Traditional software development life cycles often stretched development timelines, presenting challenges for startups and smaller companies racing against time and competition.
Then came in the Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), a dynamic alternative designed for efficiency and adaptability.
Agile SDLC is a newer, more flexible way of developing software. It is an alternative to the traditional waterfall model, which can be inflexible and lead to missed deadlines and budget overruns.
This blog post will discuss the definition of Agile SDLC, its phases, disadvantages, methodologies, and reasons for popularity. The post also compares the agile model with the waterfall model.
Definition
Agile software development is a process that allows for incremental and iterative changes to the software.
The agile SDLC is a framework that allows for these gradual changes and emphasizes close collaboration between developers and consumers throughout the software development process.
This close collaboration will enable customers to give feedback early and often, which helps ensure that the software meets their needs.
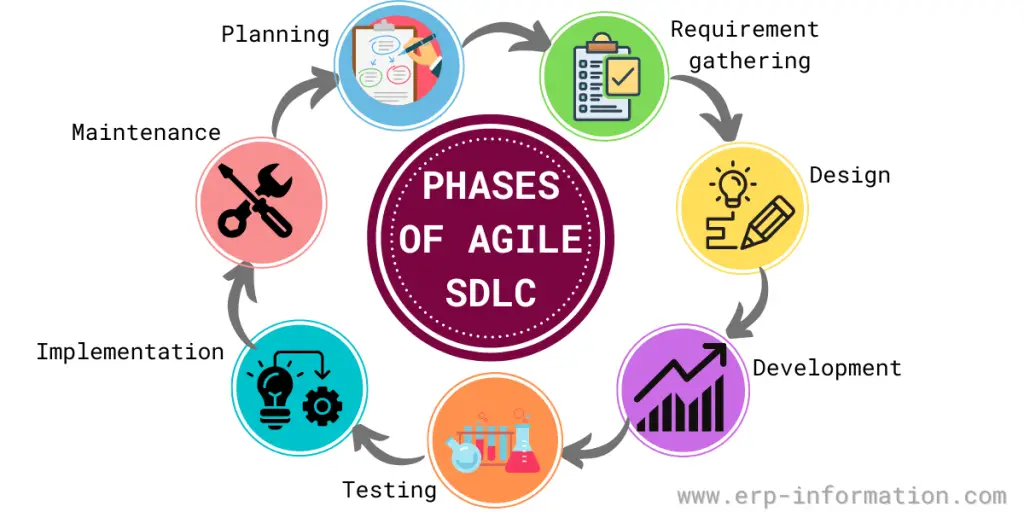
What are the Agile SDLC Phases Involved in the Process?
- Planning: In the planning stage, the team creates a roadmap for the project. This roadmap outlines the goals, objectives, and timeline for the project.
- Requirement gathering: The team gathers data about the customer’s requirements in the analysis stage. This information determines the software’s features and how it should work.
- Design: In the design stage, the team creates a software prototype. This prototype tests the design’s feasibility and gathers customer feedback.
- Development or coding: The developers review and break down requirements into smaller tasks that can be completed efficiently and quickly. In the development stage, the team writes the code for the software.
- Testing: The software is tested in the testing stage to ensure that it meets the customer’s requirements. If the team finds bugs, they fix them.
- Implementation: The software is ready for implementation once it passes the testing stage. The team helps the customer install and use the software in this stage.
- Maintenance: The team provides maintenance and support after the software is up and running. That also makes sure that the software is updated as needed.
Agile SDLC Process Flow
The Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a flexible, iterative approach to creating software that prioritizes collaboration, customer feedback, and quick, incremental releases. Here’s an overview of the Agile SDLC process flow:
Concept
In the concept phase, project ideas are generated and prioritized based on their potential value and feasibility. This stage involves brainstorming sessions and discussions to identify the scope and objectives of the project. Stakeholders outline the vision and goals, ensuring alignment with business strategies and user needs.
Inception
The Inception phase signifies the official kickoff of the project. During this stage, the team is formed, funding is arranged, and essential groundwork is laid. Key activities include:
- Team Formation: Choosing and assigning team members with the required skills and roles.
- Funding Allocation: Securing budget approval and allocating necessary resources.
Iteration/Construction
The Iteration/Construction phase is the heart of Agile development. Here, the software development team works iteratively to deliver working software based on the requirements and continuous feedback. Key activities include:
- Sprint Planning: Breaking down the project into manageable iterations (sprints) with specific goals.
- Development: Writing code and building features incrementally.
- Continuous Integration: Regularly merging code changes into a shared repository.
- Daily Stand-ups: Hold short, daily meetings to discuss progress, obstacles, and next steps.
- Iteration Review: Demonstrating completed work to stakeholders at the end of each sprint.
- Retrospective: Reflecting on the iteration process to identify improvements for the next sprint.
Release
In the Release phase, the focus shifts to preparing the software for deployment. This involves:
- Quality Assurance (QA) Testing: Conducting thorough testing to ensure the software meets quality standards and requirements.
- Internal and External Training: Providing training sessions for both team members and end-users to facilitate a smooth transition.
- Documentation Development: Creating comprehensive documentation to support users and maintainers.
- Finalizing Iteration: Incorporating feedback and making necessary adjustments to deliver the final version of the iteration into the product.
Production
The Production phase involves the ongoing support and maintenance of the software. This includes:
- Deployment: Releasing the software into the live environment.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the software to ensure it runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Support: Providing ongoing support to resolve any issues or bugs that arise.
- Updates and Enhancements: Implementing updates and new features based on user feedback and evolving requirements.
By following the Agile SDLC process flow, teams can deliver high-quality software that meets user needs more effectively and responds quickly to changing requirements.
The iterative nature of Agile allows for continuous improvement and adaptation, ensuring that the final product is both functional and aligned with business objectives.
Agile SDLC Best Practices
- Customer involvement: Customers should be involved throughout the agile SDLC process to meet their needs.
- Self-organizing teams: Teams should be self-organizing, so they can make decisions and solve problems quickly.
- Incremental delivery: The agile model focuses on incremental small development sprints, allowing for more customer feedback and a better final product.
- Working software: Agile aims to produce software that meets customer needs rather than focusing on documentation or other deliverables.
- Continuous improvement: Agile teams should constantly look for ways to improve their process and the software they deliver.
Agile Model vs Waterfall Model
The agile model is becoming the preferred model for software development as it is more effective and responsive to change than the traditional waterfall model.
| Agile SDLC model | Waterfall model |
| It is iterative; takes small steps and changes along the way based on customer feedback. | The waterfall model is linear, which means that the waterfall model progresses straight. |
| It embraces change. | It doesn’t allow for change. |
| Allows multiple jobs to be completed simultaneously. | Focuses on completing tasks one at a time. |
| Allows for needs to emerge during the development process. | The waterfall model requires all requirements to be known upfront. |
| It allows for overlap and parallelism between phases. | It is based on sequential phases. |
Agile SDLC Methodologies
Scrum
It involves short development sprints (usually two weeks) during which a team works to complete a set amount of work.
After finishing each sprint, the team shows the completed work to the customer and gathers feedback. This feedback is then used to guide future sprints.
Kanban
Kanban helps teams visualize their work, so they can see what needs to be done and who is working on what tasks. This transparency can help teams manage their workflow and improve their process over time.
Lean
Lean focuses on eliminating waste and reducing unnecessary work. In software development, this means creating a lean process that delivers value to the customer quickly and efficiently.
XP (Extreme Programming)
XP is a method that focuses on delivering working software early and often. XP teams work in short development cycles (usually two weeks) and aim to release new software weekly.
FDD (Feature-Driven Development)
This methodology focuses on delivering software in short development cycles (usually two weeks). FDD(Feature-driven development) teams work to break down requirements into smaller tasks that can be completed efficiently and quickly.
DSDM (Dynamic Systems Development Method)
It is an agile methodology that focuses on delivering working software quickly. DSDM teams work in short development cycles and use a timeboxing approach to ensure that each sprint is completed on time.
Crystal
This a family of agile methodologies that deliver software based on customer needs. Crystal Clear, for example, is a methodology that focuses on transparency and communication to ensure that the customer’s needs are met.
Advantages of the Agile Model
The Agile Model offers numerous benefits, including:
- Realistic Approach: Agile provides a practical method for software development.
- Teamwork and Cross-Training: It encourages collaboration and skill-sharing among team members.
- Rapid Functionality Development: Features can be quickly developed and showcased.
- Minimal Resource Requirements: The model operates efficiently with minimal resources.
- Adaptability: It works well with both fixed and evolving requirements.
- Early Delivery: Agile delivers early, partially functional solutions.
- Suitable for Changing Environments: It is ideal for environments that experience constant change.
- Simple Rules and Documentation: The model employs minimal rules and easy-to-use documentation.
- Concurrent Development and Delivery: Agile supports simultaneous development and delivery within a structured plan.
- Minimal Planning Needed: It requires little upfront planning, making it easy to manage.
- Developer Flexibility: Developers have significant flexibility in their work processes.
Disadvantages of the Agile Model
Despite its advantages, the Agile Model also has some drawbacks:
- Complex Dependencies: It is not ideal for managing intricate dependencies.
- Sustainability and Maintainability Risks: There are higher risks regarding the sustainability, maintainability, and extensibility of the software.
- Need for Leadership and Planning: Successful implementation requires a comprehensive plan, an agile leader, and effective agile project management practices.
- Strict Delivery Management: The approach often involves strict management of scope and functionality to meet deadlines.
- High Customer Interaction: It relies heavily on customer input, which can mislead the team if the customer’s requirements are unclear.
- Individual Dependency: There is a high dependency on individual team members due to minimal documentation.
- Challenging Knowledge Transfer: The lack of extensive documentation can make it difficult to transfer knowledge to new team members.
FAQs
Why is Agile becoming a more popular model?
It’s more effective than the traditional waterfall model in delivering software that meets customer needs.
It’s more responsive to change, which makes it well-suited for today’s fast-paced, ever-changing business environment.
It allows teams to be self-organizing and self-managing, which fosters creativity and empowerment.
It’s been shown to improve productivity and decrease costs.
what are the 4 c’s of the agile model?
Clarity: Define clear purpose, strategy, and roles to establish expectations and accountability.
Commitment: Mutual commitment in daily stand-ups where team members vow to their tasks for the day.
Comment: Provide constructive feedback when objectives aren’t met to identify and address obstacles.
Coach: Agile managers act as mentors, offering support and guidance to enhance team productivity and professional growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Agile SDLC stands as a versatile family of software development methodologies renowned for their ability to deliver functional software in tune with ever-evolving project requirements swiftly.
Yet, like any approach, Agile methods come with their set of advantages and limitations.
Observing the characteristics of Agile, you’ll find a diverse range of methodologies, each offering unique strengths and grappling with distinct challenges.
The key lies in your team’s ability to discern and adapt, selecting the methodology that harmonizes best with your project’s nature and objectives. Thank you for the readership.