XaaS is an acronym that stands for “anything as a service.”
It is like a new way to use technology services. Instead of buying and handling your own software, platforms, or infrastructure, you can just rent them from a cloud provider. This not only saves you money but also gives you more time to focus on your main business stuff.
As the name suggests, This refers to any service that can be delivered over the Internet. That could include software as a service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), or even Business Process as a Service (BPaaS).
This post will give you a closer look at XaaS with examples, benefits, limits, and trends.
What is XaaS?
It is a term in cloud computing that refers to a model where services are delivered through the Internet using a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
XaaS companies offer products that do not need you to build storage and web services. You can buy a product from the company for a long time and use their technology.
This can save you money. XaaS covers many different types of products. With this, customers can purchase only the computing resources they need and pay for them monthly.
This type of service delivery is sometimes called “on-demand computing” or “pay-per-use computing.”
Lots of people are getting into XaaS because it’s better than the old-fashioned IT solutions. With XaaS, you can easily change the amount of resources you use and add more when you need them or remove some when you don’t.
Plus, it’s cheaper since you only pay for what you use. XaaS is safer and more reliable because cloud providers are pros at keeping your data secure and your systems working well.
XaaS Examples
Important examples of “Anything as a service” include
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Join the millions benefiting from cloud-based software applications like Salesforce, MS Office 365, and Google apps.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Supercharge your development and testing processes with preconfigured virtual machines and resources from applications such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, Apache Stratos, Heroku, and Microsoft Azure.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Unleash your creativity and innovation by harnessing the power of storage, servers, and networking resources offered by the likes of AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Google Compute Engine (GCE), and Microsoft Azure Compute.
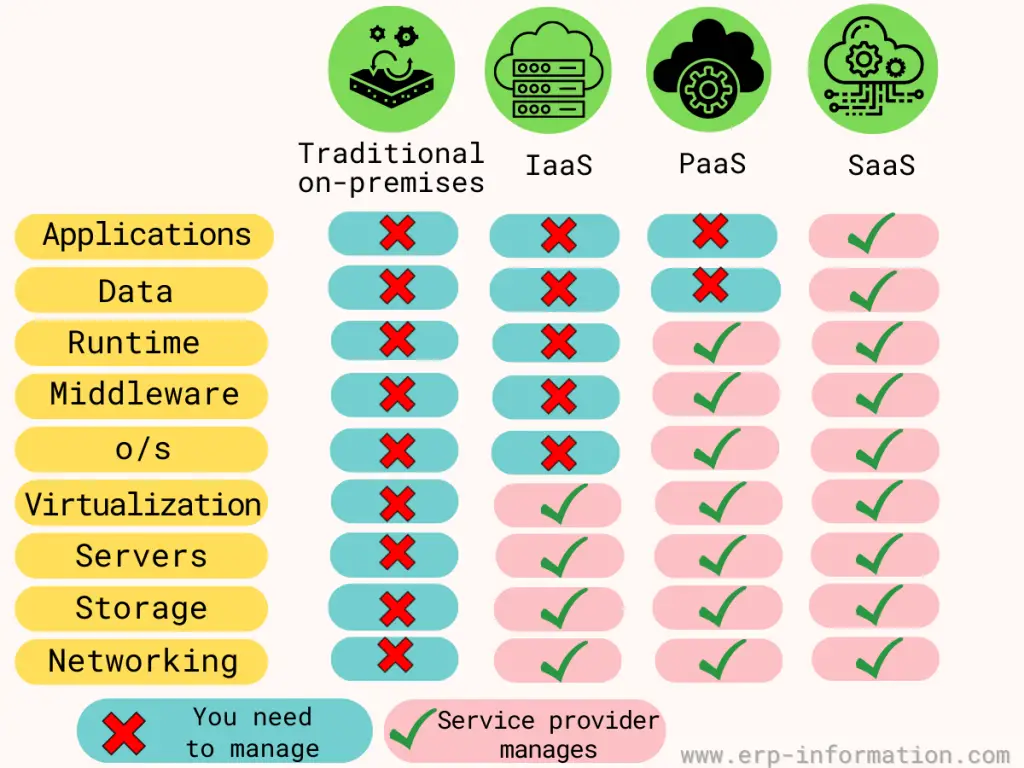
The below image shows the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Apart from these, some other examples are
- Database as a Service (DBaaS) – It offers access to database platforms via the cloud. For example, applications such as Azure and AWS.
- Containers as a Service (CaaS) – Deployment and management of containers will be based on container-based virtualization.
- Device as a Service (DaaS) – A third-party vendor provides devices like PCs, mobile computing devices, and smartphones as a paid service.
- Authentication as a Service (AaaS) – Identity and access management will be done through cloud services.
- Function as a Service (FaaS) – Customers must pay while executing functionalities.
- Malware as a Service (MaaS) – It helps organizations to protect themselves from ransomware and distributed denial of service. VMware and AppDefense are examples.
- Network as a Service (NaaS) – Third-party vendor hosts network infrastructure
- Storage as a Service (STaaS) – Offers application, data, and backup storage in the cloud.
XaaS Benefits
Easy access to resources
Customers can access computing resources quickly and easily without purchasing and managing hardware and software, which helps them to simplify and speed up the process of setting up new applications.
More Agile
It also allows businesses to be more agile, responding quickly to changes in market conditions or customer demands. New services can be deployed faster, and existing ones can be scaled up or down as needed without upfront investment in infrastructure.
Cost-effective
The provider can often offer more cost-effective solutions than traditional IT infrastructure deployments, which means customers can pay only for the resources they need when they use them.
Easy access to the latest technology
Provides fast and easy access to the latest software and technology updates. Customers don’t need to wait for an IT department to install new software or make changes; they can access the latest version from this provider.
Enhanced security
Offers enhanced security features that keep your data safe and secure – often more so than if it were stored on your premises.
Reduction of carbon footprint
It can help you to be more green by reducing your carbon footprint. Since these application providers manage and maintain the infrastructure, customers do not need to run their own data centers, which use much energy.
Flexibility
This enables you to work from anywhere, at any time, giving you the flexibility to work when and where you want. All you need is an internet connection.
Saved time and money
It has capabilities to quickly deploy applications and services without having to wait for installation or configuration, which can save time and money.
Limitations
Security
Since XaaS is a model that allows users to access applications and data from a remote location, it can be more vulnerable to security breaches than traditional software models. You may not have as much control over the data or applications.
Cost
The cost of this application can be higher than traditional software models, especially if the user needs to purchase hardware and software to support the “Anything as a service” model. And the pricing model can be unpredictable since it depends on usage.
Downtime
Your ability to work is dependent on the service provider, meaning that if the provider experiences downtime, you won’t have access to your work.
Integration
This application may be difficult to integrate with other applications in the company’s IT infrastructure.
Quality
The quality of service can vary from provider to provider, so it’s important to do your research before selecting one.
Scalability
The scalability of these applications can be challenging, especially if the company experiences rapid growth.
XaaS vs SaaS
| XaaS | SaaS |
| It is a more comprehensive model that includes software, infrastructure, and platform services. | SaaS is only a software service. |
| It is usually offered by both large and small companies. | SaaS is usually offered by larger companies than XaaS providers. |
| It typically offers more customization and flexibility than SaaS in terms of the type of applications and infrastructure. | It does not offer more customization and flexibility. |
| It often requires more customization than SaaS to meet the needs of individual organizations. | It does not require more customization. |
| It is typically more expensive than SaaS. | It is less expensive. |
XaaS Trends
It has quickly become one of the most popular trends in enterprise computing and for a good reason.
By moving away from traditional software and hardware purchases, companies can enjoy faster deployment times, increased flexibility, and lower upfront costs.
The benefits of Anything as a Service are many and varied, which is why this trend will only continue to grow in popularity.
How is the Future Market of Xaas?
Cloud technology and the internet make it easier to use XaaS. Companies are using more XaaS so it will become very popular soon.
By 2029, people expect $2.4 trillion in XaaS money! Some companies worry about security and safety when using XaaS, but service providers are working hard to ensure everything is okay. 5G and 6G technology, big data, AI, automation, machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) will help people use XaaS even more.
When businesses need to do a lot of work online, it’s better (and cheaper) to use cloud services instead of doing it all by themselves on their computers!
Conclusion
XaaS, as we learned is an umbrella term for any type of service that can be delivered over the Internet. That could include software, storage, infrastructure, or anything else that can be delivered this way.
It has become increasingly popular in recent years due to the flexibility and scalability it offers businesses. It offers many benefits to businesses and consumers alike. However, there are some limits also.
In this article, we explored the definition of XaaS, examples, the benefits and limitations of this delivery model, and where it might be headed in the future.