We encounter bottlenecks between busy intersections during peak times and airport security check-ins. When faced with bottleneck problems, it becomes easy to forget about the costs to the businesses they operate.
Of course, nowhere has bottlenecked processes impacted revenue more than in manufacturing industries. However, in many industries, bottlenecks are often due to overproduction and slowing production.
Bottlenecks are common in manufacturing but can be costly if not managed properly. They cause delays in production lines, increase costs, and reduce efficiency.
Learning the essentials of solving bottlenecks in production lines is crucial. With the help of our guide, understand and manage them efficiently.
The article will disclose the term “bottleneck.” It will discuss bottlenecks in manufacturing, how to identify them, and tips to prevent bottlenecks in manufacturing. It also informs you about the types of bottlenecks and causes of bottlenecks.
What are bottlenecks?
Bottlenecks are congestion points in a system or process that limit the resources’ throughput or flow rate.
In computing and engineering, bottlenecks can refer to a slow component in an otherwise efficient system or a resource-allocation issue that impacts execution speed.
In business and operations, bottlenecks can be used to identify critical points in production processes that need to be improved. For example, introducing automation at bottlenecked areas could help increase efficiency and productivity.
You know, the bottleneck is a narrow part of the bottle where congestion occurs and slows down the liquid flow from the bottle.
What is a bottleneck in manufacturing?
A bottleneck in manufacturing is a limitation or constraint that impedes or restricts production flow. It can occur at any stage of production and can be caused by many factors, such as limited resources, lack of staff, inadequate technology, and inefficient processes.
Types of bottlenecks
Two types of bottlenecks are short-term and long-term.
Short-term bottlenecks
Short-term bottlenecks refer to temporary conditions that limit the throughput or flow rate of resources for a limited time.
These bottlenecks typically occur when unexpected events put an extra strain on operational capacity, as employees leave or when there is a delay in the delivery of required materials.
Long-term bottlenecks
Long-term bottlenecks refer to cognition points in a system that limits the throughput, or flow rate, of resources for an extended period.
These bottlenecks often occur when capacity is limited due to aging infrastructure and equipment, inefficient processes, or lack of access to qualified personnel.
Other types of bottlenecks
Performance-based bottlenecks
These occur when you do not meet your required level for the task as an individual. Most of the time, it wasn’t your teammate’s fault. Instead, it was the lack of resources or clarity that created the bottleneck.
Delay-based bottlenecks
These occur when something external causes a delay in the task. That could include insufficient access to supplier parts, bad weather causing transport delays, etc. The best way to tackle this type of bottleneck is to have contingencies in place.
For example, if you are waiting on a supplier to deliver parts, ensure you have an alternate supplier that can provide the parts quickly in case of a delay.
Capacity-based bottlenecks
These are bottlenecks caused due to limited capacity or resources. To tackle these, you will need to increase capacity or resources. That could mean hiring more people with the required skills, buying new equipment, or automating processes.
You can maintain a smooth flow of operations and maximize efficiency by accurately identifying, analyzing, and addressing bottlenecks in your production process.
How to identify bottlenecks in manufacturing?
Identifying bottlenecks in manufacturing can be a difficult process. However, understanding the production process and observing areas where throughput is limited is important.
Additionally, monitoring key metrics such as cycle time and inventory levels can help uncover any potential congestion points.
Other factors may include machine downtime, personnel shortages, or a lack of resources. Once potential bottlenecks have been identified, organizations should focus on implementing solutions such as adjusting processes, investing in automation, or introducing process improvements and upgrades to prevent them from occurring again.
More about bottlenecks
Bottlenecks occur in many different processes and scenarios, but they all refer to a point at which the flow of something is reduced or stopped.
Let us take an example of toy manufacturing. First, the manufacturer provides the required raw materials for production, and once the product is completed, there are added machine and labor costs. Finally, the final product is stored in the warehouse.
Once goods are sold, the inventory cost changes into the cost of goods sold(COGS).
If any bottleneck occurs at production because of a delay in raw material supply, the toy manufacturer can not provide sufficient raw materials for the production process.
As a result, machines will be idle, and workers will not have enough work. That leads to the underutilization of available resources, which increases production costs. As a result, even the final product will not reach the customer on time.
Production capacity and bottlenecks
A Bottleneck impacts more on production in the manufacturing industry. The organization assumes that it will always produce products with full efficiency. That is a theoretical assumption, but practically it is impossible to achieve.
Hence it is better to use practical capacity management in businesses. This practical capacity considers machine maintenance downtime, and staff leaves downtime, etc.
Practical capacity fixes the range within that production processes operate efficiently. Businesses can adjust their production goals to production capacity if they feel that their capacity is inadequate to meet goals.
Or they can use capacity requirements planning solutions to reach the goal. These methods help businesses to decrease the risk of bottlenecks and increase productivity.
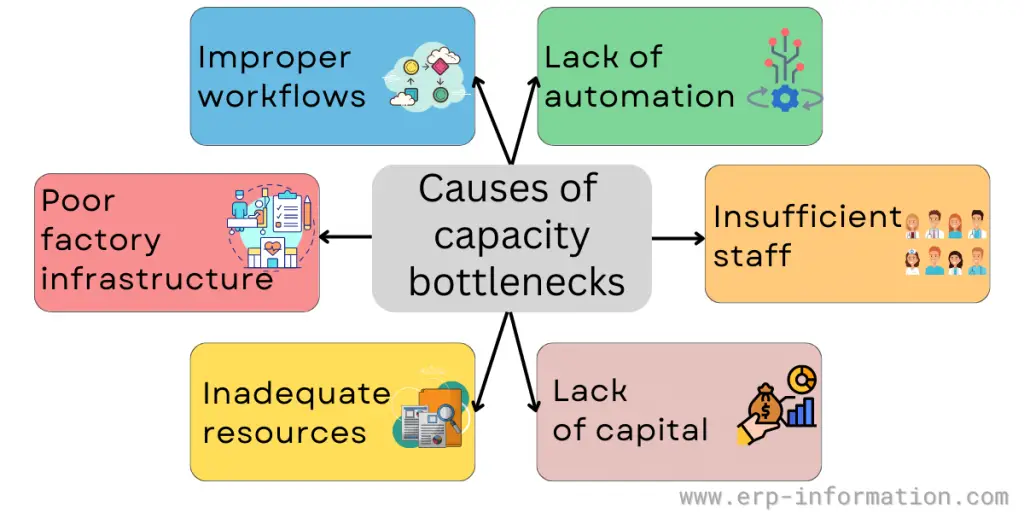
Causes of bottlenecks
Capacity bottlenecks occur when a process can produce more than what is currently being produced. That can be due to multiple reasons, such as improper workflow, inadequate resources, lack of automation, poor infrastructure, insufficient staff, and lack of capital.
Improper workflows
Improper workflows are one of the major causes of capacity bottlenecks in manufacturing. Outdated workflow plans and improper equipment maintenance are the reason for that. If you are not maintaining equipment properly leads to inefficient functioning of equipment.
Poor factory infrastructure
Poor factory infrastructure also causes bottlenecks. Sometimes it leads to unnecessary delays. For example, if you are not properly handling and storing materials, there is a risk of damage. That leads to delays in production.
Inadequate resources
It can cause capacity bottlenecks if they cannot meet the demand of a process. That can include insufficient equipment, materials, or technology. For example, if a factory requires five machines to produce the same amount of product as four but only has four available, it will be at a capacity bottleneck.
Lack of automation
If there is a lack of automation, you must do more manual work. But, unfortunately, that leads to human error, and processes will not run at full efficiency.
Insufficient staff
Insufficient staff can also cause capacity bottlenecks as insufficient people may be available to carry out a process at full speed. In this case, increasing the number of staff members would help reduce any bottlenecks.
Lack of capital
Lack of capital can cause capacity bottlenecks as resources may not be adequately funded to keep up with demand. In this case, investing more money would help reduce capacity bottlenecks.
Production variances and bottlenecks
Production variance is the difference between budgeted and actual outputs. For example, if there is a variance in actual labor cost (more than the budgeted cost), then the production manager will come to know that there is a bottleneck in the production line, and that is wasting staff time.
If the manager prevents the bottleneck, then labor costs will reduce. It is true for material variance, also.
Strategies to overcome production line delays
Strategies to Overcome Production Line Delays include improving processes, investing in new technology and equipment, and training staff.
Improving processes
Improving processes is one of the most effective ways to reduce production line delays. That can include streamlining workflows, reducing waste and defects, and focusing on efficiency rather than speed. Additionally, automating repetitive processes can also help streamline the production line.
Investing in new technology and equipment
Investing in new technology and equipment can also help reduce delays on the production line. That could include purchasing machinery, introducing automated systems, or upgrading existing technologies.
Training staff
Training staff is another effective way to reduce delays on the production line. Staff should be adequately trained on the process and be able to identify potential problems before they arise. Additionally, having an experienced staff can help ensure that processes remain efficient.
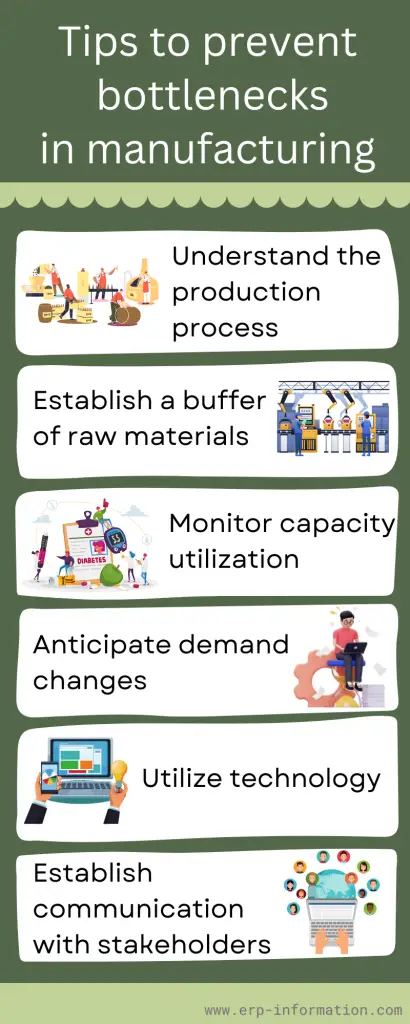
Tips to prevent bottlenecks in manufacturing
Manufacturing bottlenecks can majorly impact a company’s production and profits. Therefore, it is important to take the proper steps to identify and address potential bottlenecks before they arise to avoid these costly delays. Here are some tips for preventing manufacturing bottlenecks:
Understand the production process
Understanding the entire process can help identify potential problems and provide solutions before they become an issue.
Establish a buffer of raw materials
Manufacturing operations typically require storing large amounts of raw materials to ensure that production can continue uninterrupted. Having a cushion of extra inventory can help to prevent disruption due to an unexpected shortage.
Monitor capacity utilization
If the rate at which machines are used is too high, it may lead to bottlenecks in production. Monitoring capacity utilization can help to identify areas of the process that need improvement or additional resources.
Anticipate demand changes
Staying ahead of potential fluctuations in market demand and customer orders can help prevent unexpected production delays due to a lack of materials or personnel.
Utilize technology
Adopting new technologies, such as automated equipment or software systems, can help optimize production processes and reduce bottlenecks.
Establish communication with stakeholders.
Keep all stakeholders informed of the production process. Establish an effective communication system to ensure production runs efficiently without delays or unexpected stoppages.
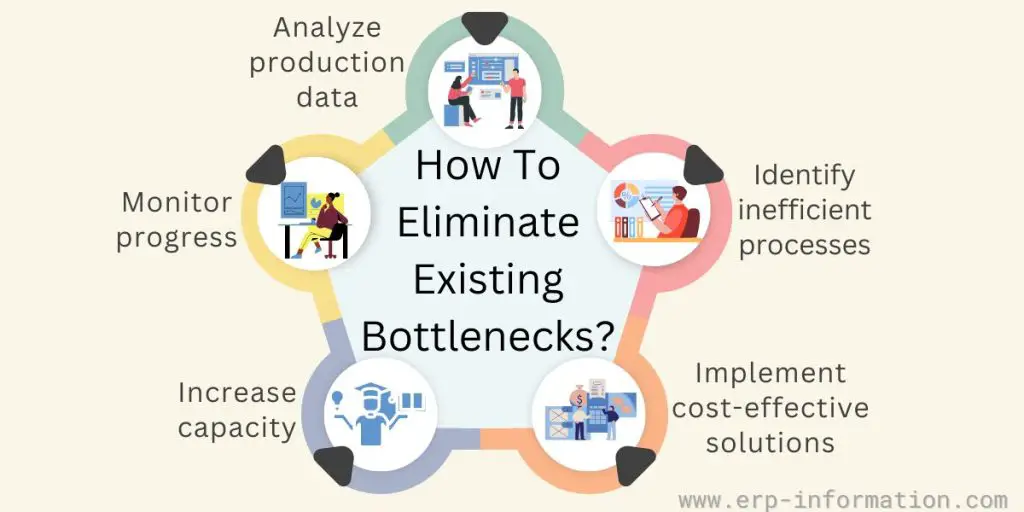
How to eliminate existing bottlenecks?
- Analyze production data: Collecting and analyzing data from each production stage can provide valuable insight into what is causing the bottleneck.
- Identify inefficient processes: Look for any inefficient or outdated processes contributing to the problem and implement changes to make them more efficient.
- Implement cost-effective solutions: Consider automation, outsourcing, or new technology to reduce bottlenecks.
- Increase capacity: If necessary, add new machines or personnel to increase production capacity and reduce delays.
- Monitor progress: Regularly monitor progress and adjust to address the bottleneck effectively.
These steps can help manufacturers eliminate existing bottlenecks and improve their efficiency.
FAQs
How does bottleneck affect production capacity?
Bottlenecks can have a significant impact on an organization’s production capacity. By slowing down the throughput of resources, bottlenecks limit the rate at which products or services can be produced.
Unfortunately, that often results in higher costs and lost opportunities due to delayed delivery times or unsatisfied customers.
Furthermore, if left unresolved, bottlenecks can cause critical equipment to become overloaded and lead to unexpected downtime and production delays. Therefore, organizations must identify and address key congestion points as quickly as possible with necessary upgrades and process improvements.
Conclusion
Bottlenecks in manufacturing can be a major impediment to the production process. When left unchecked, they can cause delays that prevent companies from meeting their deadlines and goals.
By understanding what bottlenecks are, how they manifest themselves in the factory or office environment, and using appropriate strategies to address them, businesses will be better equipped to optimize their operations for maximum efficiency.
With an effective bottleneck strategy, manufacturers can avoid costly disruptions and increase capacity while ensuring the consistent quality of products produced.