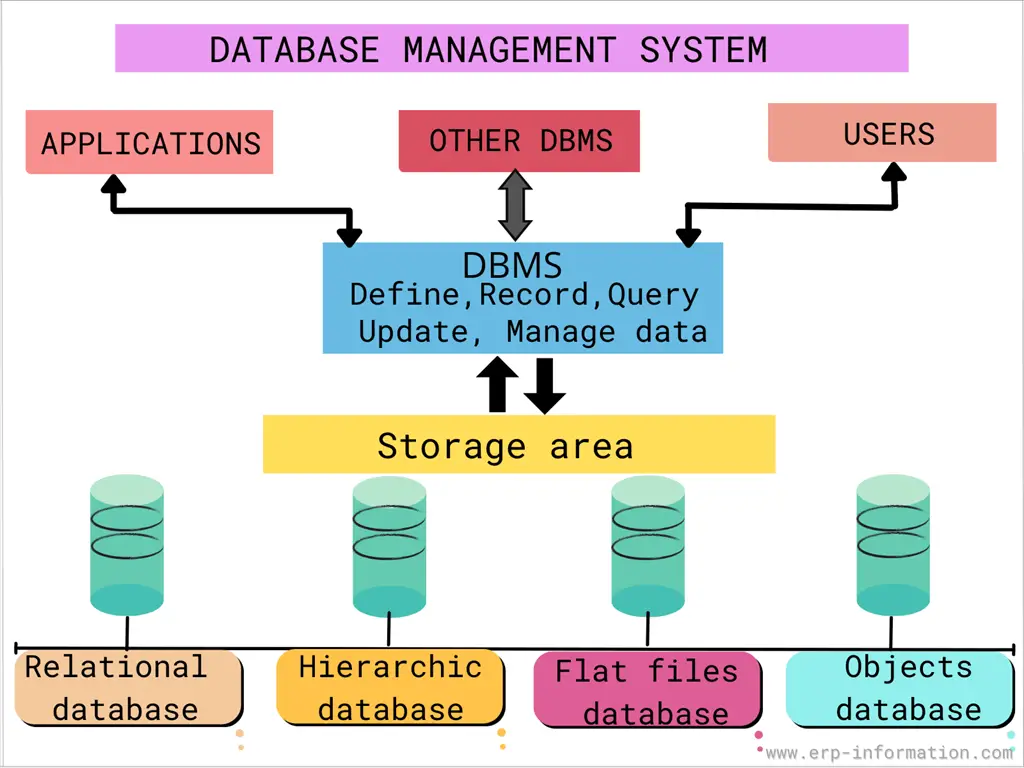
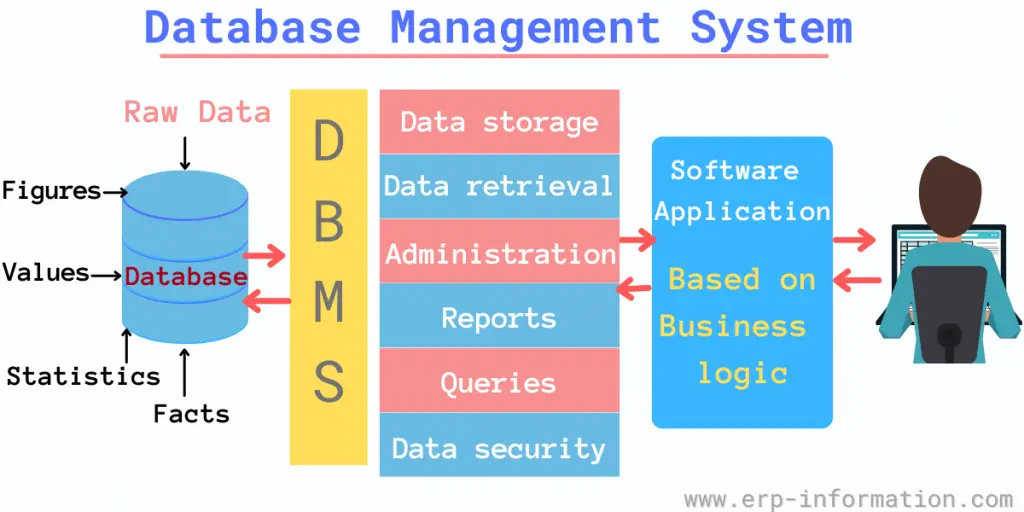
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a computer software application that enables users to create, manage, and query databases. In addition, it can be used to store data for various purposes, such as tracking customer information or managing inventory.
Many different DBMS applications are available today, each with its unique features and capabilities. Therefore, when deciding which database suits your needs, it’s essential to understand what these systems do.
This blog post will provide an overview of DBMS along with examples, components, and architecture. It will also discuss some of its functionalities, advantages, and disadvantages.
Definition of DBMS
Before learning about Data Base Management Systems, we have to learn what a database is.
What is a database?
A database is a group of interrelated data. It helps to track, retrieve, insert, and delete information easily and efficiently.
A Database Management System is an assortment of programs and applications used to manage the database.
Various users extract and manipulate the data for different business and personal requirements.
It might be used by an administrator who ensures that the data stored in the system is secured and limits free access to other users.
Some designers access the database to handle the same design aspect, making it more flexible and data-pro.
The last sect is the end-users who access it to collect and analyze the existing data for their needs.
How does it work?
A DBMS acts as a middleman between the user and the database. It simplifies the data management process and ensures the data’s security, consistency, and integrity. It works in the following way:
- Organizing Data: The DBMS organizes your database files, categorizing them in a way that makes them easily retrievable. Data organization can be based on various factors such as the data type, relationships between the data, etc.
- Access Control: The system provides end users more access and control over the data. It ensures appropriate security measures are in place so that only authorized persons can access specific parts of the database.
- Data Interaction: System users are given facilities to perform various operations on the data, such as creating new data, updating existing data, deleting unnecessary data, and retrieving required data.
- Concurrency: The DBMS also manages concurrency, which means it allows multiple users to access and modify the data simultaneously without compromising data integrity.
- Backup and Recovery: Another crucial function of a DBMS is managing backups and recovery. It ensures that the data can be recovered from backups without any discrepancies in case of any failure or data loss.
- Data Integrity: The DBMS ensures data integrity by enforcing rules on the data. These rules ensure that the data remains consistent and accurate.
Some Examples of Database Management Systems
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Microsoft Access
- SQL Server
- File Maker
- Oracle
- RDBMS
- dBASE
- Clipper
- FoxPro
We can take a school database, for example.
This school database maintains information about students, sections, grades, staff, and related information. The database will be arranged as follows.
- Student file: It stores all the data like the name, residential address, and phone number of the parents of each student
- Section file: It stores the information of sections of each class
- Grade file: It stores the data of scores of each student
- Staff file: It keeps the information about all the faculties of the school
Types of the Database Management System
Relational (RDBMS)
Relational databases are the most popular type of DBMS. They store data in tables with rows and columns, making them easy to query and update. They’re often used for storing financial data, customer information, and other types of business data.
Hierarchical
Hierarchical databases are based on a parent-child relationship between data records. They’re typically used when data is structured and doesn’t often change, such as in EHR systems.
Flat-files
Flat-files DBMS is another type of database, but they store data in a simple text file instead of using more complex structures like tables and objects.
While they’re not as common today as other types of databases, flat files are still helpful for simple applications that don’t need to store much data or perform complex queries.
Object DBMS
Object-oriented databases are similar to relational ones, allowing you to store data as objects rather than tables and columns.
This makes them more intuitive for programming applications and easier to work with when developing new software products.
Overall, each DBMS type has advantages and disadvantages, so it’s essential to carefully consider your needs and requirements before deciding which one to use.
Network databases
Network databases are similar to hierarchical ones but have a more flexible structure allowing multiple paths between records. This makes them well-suited for applications where data is constantly changing, such as inventory management.
The DBMS Architecture Classification
Its architecture of it can be classified as
- 1-tier: The user directly works on the system and is solely responsible for all the actions he carries out on it.
- 2-tier: Here, an application acts as a barrier through which the user can access the database. He cannot directly alter the data and hence is comparatively secure.
- 3-tier: Based on how the users use the existing data in the server, this system will divide it into three tiers: Presentation tier, Application tier, and Database tier. Depending on the complexity of data that prevails and its use, companies build a multi-tier system that restrains the users from making any changes and ensures proper controls to keep it safe.
Components of DBMS
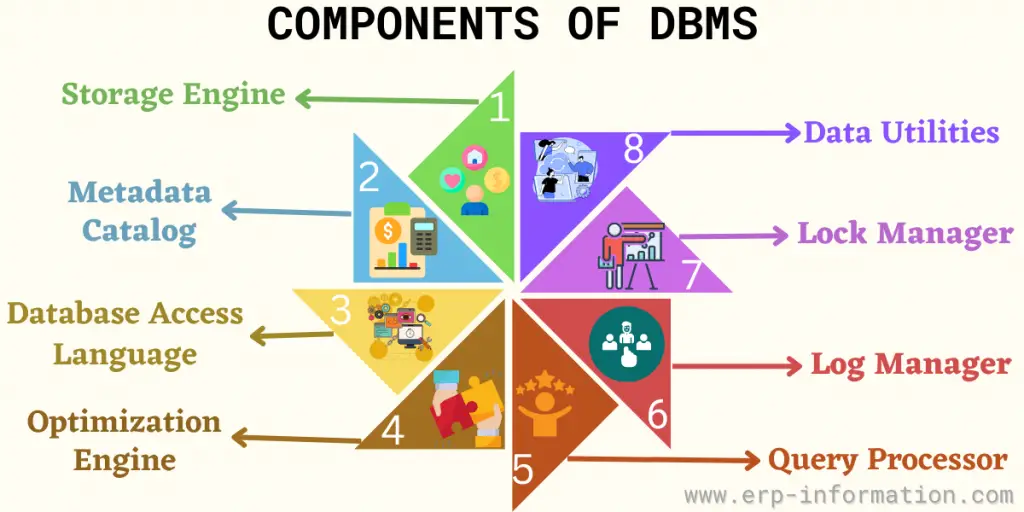
Storage Engine
This is the major component that stores data. DBMS should interface with a file system in the operating system to store data. This engine can also use extra components to store data.
Metadata Catalog
It is also called a database dictionary. It acts as a storehouse for all created database objects. One of the major functionality of the metadata catalog is verifying users’ requests for data.
It contains information about schemas, programs, database objects, security, communication, and performance.
Database Access Language
SQL is a good example of a database access language. It consists of many sets of commands, such as
- Data Control Language: Authorizes data access
- Data Definition Language: Defines database structure
- Data multiplication Language: Reads and modifies data
Optimization Engine
It reviews database access language requests and converts them into actionable commands for modifying data.
Query Processor
It processes the query and returns the results.
Lock Manager
It helps to manage concurrent access to the same data. It prevents to do changes in the same data simultaneously.
Log Manager
It manages all the changes made to data that DBMS manages. It keeps accurate log records of data. It is helpful to ensure data integrity during shutdown and startup to maintain backups.
Data Utilities
Data utilities consist of runstats, reorganization, recover, load and unload data, and repair database.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DBMS
Advantages
- Increases the data quality and ensures that the business structure and needs to maintain the data.
- Because of its centralized nature, it is easily maintainable.
- It reduces program maintenance and data hacking.
- Allows authorized users of an organization to share data with multiple users.
- It protects the database. If there are multiple users, it allows for maintaining data consistency.
- Allows users to insert, modify, and delete the data in the database.
Disadvantages
- DBMS can be slow and cumbersome to work
- They can be challenging to scale up or down as needed
- The security of your data is only as good as the security of the DBMS itself
- If something goes wrong, it can be challenging to troubleshoot and fix
Functions of DBMS
- Create structured databases and supporting platforms for enhanced performance.
- Appropriate backup and data recovery operations to be set
- Adequate security and anti-virus measures
- Read and modify existing data if required
More significant organizations have complex databases. That is because they must support several users simultaneously, including several supporting applications, and involve several databases.
Applications of DBMS in Different Sectors
Manufacturing
Product-based industries manufacture various products and deliver them daily, weekly, or monthly. This sector stores information about products, like the quantity of the products, product bills, and supply chain management.
Banking & Finance
In banking, it is used to store customer transaction details, and in the finance sector, it is used to hold data about sales, stocks, and bonds.
Education sector
Information about the students, their attendance, courses, fees, and results are stored in the database. Apart from this, it is used to store staff data also. In addition, many colleges and universities use it for conducting online examinations.
Credit card transaction
It purchases a credit card and creates a monthly statement.
Social media sites
Nowadays, social media are the popular platforms to share our thoughts and views with the world and our friends.
Social media also allow us to connect with our friends. Millions of sign-ins and sign-ups happen daily on social media like Facebook, Twitter, Linkedin, etc. All these things happen with the help of database systems that allows us to connect with others.
Telecommunication
All telecommunication companies use it. The DB is crucial for this sector to store monthly postpaid bills and customer call details in the database.
Railways & airlines reservation system
A database is necessary to store ticket booking data and keep the information on train/ airplane arrivals, departures, and delay status.
Human resource management
Big industries have more employees. A database is required to store employees’ information like their permanent address, salary, tax, and other details.
Online shopping
Online shopping helps save time. Present-day online shopping created a trend. People love to do online shopping through websites like Amazon.
All the transactions, such as products added, the products sold, generation of invoice bills, and payments, happen with its help.
Relational Database Management System (RDBMS)
RDBMS stores data in a row-based table structure.
IT staff can easily create, update, monitor, and retrieve the database. Generally, RDBMS uses SQL( Structured query language) to access the database.
It is the most desired type of DB worldwide because it enables companies to store and retrieve vast amounts of data. Apart from that, it is easy to implement.
Difference between RDBMS and DBMS
| DBMS | RDBMS |
| Only one user can operate at a time. | Multiple users can use it at a time. |
| It requires less hardware and software. | It requires more software and hardware. |
| It controls a small amount of data. | It controls a vast amount of data. |
| Data is stored hierarchically. | Data is stored in a row-based table structure. |
| It does not support distributed databases. | It supports distributed databases. |
| It maintains databases present in the computer network and system hard disk. | It maintains the relationship between its integrated tables of data. |
| It does not follow the ACID manner. | It stores data with atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID). |
Distributed Database Management System (DDBMS)
Before knowing about DDBMS, let us know about a distributed database.
A distributed database is a set of various interconnected databases spread physically throughout all the locations and communicated through a computer network.
A DDBMS is a single centralized software system that controls a distributed database. It is mainly used for creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting the distributed database.
FAQs
What is database management software?
Database management software is a type of software that helps you manage your databases. It can help you create, edit, and delete databases and add and remove users from those databases.
It can also help you back up your data and restore it if necessary. Many different kinds of database management software are available, and you can find one that meets your specific needs.
What are the business sectors that use DBMS?
Many business sectors use DBMS, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and retail.
It is necessary for these businesses because it helps them store and access data quickly and easily. This allows them to make better decisions and improve their operations.
Conclusion
A database management system is a program that enables you to store, modify, and query data.
This article looks at the different types of DBMS software available and how they can benefit your business. We also looked at the features offered by some of the most popular DBMS programs on the market.
Consider your organization’s needs if you’re looking for a database management system for your business. Then, with a suitable DBMS in place, you can streamline your operations, improve efficiency, and make better decisions. Thanks for reading!