Effective integration and efficiency are critical to business success, making Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems essential tools. It is a comprehensive system that includes various functionalities needed for the smooth running of the business.
Our comprehensive blog post discloses its functional and technical modules and its extensive application suites. We also explore the numerous benefits of ERP and its pivotal role across various industries.
Introduction to ERP System Modules
Each ERP module is tailored to specific business functions, supplying essential data and supporting processes that help employees perform their tasks efficiently. All modules integrate seamlessly into the ERP system, ensuring a single, accurate source of data, even as new modules are added.
Consider the ERP system as a symphony orchestra, with each module akin to a different instrument. Just as each instrument contributes its unique sound to create harmonious music, each ERP module fulfills a specific role in the business process, combining seamlessly to orchestrate efficient operations and drive organizational success. This integration ensures cohesive and streamlined operations across the entire business.
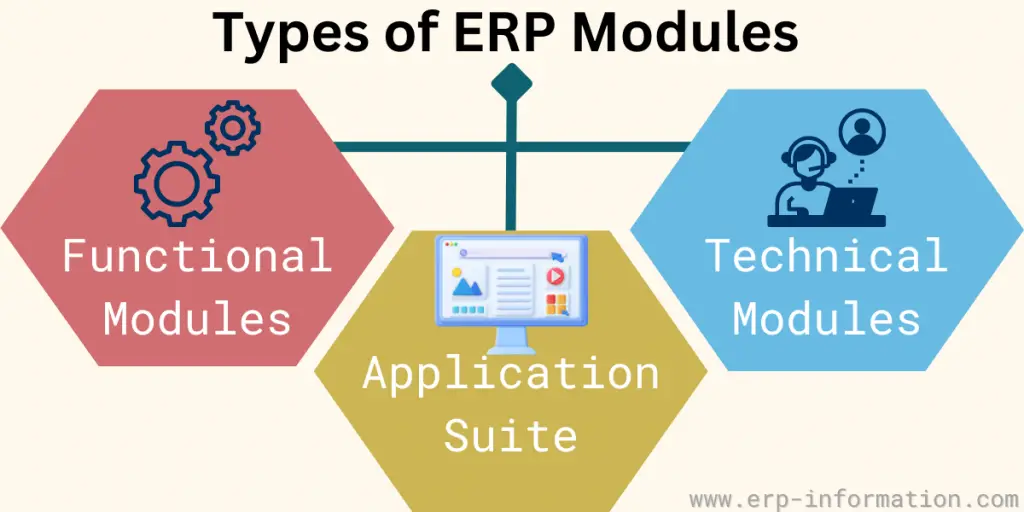
Types of ERP Modules
Three types of core ERP modules are
- Functional modules
- Technical modules
- Application suites
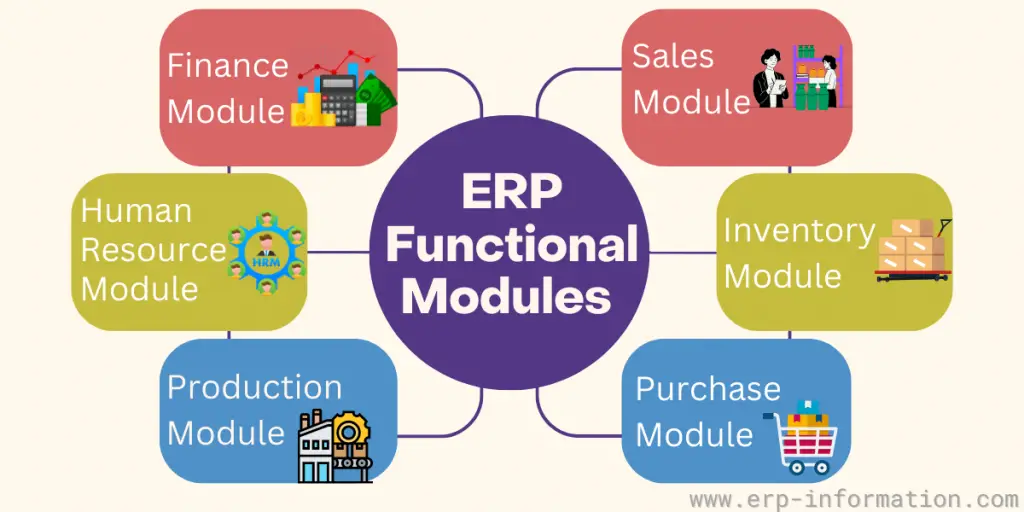
ERP Functional Modules
Below is the list of ERP modules. They are basic modules of the ERP system.
1. Finance Module in ERP
ERP financial modules are one of the central core ERP modules. It records transactions in the general ledger accounts. In addition, this module generates financial statements for external reporting purposes.
To know more about this module check ERP Finance Module – 7 Types of Reports and Valuable Features
2. HR (Human Resources) Module
It facilitates employee recruiting, hiring, and training. This module also includes payroll and benefits.
To know more about this module check ERP HR Module – 6 HRM Submodules & Features Explained
3. Production Module
It maintains production information. This module will help plan, schedule, and record production activities.
To know more about this module check ERP Production Planning Module (Features, Types, Objectives)
4. Procurement Module in ERP
The purchase module or procurement module streamlines the procurement of required raw materials. It automates the processes of,
- Identifying potential suppliers
- Negotiating price
- Awarding a purchase order to the supplier
- Billing processes
The purchase module integrates with the inventory control and production planning modules. In addition, the purchasing module combines with supply chain management software.
To know more about this module check ERP Purchasing Module – Features & Procurement Process Flow
5. Inventory Module
Inventory is the term for merchandise or raw materials that a company has on hand.
This module manages,
- Acquisition of raw materials from suppliers (purchasing)
- Handling of raw materials inventory in storage
- Work-in-progress goods
- Shipping of finished goods to the customer
To know more about this module check ERP Inventory Module (Features & Types)
6. Sales Module in ERP
It records sales orders and scheduled deliveries. Maintaining and accessing customer information is the responsibility of this module.
Customer information includes pricing, address and shipping instructions, billing details, etc.
To know more about this module check ERP Sales Module – Features, Flowchart, and More
Apart from these 6 basic modules, we will discuss other modules also.
1. Order Management Module
The Order Management module within an ERP system handles the lifecycle of sales orders from inception to fulfillment. It consolidates order information, manages order entry, and tracks order status, ensuring smooth processing from customer inquiry to final delivery.
Features include order creation, customization, order tracking, and order fulfillment synchronization with inventory and production modules.
2. Warehouse Management Module
Warehouse Management in ERP oversees the movement and storage of goods within the warehouse. It optimizes warehouse operations by efficiently managing inventory levels, picking, packing, and shipping. The module includes functionalities for inventory tracking, bin allocation, space utilization, and real-time visibility into stock levels and locations.
To know more about this module check Warehouse Management System (WMS)
3. Professional Services Automation (PSA) Module
The Professional Services Automation module streamlines project management and service delivery for service-based businesses. It covers project planning, resource allocation, time tracking, billing, and invoicing.
It ensures project timelines, budgets, and resources are effectively managed, fostering better project execution and client satisfaction.
4. Workforce Management Module
Workforce Management in ERP focuses on optimizing human resource allocation and productivity. It includes features for employee scheduling, time and attendance tracking, performance management, and skill development.
This module helps businesses streamline workforce operations, manage labor costs, and enhance employee engagement.
You can analyze your workforce using our Workforce Planning Calculator.
Related article: 10 Best Workforce Management Software List
5. E-commerce Module
The E-commerce module integrates online sales channels with the ERP system. It helps organizations to create B2B or B2C e-commerce websites. It synchronizes product information, inventory levels, and customer data between the e-commerce platform and the ERP.
This integration streamlines online transactions, ensuring accurate product listings, inventory availability, order processing, and customer data consistency across channels.
Related article: 10 Best B2B eCommerce Platform
6. Marketing Automation Module
Marketing Automation within an ERP system automates marketing tasks and workflows. It manages campaigns through email, social media, and SMS, tracks customer interactions, and analyzes data to personalize marketing efforts.
This module helps in lead generation, customer segmentation, email marketing, and measuring campaign effectiveness, enhancing overall marketing efficiency.
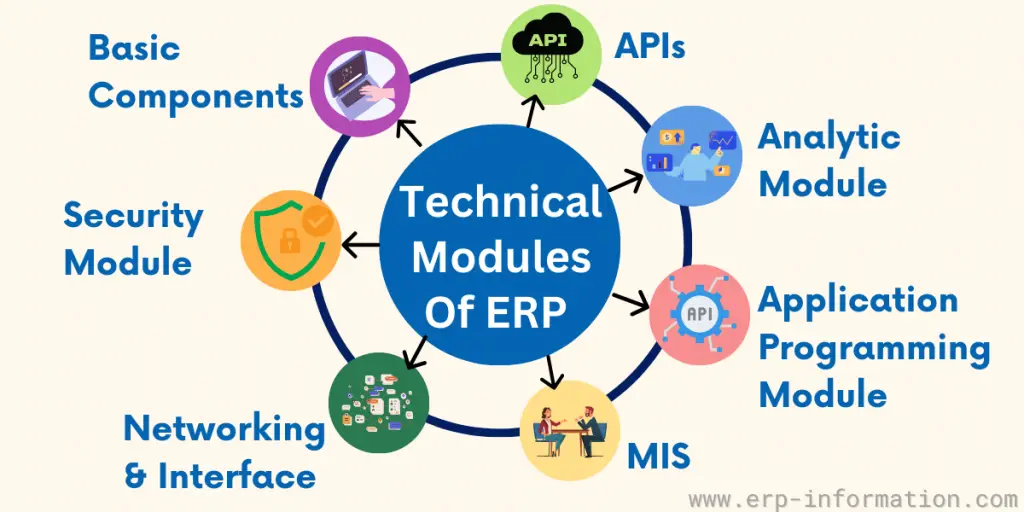
Technical Modules of ERP
Technical modules come under application platforms. And it is like the role of the operating system for your laptop. Technical modules integrate tightly with functional modules. They help smooth integration with different functional modules and application suites.
Technical components found in ERP systems are,
Basic Components
This includes the hardware, software, databases, and networks that make up the system. In addition, the system administrator also manages user accounts, security, and data backups.
Without these essential components in place, it would be difficult for the business to use an ERP system efficiently.
Security Module
It is designed to establish robust internal security to allow or prevent access wherever needed by utilizing various tools, such as firewalls and encryption.
ERP security modules help to safeguard data and information from unauthorized access and misuse. In addition, it can also provide auditing capabilities so that organizations can track and monitor activity on their systems.
Networking and Interface
The networking and interface module ensures that data can flow freely between different parts of the system and that users have the necessary permissions to access the information they need.
In addition, the module must be compatible with the hardware and software used by the organization.
Without a well-designed networking and interface module, an ERP system will be unable to function correctly, limiting its potential benefits.
Management Information System
Management Information System (MIS) is a system that provides managers with the information they need to make informed decisions about the operation of their business. It typically includes a database, software to generate reports, and tools for data analysis.
It was used primarily by large businesses in the past, but the advent of ERP systems has made MIS available to small and medium-sized companies.
Application Programming Module
This module allows the user to create custom code to extend the functionality of the ERP system. The Application Programming module also provides a library of standard code modules that can be used to create new applications or modify existing ones.
It is a powerful tool that can tailor the ERP system to the organization’s needs.
Analytic Module
An analytic module within an ERP system can provide even more insight by performing data analysis and generating reports. This way, managers can quickly identify trends and issues and take action to resolve them.
As a result, an analytic module is a valuable tool for any business that wants to use its ERP system to its full potential.
APIs Opened for External Use
With the rise of the internet and cloud computing, many organizations now use ERPs to share data and applications with external partners. This trend is driven by the need for greater business agility and flexibility.
By opening their APIs for external use, ERP providers enable their customers to extend their systems’ functionality and better meet their business ecosystem’s needs.
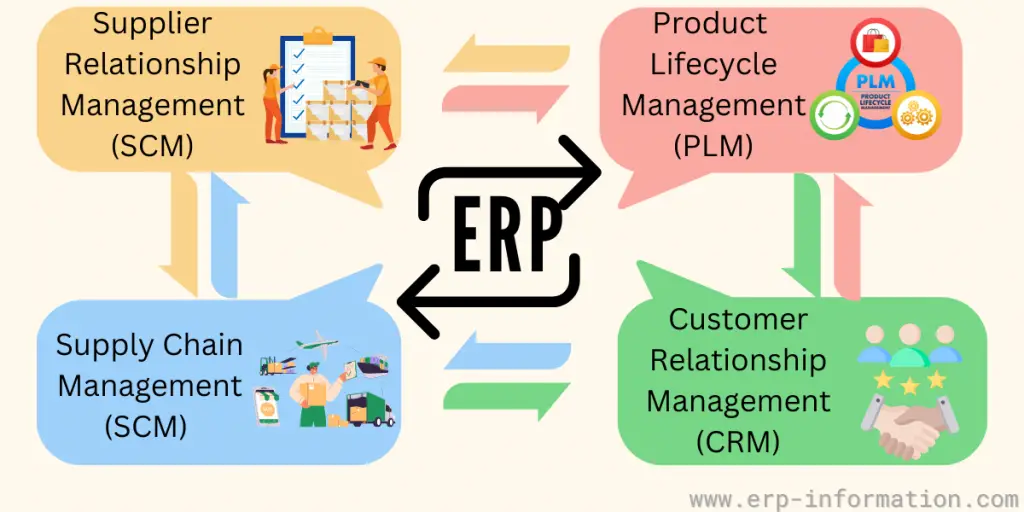
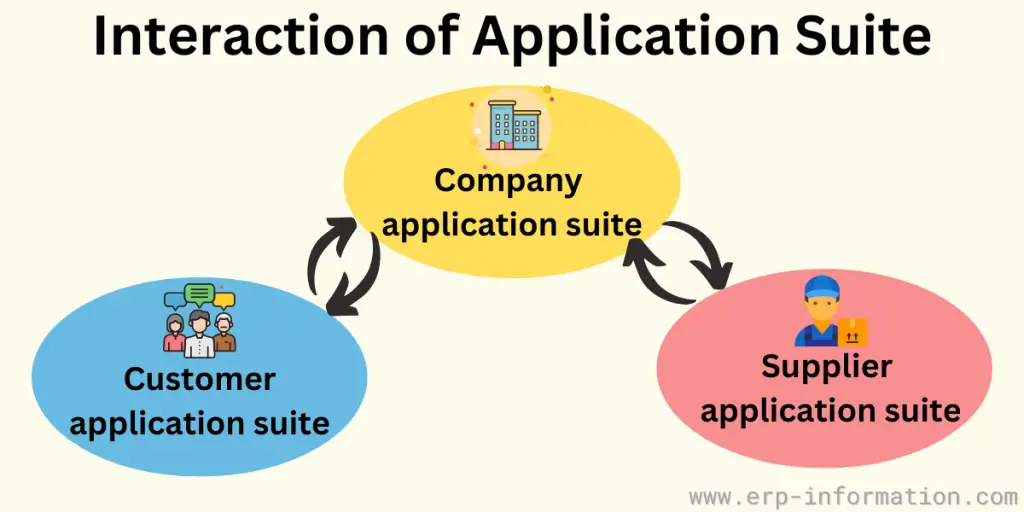
Integration of ERP with the Application Suite
The application suite is a collection of interconnected information systems. That could be within and across different companies.
Currently, more and more organizations are utilizing ERP frameworks. The next stage is to interface these frameworks. That will support interactions that occur between and among organizations.
A few of the popular inter-company systems are,
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SCM interfaces an organization with different organizations that supply the materials. Common SCM frameworks help organizations in planning. For example, they plan their creation necessities and improve complex transportation and materials coordination.
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
SRM frameworks usually deal with general associations with the materials providers. In addition, SRM frameworks help cope with quotation and contract processes.
Companies can have more intra-company systems. But, again, that is an extension of the fulfillment process of ERP systems and ERP modules.
Examples of intra-company systems are,
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM frameworks associate an organization’s ERP framework with its customers. CRM frameworks furnish organizations with the ability to oversee showcasing, deals, and client administration. These frameworks are an expansion of the satisfaction procedure of ERP frameworks.
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
Product lifecycle management frameworks help organizations watch the research procedures, plan, and itemize the board. They help take new item thoughts from the virtual drawing board to the manufacturing unit.
Related article: What is Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)?
Benefits of ERP Modules
- ERP modules help your business attain the desired efficiency and enhance day-to-day activities by automating all business processes.
- It keeps all the data centralized and gives clear data whenever needed.
- It improves business reporting with the help of reporting features with real-time data.
- It helps to eliminate the manual process and reduces errors done by manual errors. Thus, it increases the efficiency and productivity of the business.
- It provides better communication within the department as well as between the departments. Cooperation in the workplace also increases when there is a smooth flow of information.
- It helps the business provide good customer service by enhancing on-time delivery and order accuracy.
- It allows the business to control who can use, share, and edit the data.
- ERP modules analyze the real-time data.
- Enhances profitability by avoiding extra expenses like an additional store of inventories.
- It improves the cash flow with better invoicing.
Role of ERP Modules in Different Industries
Manufacturing and distribution industry
ERP modules allow manufacturers and distributors to effectively manage and control their inventories, purchases, sales, and accounts.
It also provides human resource management to manage and control employees. All these things help in the improvement of the business.
Health care sector
ERP module will benefit payroll, patient care, controlling instrument supplies, compliances, etc. It also helps in operational assistance.
Education sector
ERP module helps improve the management of students’ enrollment process, teaching sessions, etc.
It is also helpful in scheduling parent-teacher meetings, conducting the monthly test, etc. In addition, it helps monitor the admission fees, student attendance, staff attendance, and staff leaves.
Hospitality sector
In this sector, customer service is very, very important. So it would be best if you concentrated more on customer satisfaction.
ERP system helps to automate the workflow smoothly, reducing the waste of time and decreasing stress on management and workers.
Construction sector
Construction industries’ equipment rental cost control, inventory handling, and deadlines are critical.
Good and efficient ERP software helps the industry with automated workflow and streamlines the process.
Professional services
ERP modules help this sector maintain expenses and profits, keep accurate employee data, and control inventories. Hence billing cycle and cost decrease, and gain increases.
Food industries
The food industry contains many fruits, dairy, vegetables, beverages, chocolates, biscuits, meat, poultry, fishery, etc.
This industry has many phases in the production process. ERP modules help improve quality management in all stages of the production process.
It helps to decrease production waste and improves productivity.
Non-profit sector
An accurate reporting system is crucial for this sector. ERP systems help by providing efficient financial reports, budget control systems, and self-service payroll solutions.
SAP ERP Modules
- Financial Accounting (FI)
- General Ledger
- Accounts Payable
- Accounts Receivable
- Contract Accounts Receivable and Payable
- Banks
- Fixed Assets
- Special Purpose Ledger
- Additional Functions
- Lease Accounting
- Travel Management
- Shared Service Center
- Controlling (CO)
- Cost Element Accounting
- Cost Center Accounting
- Activity-Based-Accounting
- Internal Orders
- Product Cost Accounting
- Profitability Analysis
- Profit Center Accounting
- Materials Management (MM)
- Inventory Management
- Purchasing
- Material Planning
- Material Requirement Planning
- Invoice Verification
- Vendor Valuation
- Warehouse Management
- Sales and Distribution (SD)
- Sales
- Billing or Invoice Generation
- Bills of Material
- Shipping and Transportation
- Electronic Data Interchange
- Sales Information system
- Credit Control
- Human Capital Management (HCM)
- Organizational Management
- Recruitment
- Training and Event management
- Wages
- Personnel Development
- Payroll
- Travel Management
- Personnel Management
- Time Management
- Compensation Management
- Workforce Administration
- Personnel Administration
- Production Planning (PP)
- Demand Management
- Sales and Production Planning
- Capacity Requirement Planning
- Material Requirement Planning
- Bill of Materials
- Shop Floor Control
- Production Orders
- Routing
- Work Center
- Quality Management (QM) Planning
- Process Inspections
- General Functions
- Notifications of Quality
- Test Equipment
- Quality Control
- Quality Certifications
- Planning
- Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM)
- Credit Management
- Cash & Liquidity Management
- Dispute Management
- Collections Management
- Payments
- Treasure and Risk Management
- Project System (PS)
- Project Preparation
- Project Planning
- Project Tracking
- Project Reporting
- WBS Elements
- Project Costs
- Plant Maintenance (PM)
- Project Maintenance
- Maintenance Planning
- Predictive Maintenance
- Preventive Planning
- Service Management
Oracle ERP Modules
Following are the Oracle ERP modules that are important and their functionalities,
- Financial Management
- Accounting hub
- Reporting and analytics
- Payables and assets
- Revenue management
- Receivables
- Collections
- Expense management
- Joint venture management
- U.S. Federal Financials
- Project Management
- Plan, schedule, and forecast
- Resource management
- Cost management and control
- Billing and revenue management
- Grant management
- Project asset management
- Procurement
- Source
- Pay
- Purchase
- Supplier management
- Supplier portal
- Procurement contracts
- Procurement analytics
- Self-service procurement
- Risk Management and Compliance
- ERP role and security design
- Separation-of-duties automation
- Continuous access monitoring
- User access certification
- Configurations controls
- Transactions controls
- Audit and SOX/ICFR workflows
- Enterprise risk management (ERM)
- Business continuity planning
- Enterprise Performance Management
- Planning
- Profitability and cost management
- Account reconciliation
- Financial consolidation and close
- Tax reporting
- Narrative reporting
- Enterprise data management
- ERP Analytics
- KPI management
- Best practice metrics library
- Prebuilt analytic models
- Extensible architectue
- Business content areas
- Self-service data discovery
- Augmented analytics
- Collaboration and publishing
- Enterprise architecture and security
- Mobile exploration
FAQs
What are ERP modules?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) modules are individual components or segments within an integrated software system designed to manage and streamline diverse business functions.
These modules serve as specialized units, each focusing on a specific aspect of an organization’s operations. They function cohesively to centralize data, automate processes, and enhance efficiency across various departments.
Conclusion
ERP modules are essential for optimizing business processes across various industries. By seamlessly integrating functional and technical components, ERP systems enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
From managing finances and human resources to streamlining production and inventory, ERP modules provide a comprehensive solution tailored to specific business needs.
Embracing ERP technology not only improves operational performance but also fosters better decision-making and customer satisfaction. As businesses continue to evolve, the strategic implementation of ERP modules will remain a key driver of growth and success.