If you work in a warehouse, you know that having a sound warehouse management system is critical to your success.
But what is it, and why do you need one?
This blog post will discuss WMS, its types, key features, advantages, and how it can help you run your warehouse more efficiently. It’ll also provide the best vendors list and case studies for optimizing the warehouse.
Warehouse Management System Definition
A warehouse management system is an integrated set of system functions designed to manage a warehouse or distribution center’s locating, putaway, movement, picking, and cycle count/inventory verification activities.
It usually receives purchase, sales, and interplant order data from a base ERP system that serves as the authorization to initiate activities.
Warehouse locations are described in their weight and volume capacities to enable proper direction when moving or stocking material.
Inventory and order status data, collected in real-time, often through data collection devices, are typically uploaded to the base ERP system on a batch basis.
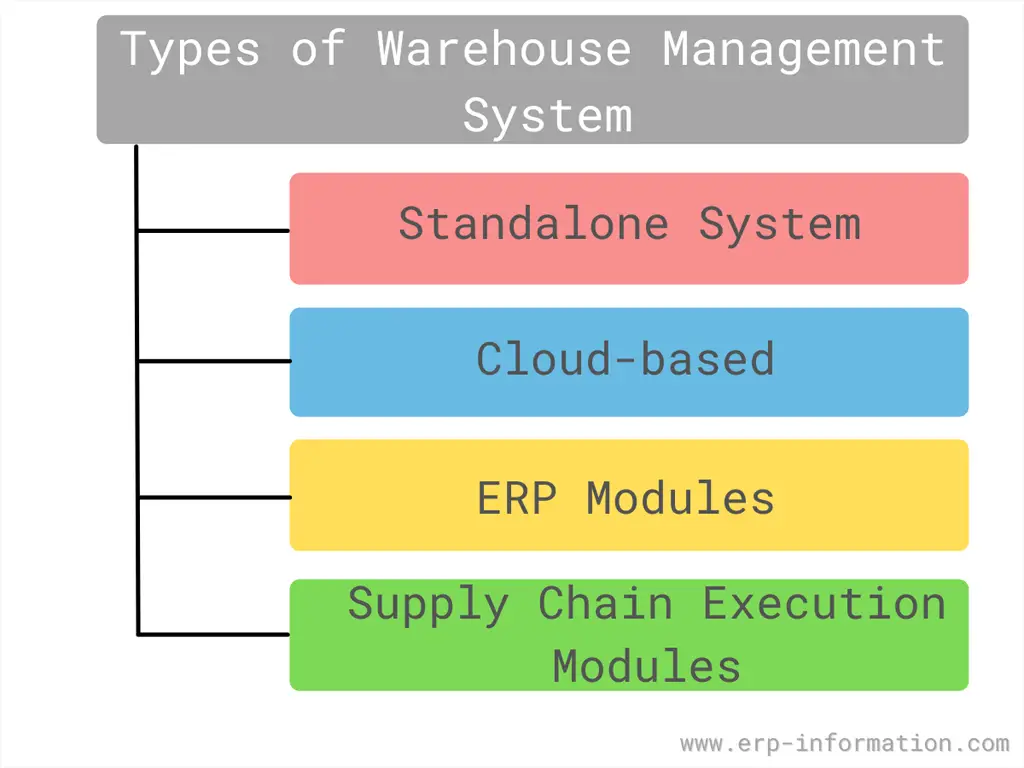
Types of the Warehouse Management Systems
The following are the most common and popular types of WM solutions.
1. Standalone system
This is an on-premises type system deployed on the local hardware and network. That is the lowest-price solution.
Features of the standalone system are inventory management, warehouse operations, barcode scanning, slotting, putaway, picking, packing, shipping, and validity date tracking. This system suits small businesses.
2. Cloud-based
This system is a typical web-based system such as SaaS. It provides faster implementation and helps to reduce IT maintenance as it is hosted on a separate server, depending on the vendor’s specifications.
This system allows users to update software automatically without extra expense.
3. ERP Modules
Many vendors provide WMS integrated with their ERP solutions. As a result, this system is known as one of the best.
It offers core applications like supply chain planning, CRM, accounting, human resource management, etc.
This system helps reduce labor costs, increase warehouse productivity, and increase inventory accuracy.
4. Supply chain execution modules
This system is a subcategory of the Supply Chain Management (SCM) system. It helps the entire supply chain process to go in streamlined.
Key Features of Warehouse Management System
The following are the features.
- Warehouse infrastructure: This system allows the organization to design the warehouse with sufficient space for seasonal inventories.
- Inventory monitoring: The system allows for tracking, monitoring, and moving inventories quickly with the help of a barcode scanner.
- Incoming and outgoing inventories: With the help of pick-to-light and pick-to-voice technology, this system optimizes the incoming and outgoing inventory process.
- Picking and packing of finished products: The system includes efficient picking systems like zone picking, wave picking, and batch picking that help the worker pick the goods efficiently.
- Shipping: The system allows you to create invoices and packing lists for shipping and sends shipping notifications to the customer in advance.
- Employee management: The system allows warehouse managers to manage employees and monitor their performance with the help of key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Dock management directs the drivers to find the proper ducks to load and unload the inventories.
- Documentation: The system generates all the reports that help managers analyze the warehouse processes.
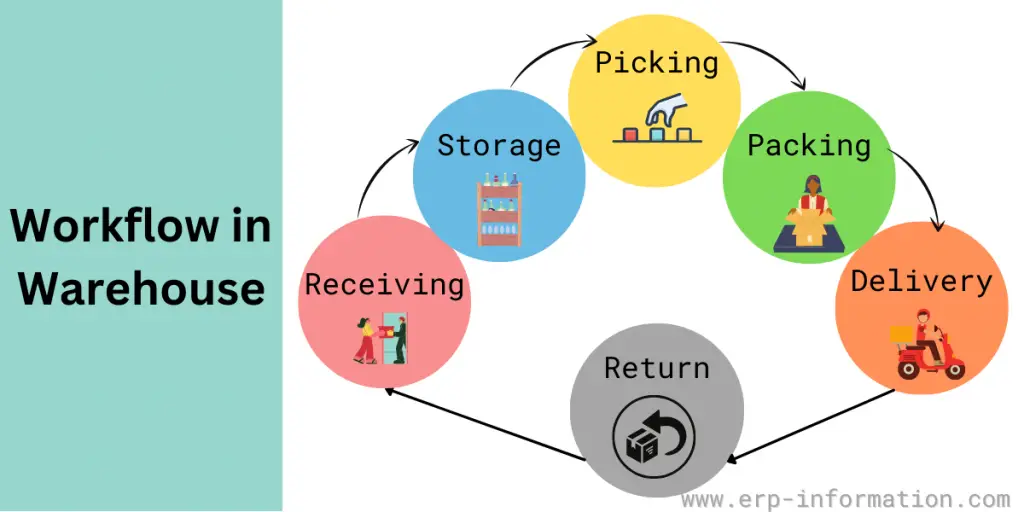
Workflow of Warehouse
The workflow process in the warehouse includes
- Receiving the goods
- Storage
- Picking
- Packing
- Delivery
- Returns
Your warehouse management should be capable of managing the workflow within the warehouse.
- Receiving: It must hold the delivery of goods to the warehouse of the exact quantity of wanted products of good quality at the correct time. This process contains the following works.
- Make space for the receiving goods.
- Unloading the goods
- Verification of the received goods
- Updating the database
- Storage: It is one of the essential responsibilities of the WMS. Move the received goods to their specified place in the warehouse, SKU ( stock keeping unit). Check out the safety measures for both goods and employees.
- Picking: Picking the products from the storage area per customer order. To reduce time consumption and error, adopt suitable picking methods like zone, wave, cluster, etc.
- Packing: In this process, checking of quality and quantity of the product and making them ready for shipping takes place.
- Delivery: Ensure the safe delivery of the goods to the customer’s place and on time. WMS should coordinate scheduling, tracking, and labor management at this stage.
- Returns: In rare cases, there will be a chance of returning the products for some reason. So this situation should be handled with special attention. Proper product identification, placing them back on the specified shelf, and sending them for repair will happen in this stage.
Advantages of Warehouse Management System
Decreases the operating cost
It lowers the operating cost by finding an excellent place to store products, materials, and equipment.
Controls warehouse activities
It controls all warehouse actions by reducing inventory levels, improving order fulfillment, and reducing order cycle time.
It helps the organization respond quickly to customer demand by providing accurate and immediate feedback. In addition, it helps to manage the inventory efficiently and rapidly.
Improves inventory visibility
It provides accurate and real-time inventory levels to estimate the supply and satisfy the customer.
Assigns work
This system gives the work to the suitable person at the right time, depending on the person’s skill level.
It helps design the schedule efficiently for day-to-day activities that improve labor efficiency.
It scans the items while entering the warehouse and keeps track of their movement. Hence saves time by avoiding double-checking.
It helps to trace the materials.
We can easily trace the materials with the help of WMS using lot/batch and serial numbers.
The Lot and Batch show the group where materials are made, and the serial number indicates the specific item.
In this way, it helps to compare the incoming receipt and dispatch receipt with the item. Hence it improves the tracing ability.
Simplifies the process through automation
It provides essential elements like sensors and bar codes to record, capture and communicate activity.
Improves customer service
It helps organize and track the shipments and improves the picking accuracy in the warehouse.
With it, we can easily plan incoming items and outgoing products. As a result, it improves the supply chain process and customer service.
Increases productivity
This system helps move the products quickly in the warehouse and allows workers to do more work with less time by providing them with what they want at the right time.
That helps to increase the productivity of the company.
Best WMS vendors
The following are the warehouse management system examples as standalone products.
10 Best 3PL Software (Pricing, Features & Reviews)
Open-source Warehouse Management Systems
Following are the open-source solutions,
- Openboxes
- OdooERP
- myWMS
- Flowspace
- Xinerji
Case Study of Optimizing Warehouse
A case study published by Infosys on the Fortune 100 telecommunications OEM is a good example. The company is known for its mobile phone and service wireless network solutions.
It faced challenges with its existing system. The warehouse could not scale on volumes of mobile phones. At times it failed to deliver during accelerated customer response.
Problem
The client had Distribution Center (DC) in Europe catering to the EMEA region as the customer upgraded to the single-most converged device. As a result, the distribution efficiency of this center decreased.
Challenges
This existing ERP system lacked integration with its AMHE (Automated Material Handling Equipment). In addition, as the solution was custom-built, it was rigid to handle the changes.
To extract and consolidate the data, the warehouse requires several tools. Using these tools resulted in reduced supply chain inventory visibility. In addition, the required shop floor processes were not streamlined.
This resulted in the idling of the assembly line. This was one of the main reasons to reduce the efficiency of DC, as it was not rolling out the products at peak times.
Solution
Re-engineering of DC leads to streamlining the required shop floor process. In addition, the AMHE was integrated with the ERP system. This offered a real-time consolidated view of the warehouse.
The integration improved to optimize the DC cost and aided the decision-making process. It also managed unexpected issues such as systematic manner by reducing manual intervention.
Future of Warehouse Management System
Advancements in technology influence the future of warehouse management. One major trend that is already having an impact on the industry is the use of automation and robotics.
Many warehouses now use machines like drones and automated vehicles to help with tasks such as picking and packing, which can help increase efficiency and reduce errors.
Another trend likely to continue is using data warehouse analytics to optimize warehouse operations. By collecting and analyzing data on inventory levels, order volume, and shipping times, businesses can identify areas where they can improve their processes and reduce waste.
The rise of e-commerce is also expected to impact warehouse management significantly. As more consumers shop online, warehouses must adapt to handle an increasing number of small orders rather than large bulk shipments.
Finally, sustainability will become increasingly important for warehouses in the future. Businesses must find ways to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize waste to meet growing consumer demand for environmentally-friendly products and practices.
Overall, the future of warehouse management will be characterized by increased automation, enhanced data analysis capabilities, a focus on e-commerce fulfillment, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
Conclusion
A warehouse management system is an automated storage and retrieval system that enables businesses to reduce inventory costs, increase efficiency, improve customer service levels, and better manage the supply chain.
Suppose you’re considering implementing a WM system into your operations or weighing options of which one to use. In that case, this post will help inform those decisions by highlighting some of its key features. We hope you’ve found it helpful!
References: