The neverending challenge in inventory management lies in maintaining well-stocked shelves and ensuring the seamless operation of your supply chain.
A key aspect of this undertaking is understanding and calculating “gross requirements.” The gross requirements represent the overall amount of a product or service required to satisfy customer needs.
Proficiency in comprehending and computing these requirements is necessary to guarantee your business maintains adequate inventory levels to fulfill customer demand. Read on to know more about it.
This blog post will discuss gross requirements, examples, formulas, and how to calculate them. It will also explore some factors that can impact gross requirements, such as seasonality and changes in customer demand.
What is the gross requirement?
Gross requirements encompass both independent and dependent demands for a component, calculated prior to adjusting for on-hand inventory and scheduled receipts.
It represents the aggregate need for raw materials, additional components, and subassemblies necessary to manufacture a specific item.
It combines elements from both dependent and independent demands, considering the availability of each in the overall assessment.
The dependent demand is processed or unprocessed items through the production line. In contrast, independent demands come from external market factors, which dictate what will ultimately become of your finished goods once you’ve completed all processes involved in creating them.
How is it evaluated?
We calculate and fix the gross requirements before netting the on-hand inventory or subtracting the demands based on the scheduled receipts.
It is the minimum inventory required to keep the firm running smoothly. It does not consider the availability of raw materials in the inventory or any predetermined evaluation of scheduled receipts.
How to calculate gross requirements?
To calculate gross requirements in Material Requirements Planning (MRP), you initially gather the demand quantities for the specific item undergoing logistics planning across different periods. Then, you consolidate these quantities listed in the MRP to obtain the total gross requirements for that item.
Examples
Example 1
A thermal plant’s total amount of input can be termed its gross requirement.
The thermal plant will measure it in tons of coal required at the end of each periodic productive cycle.
Example 2
The total amount of flour required to produce, say, 40 pieces of bread at a roadside food joint would be its gross requirement.
The above is done without considering,
- The leftover materials from the previous month or
- Any orders placed beforehand that are scheduled to arrive
Factors that impact gross requirements
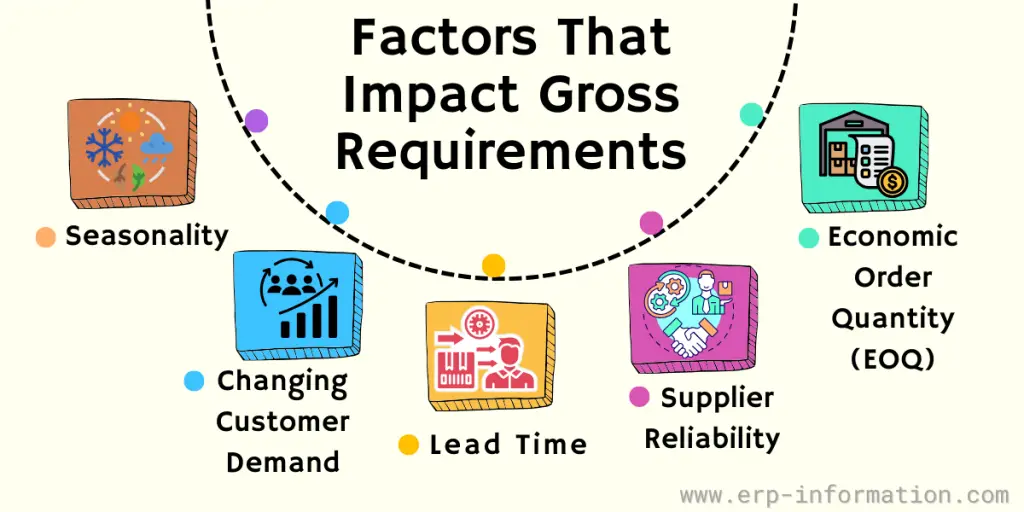
Seasonality
Many businesses experience fluctuations in customer demand throughout the year. For instance, a clothing retailer may see higher demand for winter coats in the colder months.
Understanding these seasonal patterns is crucial for accurately calculating gross requirements.
Changing Customer Demand
Customer preferences and demand can shift suddenly due to various factors, such as trends, marketing campaigns, or external events. Keeping a close eye on market dynamics helps in anticipating and accommodating changes in gross requirements.
Lead Time
The time it takes for your suppliers to deliver products can impact your gross requirements. Longer lead times may necessitate higher safety stock levels to bridge supply gaps.
Calculate Lead time demand using our Online Lead Time Demand Calculator
Supplier Reliability
The reliability of your suppliers can significantly influence your gross requirements. Frequent delays or quality issues might prompt you to maintain larger safety stock quantities to mitigate supply chain disruptions.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a calculation that helps determine the ideal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs. Optimizing your EOQ can impact both safety stock and gross requirements.
Beyond these factors, it’s essential to keep an eye on demand forecasting accuracy, technology adoption (like advanced inventory management software), and ongoing data analysis.
You can calculate EOQ using our Economic Order Quantity Calculator and use our Safety Stock Calculator to check safety stock inventory.
Why are gross requirements essential to figure out?
A firm needs to figure out its gross requirements capacity before operating. It is the amount of raw material the firm can function with at its full potential.
Based on the gross amount required, the firm can easily calculate the amount of on-hand inventory and other inventories based on rising demand.
If a company has a clear idea of the gross amount required to function, the company can cut down costs based on storage.
That gives an idea of the on-hand inventory required to avoid running a risk of massive loss due to loss of demand.
Similarly, due to loss of supply, a firm can lose out on customers if it is not stocked sufficiently for the future.
What is the gross material requirements plan in manufacturing?
The gross requirements planning process in manufacturing determines the number of units that need to be produced to meet customer demand. This process begins with a forecast of customer demand, which is then used to create a production plan.
The production plan considers the available inventory, the lead time for production, and the desired levels of safety stock. From this information, you can calculate the gross requirements.
The gross requirements will typically be higher than the actual customer demand, including an allowance for production losses and planned sales promotions.
Once the gross requirements are known, you can use them to generate a production schedule. This schedule is then used to determine the necessary raw materials and components, which are procured to support the manufacturing process.
Finally, the finished goods are produced and shipped to customers. By following this process, manufacturers can ensure that they have the necessary resources to meet customer demand without incurring unnecessary costs.
Characteristics of gross requirements
- The gross requirement does not vary from day to day or even within two periodic productive cycles.
- Gross material meaning for a firm is its position over the market it captures. The higher the demand, the more the company’s gross requirement is among the customers.
- The gross requirement can be increased by improving the facility, performing units, production units, and demand for the finished product. This is where material requirements planning (MRP) can be implemented.
FAQs
What is the gross material requirements formula?
Gross material requirements (GMR) calculate the minimum amount of materials required to produce a product. The calculation considers the raw materials’ weight of the finished product and the waste associated with production.
The GMR calculation is used by manufacturers to ensure they have an adequate supply of raw materials on hand and to help them plan for future production needs.
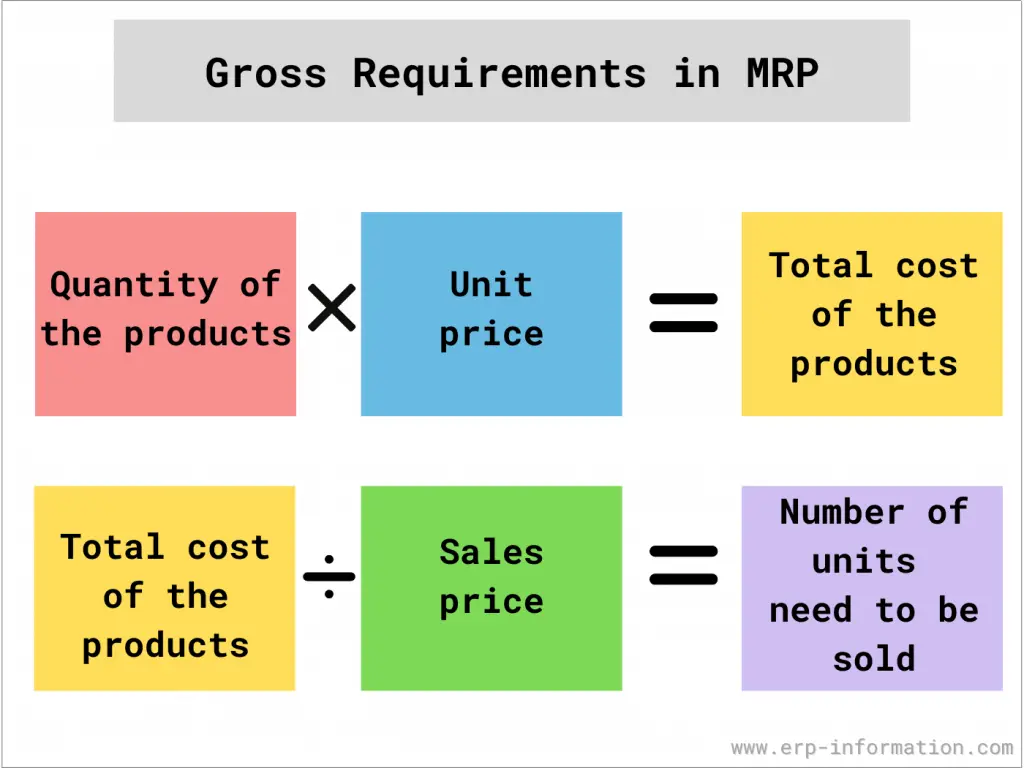
How do we find gross requirements in MRP?
One way to find gross requirements in MRP is by multiplying the quantity of a product by the unit price.
This will give you the total cost of the product for one unit. Then, to find the gross requirement, divide this number by the sale price to get the number of units that need to be sold to cover costs.
What is the difference between a gross requirement and a net requirement?
Net requirements are requirements for a product based on its gross requirements minus on-hand stock and scheduled receipt.
A net requirement plan adjusts for on-hand inventory and scheduled receipt at each level, whereas a gross requirement plan is a plan that shows the total demand for a product and it also shows when production should start to meet its requirements.
Most manufacturing industries are about maintaining the balance between the gross and net requirements and keeping in mind the on-hand inventories and scheduled receipts.
Striking a balance is very important and key to a thriving industry.
Conclusion
To sum up, gross requirements represent the total units needed by customers or retailers. This calculation includes units sold and the additional quantity for pending orders yet to be fulfilled.
Companies rely on gross requirements to predict demand, assessing both immediate and future inventory needs. This evaluation helps them understand current stock levels, empowering effective planning for future demands. Hope this post has offered you a clearer understanding of this concept.