Enterprise Resource Planning serves as the central pillar of modern business management, seamlessly weaving together every facet and function of an organization into a harmonious symphony.
This dynamic system fosters the fluid exchange of data across all business domains, fueling the engine of efficiency and driving informed decision-making.
With diverse implementation options, including on-premise, cloud-based, or hybrid systems, ERP offers versatility to match the unique needs of every enterprise. Continue reading to learn more.
This blog post will explore the definition of ERP, how to implement it, modules, advantages, disadvantages, best practices, the different types of systems available, and more!
ERP Definition
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive business management solution that enables companies to manage their core business processes in one system. ERP integrates all aspects of a company’s operations into a cohesive system, from accounting and financials to sales and marketing.
This can be a huge advantage for businesses that manage complex operations or multiple locations.
The best way to explain it in layman’s terms is to give you an example.
Imagine you are the owner of a small business. You have a shop and sell clothes. You also have a website where people can buy your clothes online.
To run your business, you need to manage two different types of resources: physical resources (e.g., the stock of clothes in your shop) and digital resources (e.g., the website where people can buy your clothes).
Enterprise resource planning systems allow you to manage physical and digital resources using a single system. This is done by integrating different applications into a single system.
For example, it might include an application for managing your shop’s stock, an application for managing your website’s content, an application for managing your human resources (e.g., employees), etc.
History Of ERP
Gartner initially used the term ERP in 1990. However, the business management software and applications used in the manufacturing sector have evolved in recent decades as industry demand varies.
ERP had its roots in the early 1960s when large American corporations began using specialized software to manage their complex businesses.
The first generation of enterprise resource planning software was designed for manufacturing companies and focused on streamlining manufacturing resource planning and improving inventory management.
The future
The pace of the digitization of businesses will accelerate. As a result, companies using digital technologies in all aspects of their business will fundamentally change their operation.
As a result, companies also demand robust ERP systems. Global ERP software will surpass the US$77.40bn mark and grow 10.2% between 2019 and 2024.
A Brief History of ERP – since 1960 and the future
Benefits of ERP Systems
Today ERP solutions provide rich features for a business. However, what each firm considers to be the best value of these systems varies according to the company’s requirements.
The following are many benefits to implementing it in a business:
Streamlined Business Processes
It integrates all core business processes into a single system, which eliminates data silos and allows companies to make connections across different departments. This streamlined workflow results in faster and more efficient operations.
Improved Decision Making
The Enterprise resource planning system provides real-time data analytics so that business owners and managers can make informed decisions based on accurate information.
Increased Efficiency And Productivity
It automates routine tasks, saving employees time and focusing on more challenging projects with more significant potential for growth.
Cost Savings
ERP systems are often more affordable than implementing and maintaining individual software applications for each department. In addition, it can help businesses reduce waste and optimize their inventory levels, which leads to increased profits.
Disadvantages of ERP Systems
Although ERP systems offer substantial advantages, various business issues persist in the market. Regrettably, many of these could have been averted through the careful selection of a fitting supplier partner.
The complexity of implementing enterprise resource planning systems, particularly in large companies with multifaceted departmental reliance, poses a significant challenge.
Hence, it is important to weigh the benefits and probable hurdles before determining if ERP aligns with your business needs.
Here are some common challenges:
Cost
The cost of ERP software varies depending on the solution you choose (cloud or on-premise) and how many modules you need. If any customization is required, it can be expensive.
Therefore, you should also consider factors in the implementation costs, which may include training employees or data migration services, etc., into your budget when deciding whether it suits your business.
Timeframe
The solution implementation process can often be lengthy, especially if you integrate it with existing systems or make significant changes to your business.
Therefore, it is essential to set realistic timeframes and goals for implementation and ensure everyone involved knows their expectations so that the process goes as smoothly as possible.
Complexity
ERP systems are complex and challenging, especially for employees unfamiliar with them. Therefore, you should provide adequate training and support to help employees make the most of its features and functionality and ensure they understand how it can benefit their role within the organization.
Otherwise, employees may struggle to use it, resulting in employees doing their work manually or using a separate system, etc., defeating the purpose.
Customization
It can be customized to meet your unique requirements, but that generally comes at an additional cost.
Therefore, one should think carefully about what software would need to do to benefit your business and whether or not the company can customize the software accordingly before deciding whether it is right for you.
Scalability
Scalability is a feature, yet it might not automatically suit your business if you anticipate rapid growth. It’s essential to evaluate its scalability and ensure it aligns with your future expansion goals before making a decision.
Features of ERP Systems
Some essential characteristics distinguish an ERP solution from any other software type. This includes,
- An ERP system gains an edge when it consolidates diverse data from various databases and integrates seamlessly with other applications. This unified, real-time data source eradicates the need for manual merging across separate data pools related to business operations.
- Additionally, a shared database offers a consistent, comprehensive view of companies, ensuring uniform user experiences and interfaces across different department roles.
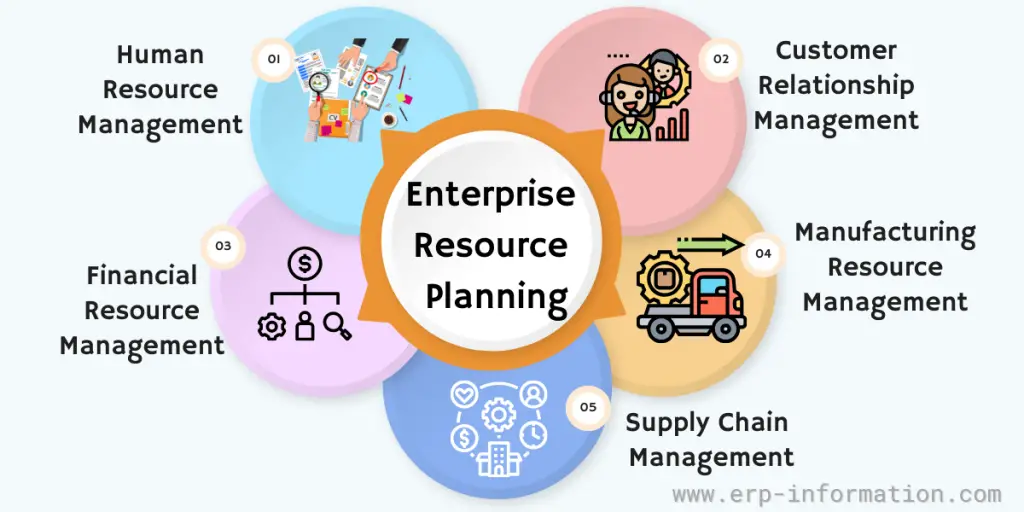
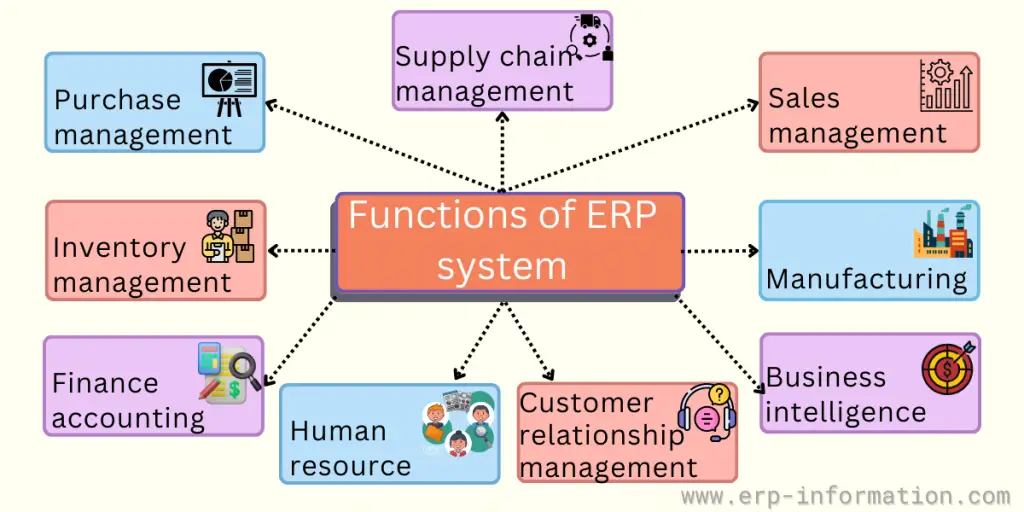
ERP Modules
Integrated ERP includes several different components based upon specific features adapted to the various aspects of the organization, including front-office tasks. This quick overview shows the most common modules.
- Accounting and Finance.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
- Supply chain inventory management.
- Manufacturing.
- Human resources.
- Business intelligence.
- Purchase management
- Sales management
What is New with Enterprise Systems?
With exponential progress in systems’ data storage and computing capacity per Moore’s law, we witness advancements in enterprise software systems.
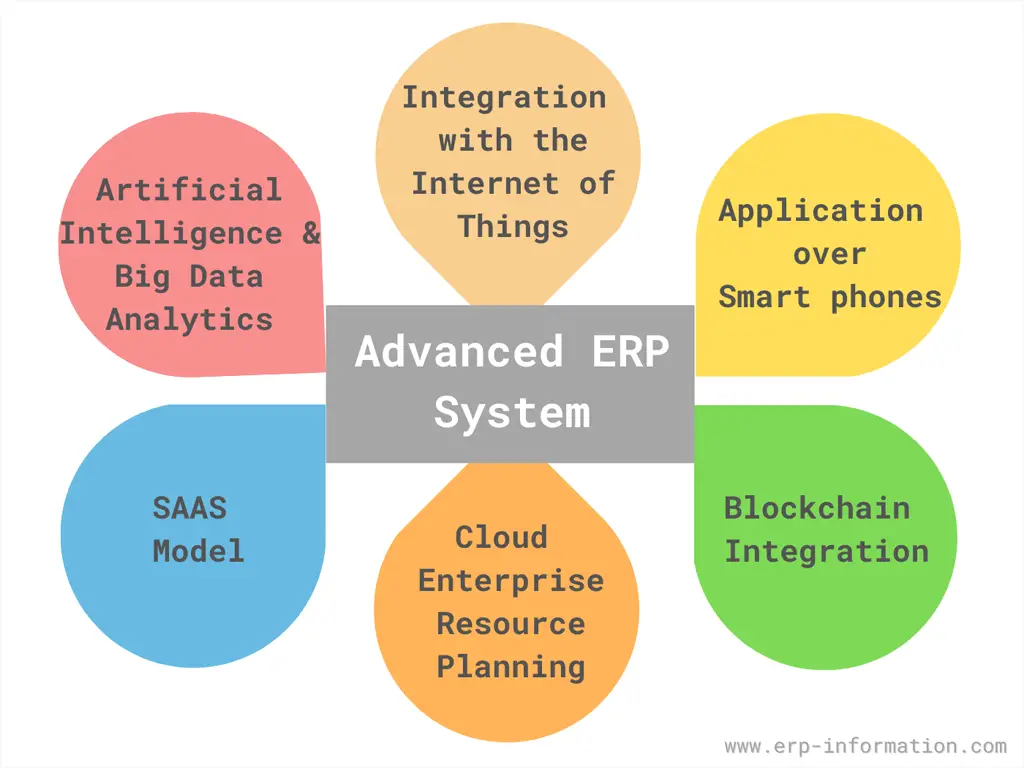
The following are a few high-impact innovations.
- Artificial intelligence and big data analytics
- Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT)
- Applications over smartphones
- Blockchain integration
- Cloud enterprise resource planning
- SAAS model
Find details of high-impact innovations below:
Artificial intelligence and big data analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) with machine learning can help make better business choices. It enables businesses to optimize all their operations.
- Business operational processes.
- Software systems.
- Management structures.
- Hardware and technology infrastructure.
Enterprise software systems gather enterprise data from day-to-day business processes and generate big data.
Extensive data analysis can predict demand and help make future business decisions more efficiently.
Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a connected physical object accessible. Automated, machine-to-machine, meaningful communication is established with it.
The following are the advantages of integrating IoT with enterprise software systems,
- It has enhanced data accuracy and availability.
- Accurate and efficient communication.
- Greater business intelligence.
Applications over smartphones
Mobile applications help in accessing information on the go. They also help in collecting job site information accurately.
The most popular mobile operating systems on which client applications are built are,
- Android.
- iOS.
Blockchain integration
Enterprise systems are adopting blockchain technology. It helps businesses in achieving,
- Enhanced transparency.
- Greater security.
- Increased traceability.
- Improved efficiency.
It helps in achieving greater control over supply chain management.
Cloud ERP
Vendors host their software on the cloud computing system instead of customers’ data centers. It helps in faster upgrading and reduces maintenance efforts.
SAAS model
Software-as-a-service models allow small and medium-scale businesses to use software systems without substantial initial investments. This model does not demand higher installation costs or IT people. Instead, it is pay-as-you-go based on how much you use.
How to Select an ERP System?
ERP software installation can be an imposing process with numerous software options. The best software must meet the requirements and the business needs while providing the necessary support for successful implementation.
The following are key factors to consider when selecting an ERP system:
- The size of the company and its industry
- Company’s business processes and needs
- Implementation timeline and resources available
- Cost of software and implementation services
- Maintenance and upgrade requirements
Once you have identified your needs, you can use the information to decide by comparing systems with similar features and functions.
The following are some of the critical factors that will help you select ERP software for your business:
- Product Functionality
- Customization and Integration Capabilities
- Vendor Support Services (implementation, training, maintenance)
- Cost of the System and Implementation Services.
It can be expensive and requires careful selection to ensure that it will meet your business needs now and in the future. When selecting software, consider all costs, such as software licenses, implementation services, hardware and software, upgrades, training, and support.
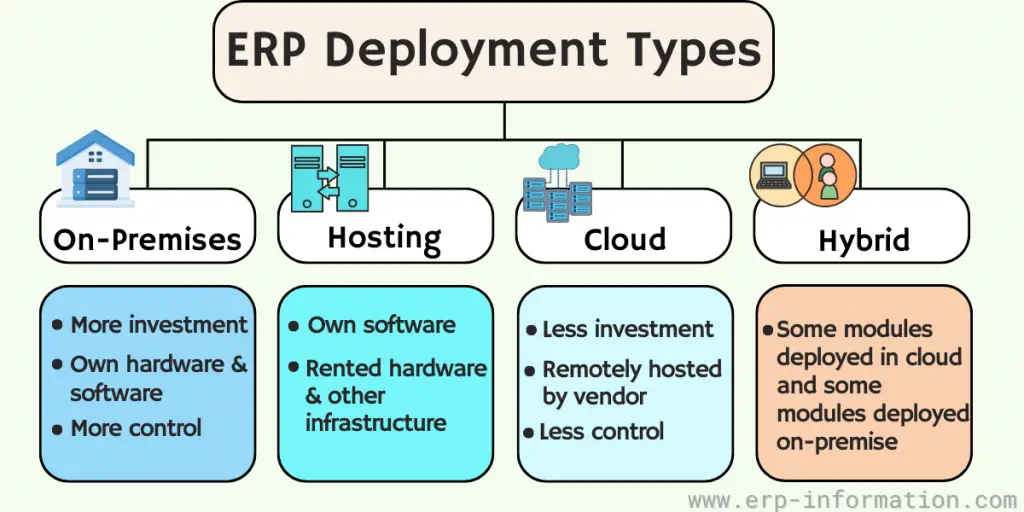
Enterprise Resource Planning Software Deployment Options
Enterprise Resource Plan systems vary in scope depending on the size and functions of a company.
Three main types of application deployment models are,
- On-Premises deployment: Traditional deployment on company premises refers to the installation of software and hardware at the customer’s site. In this setup, the company retains control over these resources, handling updates, security, and other maintenance tasks.
- Hosting – this model involves the provider hosting the application in their data center(s) and delivering it to users via a web browser. Customers have no hardware to procure or software to install but depend on their internet connection for access.
- Deploying in the cloud is a SaaS model where applications are installed at the vendor’s data center and delivered via a web browser or other thin client. Customers have minimal control over infrastructure, upgrades, and security issues; they use the software.
- Hybrid (some on the cloud or others offline) – companies increasingly use a hybrid approach to deploying software. Some system modules may be deployed in the cloud while others remain on-premises.
Depending on the solution, the system may support different parts of a business, meet business needs, or have other deployment methods.
ERP Integration
The current ERP system provides many business functions. It needs connectivity and integration with other applications and data sources, including CRM/CRO and HCM software, e-commerce platforms, industry-specific products, and ERP software.
The modern ERP System provides openness and flexibility and can easily integrate with various product suites using connectors or custom adaptors like the application programming interface or API.
Ten Things to Look for in an ERP System
A sound ERP software system may have several functions mainly determined by the industry and module they offer.
Ten basic and essential characteristics are the following:
1. Comprehensive Functionality
The best packages have a comprehensive range of essential functions. These include inventory management, warehousing, distribution, and accounting (purchasing, sales, and financial) modules. Make sure the solution you choose has all of these functions.
2. Scalability
A sound system must grow with your business. Therefore, it should be able to accommodate increasing numbers of users and transactions as your business grows.
3. Customizability
The system must be customizable to meet the specific needs of your business. The best systems offer a high degree of flexibility to configure them to work how you want them.
4. User-Friendliness
The solution must be easy to learn, use, and maintain. A single database should contain all the information you need to run your business. In addition, the system should offer a single-user interface for viewing inventory levels or processing sales transactions.
5. Robust Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics capabilities should be a standard feature of any product. The system must provide the ability to track and analyze your business’s vital information, including financial reporting.
6. Seamless Integration with Other Applications and Systems
They must integrate seamlessly with other important applications and systems of your business. This includes both back-office and front-office systems.
7. Support for Multiple Operating Systems and Databases
They must run on multiple operating systems and support multiple databases. This allows you to choose the best operating system and database for your business.
8. Cost-Effectiveness
They can be costly, especially if you purchase a customized package. You should choose a system that offers your needed features at a cost within your budget.
9. World-Class Customer Service and Technical Support
They are complex and challenging. Therefore, you must rely on the vendor for world-class customer service and technical support.
10. Timely Updates and Upgrades
They are complex and ever-changing. The vendor must provide timely updates and upgrades to ensure that your ERP system continues to meet your needs.
ERP Buyer Types
ERP vendor selection and deployment type depend on the needs of a buyer. Here are the common types of buyers.
- Small businesses – Small businesses are an important market for enterprise software systems. To grow, they must manage their finances, operations, and human resources effectively.
- Medium-sized businesses – Medium-sized businesses need software to manage their more extensive and complex operations. In addition, they need a system that can scale and integrate with other business systems.
- Large enterprises – Large enterprises have the most complex operations and need software to manage their resources effectively. They also require a system that can be customized to meet their specific needs.
- Government organizations – Government organizations need enterprise software to support their specific needs. In addition, they require a system that is secure, scalable, and compliant with regulations.
- Non-profit organizations – Non-profit organizations need software to manage their donations, volunteers, and finances. They also require a system that is easy to use and can be accessed by all employees.
- Educational institutions need software to manage students, faculty, and finances.
- Healthcare institutions need software to manage patients, staff, and finances.
- Retail businesses need software to manage inventory, sales, and employees.
- Manufacturing companies need software to manage production, inventory, and finances.
- Technology companies need software to manage employees, projects, and finances.
ERP Best Practices
Enterprise resource planning systems typically adhere to well-established best practices. These processes are designed by software vendors based on successful experiences with numerous clients, offering flexibility for the provider to adapt strategies.
This adherence to industry standards yields substantial economic benefits. Enhancing processes and driving productivity becomes more straightforward for companies, making it imperative for firms to align with best practices to meet financial standards.
Following are the 11 best practices:
- Identify your requirements
- Design the project management team with a clear vision and strong leadership.
- Define key business processes that need to be delivered.
- Involve customers in the decision-making process. It is crucial to get end-user feedback, to know what is happening, and to be more willing to use the software in the future.
- Understand the change management process because ERP implementation is a significant change for your company, and you will be forced to change your organization and use new technology.
- Ensure all costs are part of the total cost of ownership (TCO) – hardware, software, implementation, training, and support.
- Select the right partner with a strong track record in your industry
- Leverage the Partner’s Implementation Methodology (PIM) to shorten your project timeline
- Use pre-configured modules whenever possible to speed up deployment and get up and running quickly
- Train end users thoroughly and ensure that support is available when needed
- Perform a post-implementation review to identify areas for improvement.
When you implement it, you will go through a specific life cycle. This life cycle will help ensure that your implementation is successful. Here is a look at the different phases of the ERP Implementation Life Cycle.
ERP Vendors
List of ERP – 31 Best ERP Vendors of 2023 (Unbiased Ranking)
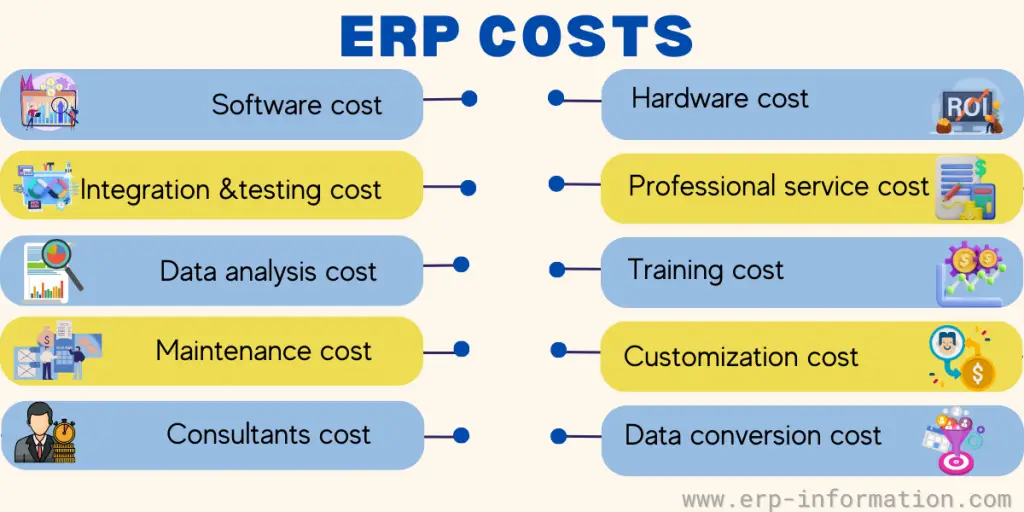
Cost of ERP
The cost of the system can vary widely depending on the size and complexity of the business.
The cost of implementation and customization can also be high, so it’s essential to factor these expenses into the overall cost of the system.
Cost of ERP (How Much Does it Cost and What Influence it)
Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning solutions monitor and unify every facet of a company’s operations, spanning accounting, inventory management, human resources, and customer relations.
Consequently, these systems serve as vital assets for businesses of all scales, streamlining operations, enhancing decision-making, and amplifying profits. Hope this post helped you understand the essentials of this system better.
[ ERP filetype PPT presentation file ]