Human-machine interface is a term you may have heard before, but what does it mean? It is defined as “how humans interact with electronic devices.” In simpler terms, it’s the way we control and monitor machines.
Human Machine Interfaces have a wide range of applications in both personal and professional settings.
This article will look closely at the Human Machine Interface definition, its uses, components, trends, and more.
What is Human Machine Interface?
It is the interface between the human operator and the machine. It encompasses hardware and software elements enabling users to interact with a machine or system.
In many cases, this interaction takes the form of commands or requests; in others, it may be feedback from the machine about its status or operation.
Whatever their specific purpose, HMIs are an essential part of modern life. They allow us to control complex systems and processes with ease and precision.
As we continue to rely more and more on technology, they will become increasingly important and fascinating tools for interacting with the world around us.
A human-machine interface aims to provide an intuitive, easy-to-use, and efficient platform for performing its intended function.
Depending on the application, this may involve simple display screens or more complex control panels with multiple displays, dedicated keyboards, trackballs, touchscreen panels, etc.
They are typically used in industrial applications to monitor and control production processes. That can involve starting and stopping equipment to view real-time process status and performance data.
Other terms for human-machine interface
It is also named operator interface terminal(OIT), Local operator interface(LOI), Man-machine interface(MMI), and Graphical User Interface(GUI).
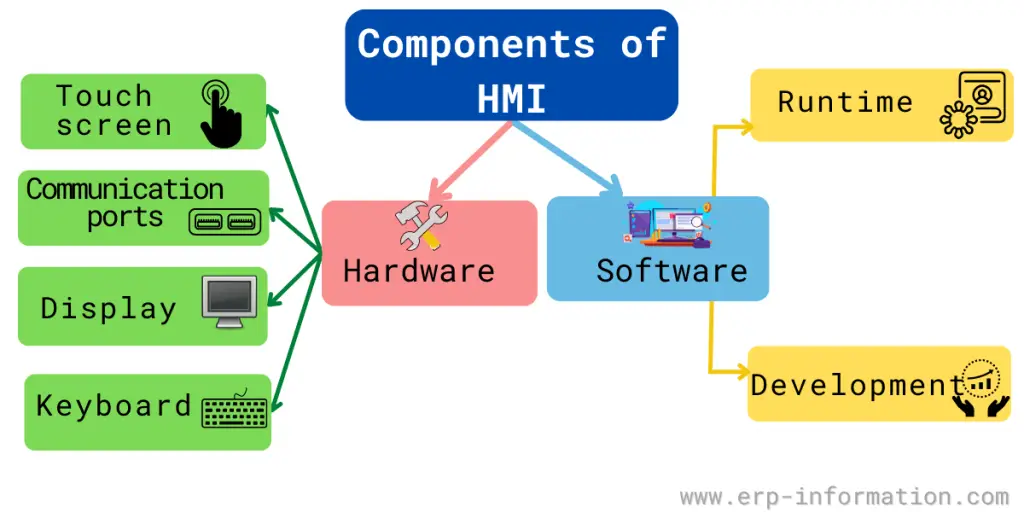
HMI Components
Both hardware and software are the main components of the human-machine interface.
Hardware includes
- Touch screen
- Communication ports
- Display
- Keyboard
Software includes
- Runtime
- Development
Uses of Human-Machine Interface
Here we are listing its most common uses.
- It communicates with input and output sensors and programmable logic controllers(PLCs).
- Monitors and controls machinery like starting and stopping machines and performs sophisticated operations.
- Allows operators to see data in graphs and charts through digital dashboards.
- Allows operators to view and manage alarms.
- Eliminates manual recording of mechanical processes by allowing PLCs to provide real-time data to display.
- It helps to decrease human errors.
- It helps to reduce machine downtime and increases accuracy by enabling operators to control machines.
- It enhances communication between manufacturing processes and between machines and men.
Role of HMI in SCADA System
SCADA system is the central control system of industrial processes.
The human-machine interface is an important part of this system. It connects to Programming Logic Controller (PLC) and displays data from PLC, and gives input to PLC from users.
In this way, it helps the manager or operator to monitor and control the processes.
HMI Examples
The most common examples are the keypad/keyboard of a computer and touchscreens. The HMI screen and other devices help human beings to communicate with machines.
Other devices used in industries are multi-touch-enabled control panels, push buttons, mobile devices, or a tablet.
They are used in older applications where GUI software is unavailable.
What is the Difference Between HMI and SCADA?
| HMI | SCADA |
| It shows visual information to help the operator to monitor the industrial process. | It collects information and controls system operation. |
| It does not connect to the database. | It connects to the database. |
| It does not collect and record data. | It collects and records data. |
| It provides a good communication tool for the SCADA system. | It is the main monitoring and controlling system. |
Trends in Human Machine Interface Software
High-performance HMI
It is becoming a trend nowadays. Operators prefer this because it is fast and interacts effectively. It focuses more on complicated indicators and allows the operator to view and respond to the problem quickly and efficiently.
In addition, it provides clear and simple graphs and charts and optimizes the user experience.
Remote monitoring
Remote monitoring allows operators to become flexible and accessible. Operators can monitor and view the information on the industrial processes even if they are far away from the shop floor or field.
Cloud HMI
With its help, operators can view and access data from field devices. You can also send information from the local human-machine interface to the cloud that can be accessed and examined remotely.
Touch screens and mobiles
Advanced human-machine interface allows operators to tap or touch the screen instead of pushing buttons or switches to monitor data and access control. In addition, mobile allows the user to instantly access and monitor remotely.
Advantages and disadvantages of HMI
Advantages
- Good coordination between the operator and machine helps to monitor and control the system.
- Operators can easily access the updates of input information and increased capacity.
- Operators have access to emergency stop buttons and other safety uses.
- As a result of improved accuracy and quality control operator can easily input and monitor the data.
- The interface can be changed to fit the operator’s needs of what he wants to do. This makes the system more flexible and easier to use
Disadvantages
- Expensive to Install and maintain. You may need special software or hardware that costs a lot of money.
- The interface can be difficult without operation skills. For effective usage, the operator will need to have training.
- Scalability is limited, which means the system might be unable to work with new changes or upgrades.
- Compatibility may also be limited, which means it will only work with certain machines or systems.
- The interface may not always work because of limited reliability, which can cause problems.
- It may face some security issues. It can also be easier for hackers to get into if it is not secure.
FAQs
What are the types of HMI screens?
There are three types of HMIs. They are the pushbutton replacer, the data handler, and the overseer.
What are the system requirements for HMI?
Depending on what kind of system you have, the HMI might need some other things. This could include multiple serial and network ports, an IRIG-B port for time, different kinds of mountings (like rack or panel mount), a keyboard, a mouse, and backup parts.
What is an HMI controller block diagram?
HMI controller block diagram is a tool engineers use when designing products. It helps to show the design with pictures. This makes planning for building and testing the HMI controller in a lab or workshop easier.
Conclusion
A human-machine interface is a part of the SCADA system. Here we discussed what it is, its components, uses, trends, and the difference between SCADA and HMI.
We hope you find this article helpful.
Reference