Ensuring quality in product development is crucial for success. Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) serves as a vital tool in achieving this.
APQP provides a structured approach that helps manufacturers and innovators create outstanding products by following a clear process and steadfast principles.
It is a quality management system(QMS) that ensures customer satisfaction and product conformity. This process has been used in various industries, including the automotive and manufacturing industries.
This blog post will discuss what APQP is, its phases, process flow, other core tools, and its benefits.
What is APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning)?
It is a structured methodology used in product and process design that ensures quality and meets customer expectations.
It involves a Cross Functional Team (CFT) from various departments to enhance communication and collaboration. APQP focuses on understanding customer needs, translating them into technical requirements, and identifying changes early to innovate while managing risks.
The planning starts with the customer’s requirements and works backward through the product development process, identifying potential quality problems and solutions.
It can be an integral part of a QMS. It is required by the OEM to validate that suppliers have a process in place to deliver products with zero defects or near-zero defects. This helps companies reduce waste and improve customer satisfaction while increasing profits.
5 APQP Phases
The APQP process consists of five phases:
- Defining Product Planning and Quality Program
- Designing and Developing the Product
- Designing and Developing the Process
- Validating the Product and Process
- Launching Production, Assessing Results, and Continuously Improving
Let us explore each phase
1. Defining Product Planning and Quality Program
When the customer demands a new product or a revamp of an existing one, preliminary planning becomes crucial before starting design discussions.
This phase concentrates on understanding customer requirements and expectations. Key tasks include gathering data to define customer requirements and using this information to outline product features.
The planning phase also involves setting up a quality program for manufacturing, which includes defining product design, reliability, and quality goals, Bill of Materials (BOM), preliminary process flow, special characteristics, product assurance plan, and securing management support.
2. Designing and Developing the Product
This phase is dedicated to finalizing the product design and is relevant if the company handles the product’s design, including a comprehensive feasibility assessment. Based on customer requirements and identified safety or critical features, the main outputs of this design and development phase include:
- Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis (DFMEA)
- FMEA Monitoring and System Response (MSR – if applicable or necessary)
- Design for manufacturing and assembly
- Design review and verification
- Prototype Control Plan
- Engineering drawings and specifications
- Defined material specifications
- Equipment, tooling, gauging/testing, and other facility requirements
- Finalized special characteristics
- Team feasibility commitment and management support
3. Designing and Developing the Process
This phase is centered on planning the manufacturing process for the new or improved product. The goal is to create a production process that meets product specifications, quality standards, and cost-efficiency. The process must be able to meet expected consumer demand while remaining operationally efficient. Key deliverables include
- Packaging standards/specifications
- A fully defined process flow chart
- Production floor plan layout
- Characteristics matrix
- Process FMEA
- Product and process quality system review
- Work instructions
- Measurement systems analysis plan
- Pre-launch control plan
- Preliminary process capability study
- Management support (staffing and training plan)
4. Validating the Product and Process
This phase is the critical testing stage that validates the manufacturing process and the final product, culminating in the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). During this stage, customers approve based on product samples and documented evidence of the manufacturing process’s capability and reliability. Necessary adjustments and refinements are made before moving to the next phase.
Key steps include:
- A significant production run
- Control plan
- Quality planning sign-off
- Measurement system evaluation
- Preliminary process capability study
- Production part approval
- Packaging evaluation
- Management support
5. Assessing Results and Continuous Improvement
The last phase involves the full-scale launch of production, emphasizing process evaluation and improvement. It aims to achieve an enhanced manufacturing process with fewer variations, improved product delivery quality, and customer service.
Key improvements are:
- Reduced process variations
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
- Improved delivery and service
- Effective use of lessons learned and best practices
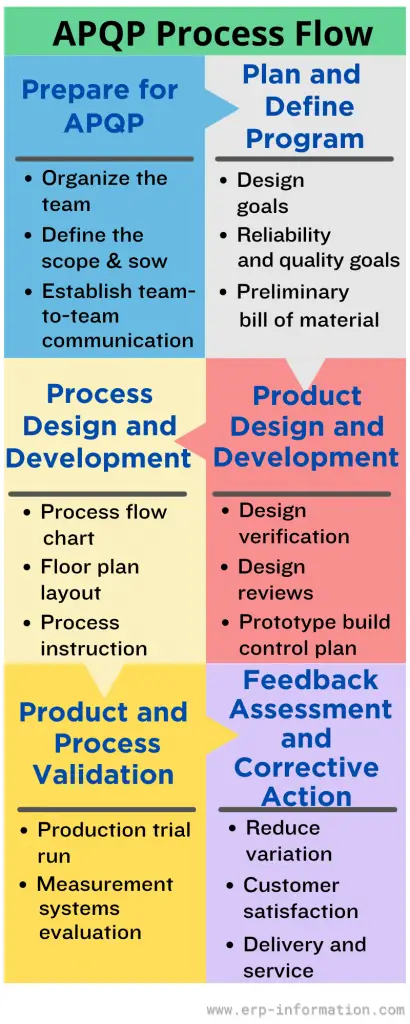
APQP process flow chart
The process flow chart is a graphical representation of the APQP process. It shows the relationships between the various steps in the process and what inputs and outputs are associated with each step.
Following is a sample visual representation.
When to Implement APQP?
New Product Introduction
APQP is crucial when introducing a new product to the market. It ensures that the product is developed with a comprehensive understanding of customer requirements and expectations.
By following the APQP process, companies can systematically plan and execute each stage of product development, from initial planning to final production launch.
This approach helps in minimizing risks, ensuring that the product meets quality standards, and ultimately leading to a successful market launch.
Product or Process Change
APQP is also necessary when making significant changes to existing products or processes. Whether it’s a redesign of a product to improve performance or efficiency, or a modification to the manufacturing process to enhance quality, APQP provides a structured framework for managing these changes effectively.
By following the APQP process, companies can assess the impact of the changes, identify potential risks, and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. This ensures that the changes are implemented smoothly, with minimal disruption to operations, and that the desired improvements are achieved.
In both scenarios, APQP acts as a proactive approach to quality management, helping companies deliver products that meet customer expectations, minimize risks, and drive continuous improvement.
Brief History
Emerging in the 1980s, APQP is a methodical approach employed for product development and quality management.
Originating from major American automotive giants such as General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler, it was forged to guarantee that suppliers could adhere to the rigorous quality benchmarks set by the automotive sector.
In the years that followed, the principles of APQP have transcended their automotive origins and are now widely adopted across diverse industries, solidifying their status as a favored technique for product innovation, quality assurance, and the effective management of risks in manufacturing and engineering processes.
APQP and Customer Satisfaction
APQP aims to ensure customer satisfaction by delivering high-quality products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
It is a crucial element of a QMS and is commonly integrated into ensuring that product design requirements are met before manufacturing begins.
It provides the framework for developing a QMS, which integrates all activities in an organization with processes and procedures designed to meet customer needs while controlling costs, maximizing productivity, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
APQP Core Tools
The Automotive Quality Core Tools serve as the foundation of a robust quality management system. APQP is one of the core tools. Other tools are
FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis)
FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) is an analytical approach used to ensure that potential issues are identified and resolved throughout the product and process development stages. Each individual will be responsible for identifying failure modes in their area. The APQP team leader will then collate the individual’s results to create a list of potential problems for the product.
PPAP (Production Part Approval Process)
It is the industry standard that outlines the production part approval process and ensures that the supplier’s manufacturing process meets engineering design records and specification requirements. This process involves submitting a sample of the part to the customer for approval. Once the customer has approved the part, companies can use it in production.
MSA (Measurement Systems Analysis)
It is a methodology for evaluating the quality of measurement systems, offering insights into areas for improvement, and providing knowledge to enhance your measurement process and ensure consistent product quality.
SPC (Statistical Process Control)
It means the application of statistical methods, such as control charts, to analyze a process or its output, enabling appropriate actions to achieve and maintain statistical control and enhance process capability.
Key Benefits
Proactive Quality Assurance
APQP enables thorough risk evaluations, employing tools such as Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Control Plans. By addressing potential quality issues early in the development process, APQP prevents the production of defective parts.
Elevated Customer Experience
Through APQP, companies deliver higher-quality products, leading to increased customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers foster stronger relationships with manufacturers, enhancing brand loyalty and reputation.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
APQP mitigates quality-related delays and reworks in development and manufacturing, streamlining processes and reducing time-to-market. This efficiency boost translates to significant savings in resources and labor.
Cost Reduction
Quality problems, reworks, and warranty claims incur substantial costs for manufacturers. APQP minimizes such issues, resulting in significant cost savings over the product lifecycle.
Strengthened Supplier Collaboration
By incorporating detailed customer insights, APQP fosters better understanding and collaboration between manufacturers and suppliers. This collaborative approach cultivates stronger partnerships and improves overall supply chain performance.
Effective Risk Management
APQP’s robust risk assessment processes empower suppliers and manufacturers to identify and mitigate potential quality issues early on, minimizing disruptions and ensuring smoother project execution.
Enhanced Process Control
Combining various methodologies with APQP’s Statistical Process Control (SPC) enables precise monitoring and control of the production process. This granular control optimizes efficiency and maintains product quality at every stage of manufacturing.
Quality Management Systems
QMS is a system used to ensure that the quality of the product meets the customer’s requirements. The QMS will typically include the following:
Policies and Procedures: The policies and procedures of the QMS should be documented and accessible to all employees.
- Quality Manual: The quality manual should be a comprehensive guide to the QMS and include all policies and procedures.
- Document Control: Documents related to the quality of the product should be controlled and tracked.
- Training: Employees should be trained on the requirements of the QMS.
- Auditing: The QMS should be audited regularly to ensure effectiveness.
FAQs
What is the history of APQP?
In 1982, American Chrysler, Ford, and General Motors created the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) to ensure suppliers had good quality requirements. In 1994, this was changed into a set of guidelines called QS-9000. This is known as APQP.
What are the inputs of APQP?
Its inputs are customer feedback, information about similar products, and the company’s goals, and it turns them into a plan. The plan includes targets for design and reliability, details about how to make the product, and early product features.
What is APQP in the supply chain?
This is a way of managing projects that includes the suppliers. All the data about the project and product will be organized, managed, and checked to ensure uniform documentation for the product.
What are the key tools or methodologies commonly used in APQP?
Some commonly used tools and methodologies include Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Control Plans, Process Capability Studies, and the 8 Disciplines (8D) problem-solving approach. These tools aid in risk assessment, quality control, and problem resolution.
How does APQP support continuous improvement throughout the product’s lifecycle?
It promotes a culture of continuous improvement by regularly assessing product quality, gathering feedback, and making necessary adjustments. This iterative process ensures that the product evolves to meet changing requirements and customer expectations.
Conclusion
APQP is crucial for ensuring product quality, meeting customer expectations, and fostering continuous improvement in manufacturing. By proactively identifying and addressing quality issues, it enhances customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Through rigorous risk assessments and cross-department collaboration, APQP strengthens supplier relationships and manages risks effectively. As a key element of quality management, it ensures consistent delivery of products that meet or exceed customer requirements, driving overall business success.
Thank you for reading this post! We hope you have found it informative and valuable!