in advance and stay ahead of the competition.
Example of Data Integrity
Let’s say you’re a data entry clerk and enter data into a spreadsheet. If you have data integrity, you’ll ensure all data is entered correctly and completely. You’ll also check for errors and ensure data consistency across different data sets.
Types of Data Integrity
Two types of data integrity need to be understood
- Physical data integrity
- Logical data integrity
1. Physical data integrity
Physical data integrity is the accuracy and completeness of data stored in a database. This data integrity is essential because it ensures data is not corrupted and can be trusted for further use.
2. Logical data integrity
As data are used in relational databases in various ways, logic integrity guarantees they remain unchanged.
There are four main types of logical data integrity: entity integrity, referential integrity, domain integrity, and user-defined integrity.
- Entity integrity dictates that every row in a table must have a unique identifier. That is typically accomplished by having a primary key column (or set of columns) that can’t be NULL and doesn’t have any duplicate values.
- Referential integrity ensures that any foreign keys in a table point to valid rows in the parent table. In other words, it ensures that there are no “orphan” rows with missing parent records.
- Domain integrity defines the allowed values for each column in a table. For example, you might specify that a particular column can only contain integer values between 1 and 10.
- User-defined integrity is any data integrity constraint that doesn’t fit into the other three categories. For example, this could be something like a “unique” constraint that ensures no two rows in a table have the same value for a particular column.
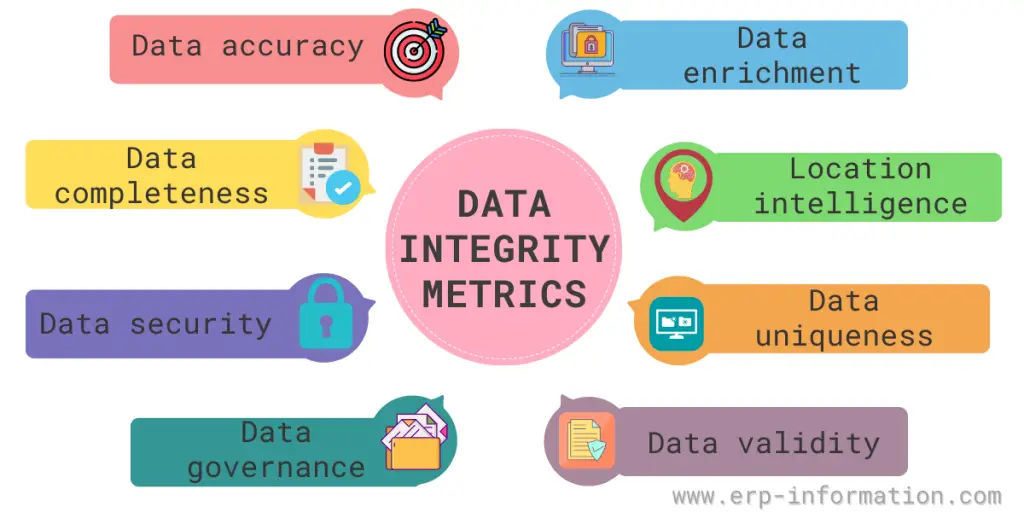
Data Integrity Key Metrics
There are a few key metrics to consider when looking at data integrity:
- Data accuracy: How close the data is to the real-world data set. for example, a data accuracy of 95% means that the data is very close to the actual data set
- Data completeness: How much data is included in a data set
- Data security: Ensuring that data is safe from unauthorized access
- Data governance: Ensuring that data is managed to meet the organization’s needs
- Data validity: Ensuring data is valid (i.e., not corrupted) by checking for errors
- Data uniqueness: Make sure data is unique (i.e., no duplicates)
- Location intelligence: With location insight and analytics, make data more actionable by providing a layer of richness and complexity
- Data enrichment: By adding data from external sources to internal data, you can give it more context, nuance, and significance. Adding business, consumer, or location details enhances your data’s completeness and context by giving you a more comprehensive and contextualized perspective.
How to Ensure Data Integrity
There are several ways to maintain data integrity, including but not limited to:
- Validating input data against known constraints: When input into a system, it should be checked against known constraints, such as data type (e.g., integer, string), length, format, and range.
- Checking output data for compliance with business rules: Data output from a system should be checked against business rules to ensure it is accurate and complete. Having a good data integrity policy in place is essential because it can help ensure that your data is trustworthy and can be relied on for critical decision-making.
- Using data cleansing tools: Data cleansing tools can be used to identify and correct errors in data.
- Storing data in a consistent format: Data should be stored consistently across all data sets.
Data Integrity Risks
There are a few risks associated with not having data integrity:
Loss in E-commerce
Inaccurate data leads to the wrong product being sent to the customer, which leads to a loss in e-commerce.
Financial loss
Inaccurate data can lead to financial loss, for example, if a company overpays for a product because the data about the cost of the product is inaccurate.
Wrong diagnosis
Inaccurate data can have severe consequences in the healthcare industry. For example, if a patient’s medical records are incorrect, it could lead to the wrong diagnosis and treatment.
Overpaying Insurance
Inaccurate data can lead to problems in the insurance industry. For example, if a company’s data about the cost of repairs to a car is incorrect, it could lead to the company overpaying for the repairs.
Benefits of Data Integrity
There are many benefits of data integrity, but the following are some of the most important:
- It provides the searchability and traceability of data to its source
- With data integrity, we can easily search and track data
- It helps to Get rid of redundant, inaccurate, or outdated data
- It avoids the misclassification or improper storage of essential data
- Data integrity helps ensure data security by ensuring data is safe from unauthorized access
- Data integrity enables data governance, which is critical for managing data
- It also helps to ensure data validity, which is vital for ensuring data is not corrupted
Difference Between Data Accuracy and Data Integrity
| Data Accuracy | Data Integrity |
| Data accuracy refers to the quality of data. | Data integrity refers to the accuracy and completeness of data. |
| Essential for businesses to make sound decisions. | Necessary to make sure that data has not been tampered with or corrupted. |
| Maintaining data accuracy requires processes for data entry, data management, and data security. | Data integrity often requires data governance and security measures beyond those needed for data accuracy. |
| Data accuracy is important because inaccurate data can lead to human errors, wasted time, and wrong decisions. | Data integrity is vital to maintaining the trustworthiness of data. |
| Ensuring data accuracy across different departments and data sets can be difficult. | Data integrity only requires ensuring accuracy and completeness within a data set. |
| Data accuracy is typically measured in terms of how close a parameter estimate is to its actual value. | Data integrity is generally measured in terms of the percentage of data that is complete and accurate. |
| Critical metrics of data accuracy are accuracy rate, completeness rate, consistency, and error rate. | Key metrics of data integrity are data accuracy, data completeness, data security, data governance, Data Validity, Data Uniqueness, Location Intelligence, and Data Enrichment. |
| Risks of not having data accuracy include wrong decision making, reputational damage, and failure in compliance. | Risks of not having data integrity include loss in E-commerce, financial loss, wrong diagnosis, and overpaying Insurance. |
| Data accuracy is essential for businesses because it ensures sound decision-making. | Data integrity is vital for businesses because it helps maintain the trustworthiness of data sets. |
Why are both Data Accuracy and Data Integrity essential?
Data Accuracy
- This is essential to an organization because it ensures the data is correct and up-to-date. That allows for better decision-making and strategic planning.
Data Integrity
- This is essential because it ensures that the data is accurate and has not been tampered with. That helps maintain the trust of customers and clients and protects the company’s reputation.
Data accuracy and integrity are essential to any organization because they help ensure that data is complete, consistent, and accurate.
FAQs
What are the factors affecting data integrity?
Many things can affect physical data integrity, including power outages, hardware failure, hacking, malicious attacks, and natural disasters. Therefore, physical data integrity is important for keeping the business running smoothly. Logical integrity means that your data has not been changed while being moved from one database to another.
How does accuracy affect data?
Data need to be accurate so that predictions are also accurate. If the predictions are wrong, it can waste time, money, and resources. On the other hand, accurate data leads to better decision-making, increased productivity and efficiency, and reduced costs.
Are data integrity and data security the same?
No, data integrity and data security are not the same. Data integrity concerns the accuracy and consistency of data over its lifetime, including during storage and transmission.
Data security, on the other hand, is concerned with protecting data from unauthorized access or modification. That can include the collection of measures such as encryption, user authentication, and access control systems.
Do data integrity and data quality the same?
Data integrity and data quality are different aspects. Data quality refers to relevant, reliable, and accurate data. That can include validating data types, removing duplicate data or inconsistent values, standardizing formats, and verifying accuracy. But data integrity means the accuracy and consistency of data over its lifetime.
Conclusion
Data accuracy and data integrity are two essential aspects of data management. Accuracy is how correct the data is, while integrity means the data has not been changed.
Unfortunately, many companies focus on accuracy over integrity, leading to problems. However, data accuracy and integrity are essential to any organization because they help ensure that data is complete, consistent, and accurate.
We hope this article helped explain the differences between data accuracy and data integrity!