Manufacturing goods is a practice as old as civilization itself. Over time, the methods and tools have evolved dramatically from handcrafting to sophisticated machinery.
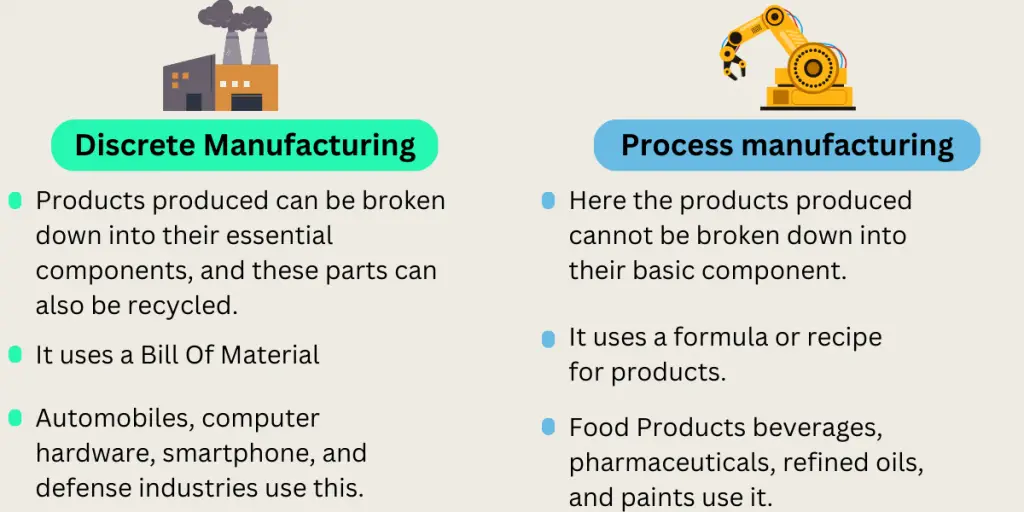
This evolution includes various manufacturing approaches, notably process manufacturing, which involves combining ingredients, and discrete manufacturing, a distinctly different method.
The article discloses the definition of discrete manufacturing, its examples, its workflow, technology trends, types of other manufacturing processes, and the difference between discrete manufacturing and process manufacturing.
What is Discrete Manufacturing?
Discrete manufacturing involves the creation of distinct, countable products, furniture, airplanes, toys, smartphones, computer hardware, automobiles, and defense systems. This process assembles various parts and components, such as nuts, bolts, brackets, and wires, into complete items.
Unlike process manufacturing, which generates undifferentiated products like natural gas or salt, discrete manufacturing produces recognizable items that can often be disassembled and recycled at the end of their lifecycle.
Production in discrete manufacturing ranges from low-volume, high-complexity items to high-volume, low-complexity goods. This necessitates either a flexible manufacturing system for complex items, ensuring quality and speed while reducing costs, or efficient inventory control and waste management for simpler items.
This method is typically not continuous; production processes can start, stop, and operate at varying rates. The final products can be made from multiple components, such as the different parts of a smartphone, or a single material, like steel for a structure.
Successful discrete manufacturing relies on meticulous organization and planning, often facilitated by project management software with features like customizable Kanban boards for tracking and managing the production cycle.
Examples
Consider products such as toys, automobiles, smartphones, and airplanes—they are all produced using discrete manufacturing methods.
To excel in this process, businesses require robust software for effective planning and execution.
The primary challenge lies in tailoring production to meet the unique needs of individual customers.
During the production planning phase, the real-time data collected across plants and resources will help the managers analyze the firm’s current production status.
Due to the unexpected demand in this system, with complete details, the production team can pull themselves up to meet the incredible demand and fulfill the orders accordingly.
It also must be quick enough to adapt to the current demand to implement a new course of action. Thus, flexibility is one of the critical factors of discrete manufacturing.
The business must also ensure equal measures to ensure its quality with minor defects.
Key Elements of Discrete Manufacturing
It involves converting raw materials into distinct, finished products. Though the specifics can vary by industry, several core elements are common across all discrete manufacturing processes.
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain is crucial in discrete manufacturing due to the need for sourcing parts and components from various suppliers. Efficient supply chain management boosts operational efficiency by tracking production, ensuring consistent product quality, and maintaining resource availability.
Effective supply chain oversight is essential for profitability and smooth operations.
Bill of Materials (BOM)
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is an essential document listing all parts, components, and assemblies needed to create a finished product.
It serves as a detailed guide for assembling the product. Proper BOM management is critical, as changes and updates to components can significantly impact the production process.
Production Routing
Production routing details the step-by-step process for manufacturing a product. It begins when an item is ordered or restocked and is outlined in the BOM.
The routing specifies the operations to be performed, the equipment or workstations involved, and any expected waste, ensuring a streamlined production process.
Assembly Line Process
In discrete manufacturing, the assembly line method organizes the production of parts and assemblies into a cohesive final product.
This involves multiple workstations, each performing specific tasks to build the product progressively. The assembly line ensures efficient and organized production of distinct components.
Quality Control
Quality control is vital in discrete manufacturing to meet customer, industry, and regulatory standards. It involves inspecting products to remove defects, documenting processes, and having plans to address any issues quickly.
Maintaining high-quality standards ensures reliable and satisfactory final products.
ERP Systems for Discrete Manufacturing
It is also vital that a firm chooses an ideal software for discrete manufacturing that will help in good inventory management so that the company doesn’t waste time getting stocks for unexpected demand.
It must also ensure that it doesn’t overstock the goods, making them obsolete and increasing expenses.
ERP systems are developed to manage discrete manufacturing processes. These ERP systems help the organization control the manufacturing process, reduce waste, save time required by the product manufacturing, and get a clear vision of the manufacturing process.
The other functionalities of the ERP systems include material management, supply chain management, financial management, and customer relationship management.
ERP vendors
Some good ERP vendors are NetSuite, Epicor, SAP, Infor, etc. ERP modules of these vendors are flexible and easily customizable to meet customers’ requirements.
Most of the ERP systems for discrete manufacturers run on-premises, but these systems also run in the cloud.
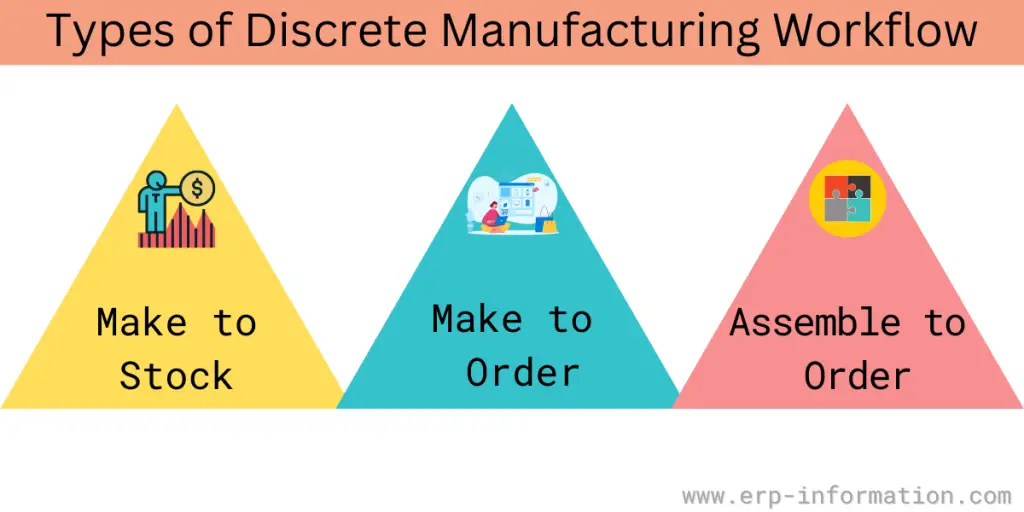
Workflow
This process supports the following workflow.
1. Make-to-stock: In this type of workflow, you keep stock of products before customers order.
2. Make to order: In this workflow, you do not keep more product stock in your warehouse. Instead, you manufacture the product only when a customer order comes in.
3. Assemble to order: This type of workflow lies between make-to-stock and Make-to-order. Here, you manufacture the components or parts before the customer orders.
You can assemble the final product once the customer order comes in immediately.
Discrete Manufacturing vs Process Manufacturing
Manufacturing vs Assembly
Manufacturing and assembly are two distinct processes within the broader context of production. The below table shows the key differences between them.
| Manufacturing | Assembly |
| It involves converting raw materials into components, parts, or products. It encompasses various stages, such as design, fabrication, and quality control. | Assembly involves assembling individual components or parts to form a complete or final product. It is a subset of the overall manufacturing process. |
| Manufacturing techniques can include casting, forging, machining, molding, extrusion, and many other methods to create the required parts or components. | Assembly can involve manual labor or automated systems, such as robots or assembly lines, to combine components efficiently. |
In simple terms, manufacturing is about making separate parts from raw materials. Assembly is when we put these parts together very carefully to create a finished product that works. It is like a teamwork of careful crafting and putting things together to make something complete and ready to use.
What is Discrete Manufacturing Software?
The software is enterprise resource planning (ERP) or manufacturing execution system (MES) software designed specifically for companies that produce distinct or separate products, such as automobiles, electronics, furniture, or machinery.
The organizations use computer-aided design and manufacturing tools (CAD/CAM) that are interconnected with ERP.
Discrete companies also use Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM) software for production. It allows companies to enhance production performance, efficiency, and flexibility by connecting virtual and physical manufacturing.
MES is crucial for discrete manufacturers to face new markets, technologies, and materials.
Features of MES for discrete manufacturing are as follows.
- Production process synchronization
- Quality Requirements and Regulatory Integration
- Real-time shop floor visibility
- Enhanced manufacturing operations and WIPs (work-in-progresses)
- Access to production documentation
- Enhanced resource allocation, material management
Discrete Manufacturing Technology Trends
1. The tech-enabled lean manufacturing process
Technology embedded in modern ERP enables mid-market manufacturers to apply lean manufacturing techniques that were formerly unavailable.
2. Greater investments in cloud
Increased global customers, enhanced competition, regulatory pressures, and decentralization of operations have led to greater industry investment in cloud-based software.
3. Improved use of smart devices connected to IoT
Smart devices have the ability to transfer data between each other. Businesses are finding ways to configure their ERP system to take advantage of these things.
4. Evaluation of business intelligence for manufacturing
BI Technology has evolved beyond an IT department responsibility into a real-time data tool to analyze big data. So, decision-makers can use it to improve the business.
5. Increased focus on maximizing the CRM process
With increased computation, buyers are more informed than ever before. Manufacturers are beginning to invest in improved CRM principles.
6. Augmented reality
Manufacturers have adopted AR to enhance workflow and productivity. It provides seamless communication and reduces errors.
7. Additive manufacturing
The additive manufacturing technique uses only the materials needed for the part, which drastically reduces waste during production.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Discrete Manufacturing
| Advantages | Drawbacks |
| Strengthened Supplier Relationships: Maintaining good supplier relationships ensures a steady supply of quality materials. | Complexity: Managing numerous components and production details can be extremely challenging. |
| Enhanced Productivity: Real-time KPI metrics and automated data capture (ADC) technology help identify production bottlenecks. | Limited Flexibility: Changing production processes or designs can be difficult and time-consuming. |
| Increased Customer Satisfaction: ERP systems with CRM features help track consumer information and order status, improving customer service. | Capital-Intensive Setup: Establishing a discrete manufacturing plant requires significant initial investment. |
| Better Supply Chain Management: ERP software can verify the quality of supplies, ensuring consistency and reliability. | Distinct Production Lines: Each component or product often needs a separate production line, increasing complexity. |
| Visibility and Control: ERP solutions provide insight into suppliers, logistics costs, market demand, and competition. | Upfront Costs: High initial costs for setting up the necessary infrastructure and systems. |
FAQs
What are the products made by process manufacturing?
Products made by process manufacturing are jam, juices, beverages, chemicals, medicines, oils, etc.
What are the key benefits of discrete manufacturing?
Discrete manufacturing offers greater flexibility and allows for customized production and quick adjustments to meet changing demands.
It provides better traceability and quality control for individual items or batches. It also streamlines the regulatory compliance and documentation processes.
This industry helps in reducing production costs and ultimately leads to increased customer satisfaction.
What are the challenges faced with discrete manufacturing?
Some of the challenges associated with discrete manufacturing are
* Managing inventory for various components
* Production complexity of processes
* Dealing with frequent changeovers during the production of a variety of
products.
* Global competition
What strategies can be used for managing the complexities of discrete manufacturing operations?
Strategies that could help in reducing the complexities are
* Implementation of efficient production planning and scheduling systems
* Utilization of advanced ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) platform
* Adoption of agile manufacturing practices
How can discrete manufacturing benefit from Industry 4.0 and IoT?
Industry 4.0 and IoT technologies can lend a helping hand to discrete manufacturing by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making to optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime.
How are lean manufacturing and discrete manufacturing related?
Lean manufacturing is a methodology that focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency in production processes. It is applicable to discrete manufacturing as it can help reduce costs and enhance quality by minimizing non-value-added activities.
Conclusion
Discrete manufacturing is a production method where products are made one at a time. This approach is practical as it demands lower initial investment compared to producing goods in large batches.
In this blog post, we have elaborated on discrete manufacturing, shedding light on its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. We hope this post has been informative and helped you understand manufacturing strategies.