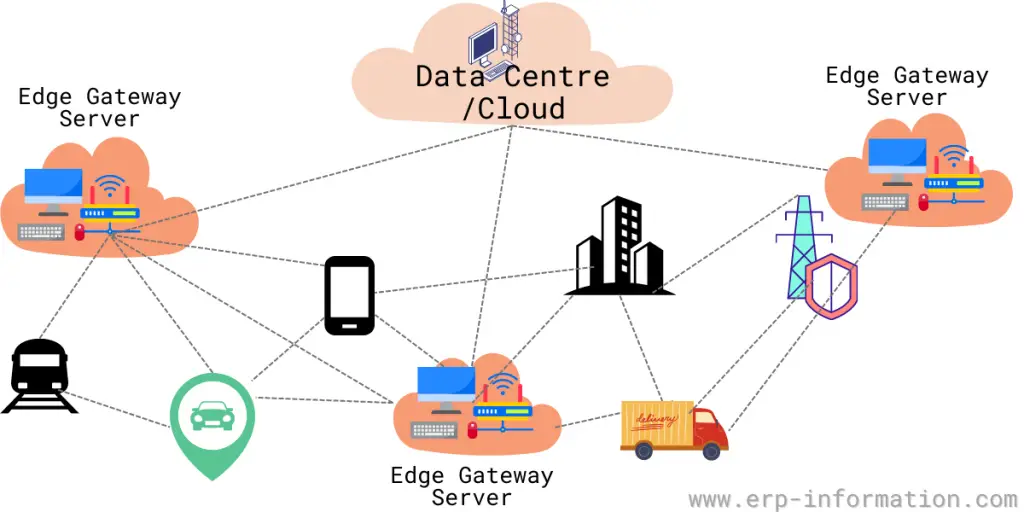
We all know that computing power is moving away from centralized data centers to the network’s edge.
Edge computing is a computing type where data processing and content delivery are moved closer to the end user. That can be done using local servers, fog nodes, or edge nodes.
This article will explore edge computing, its working, components, benefits, limits, and edge computing vs. cloud computing.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a term used to describe a type of computing occurring near the edge of the network, unlike a traditional data center.
The edge of the network can be defined in several ways, but typically it refers to the extremities of the network, places where data is generated and consumed.
Rather than sending all data to a central data center, the data is processed closer to where it is generated. This can improve performance, reduce latency, and save bandwidth and energy costs.
How does Edge computing work?
Edge computing has been around for decades. It was first introduced in remote locations like remote offices and branch locations, where it made sense to place resources at the desired location rather than depend on a single central point of access or distribution systems that were less reliable due to their distance from consumers.
Edge computing works by placing processing power and storage near the points where data is generated and consumed. Many ways can do it, but one of the most common is to use small, low-power devices called edge nodes.
Edge nodes are connected to the network and each other, allowing them to exchange data and share resources. This will enable them to act as intermediaries between the devices that generate data and those that consume it.
Edge nodes can be used to perform a variety of tasks, including data processing, content caching, and load balancing. They can also manage and monitor the devices that generate data.
Migrating away from traditional data centers facilitates another benefit: reducing network traffic between devices within an organization’s infrastructure.
Especially those which would only need local storage capability, like printers connected wirelessly via Wi-Fi networks.
Edge Computing Architecture
Importance
Now we are moving towards a more connected world; edge computing technology is becoming increasingly important.
With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), there is an ever-growing demand for data processing and storage closer to the edge of the network, where devices are located.
That enables faster response times and reduced latency, essential for applications requiring real-time interaction, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial IoT deployments.
It can also help to address security and privacy concerns. For example, keeping data closer to the source is less likely to be compromised in transit or stolen by hackers.
And reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent to central cloud servers can help to protect users’ personal information.
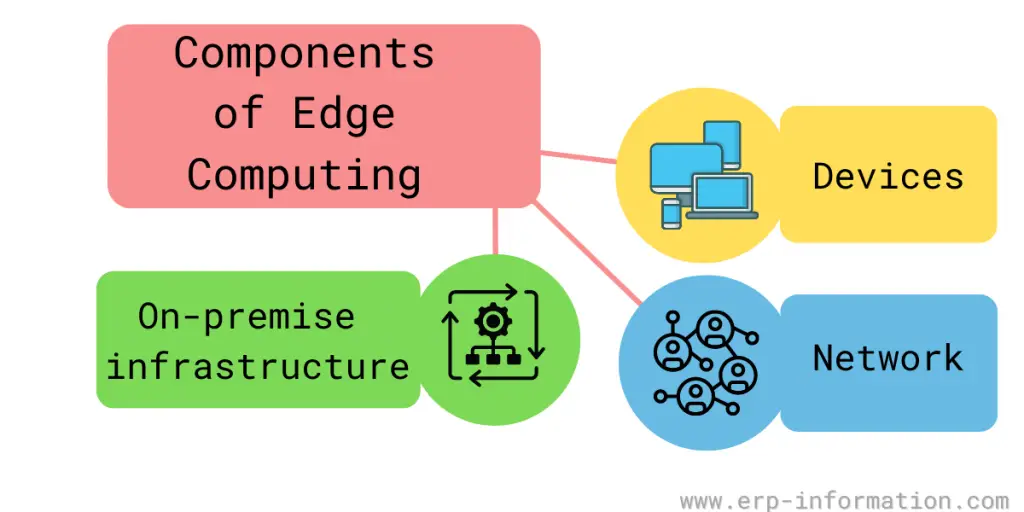
Components of Edge Computing
Edge devices
Edge devices are crucial elements, the physical or virtual machines that process and act on data near the source of its creation.
Edge devices include smartphones, sensors, laptops, industrial robots, and autonomous vehicles. They act as a bridge between the cloud and the physical world, processing data and sending it back to the cloud for further analysis or action.
Network edge
The network edge is another important part. This is the point where data enters or leaves the network, and it’s where edge devices connect to the internet or other networks.
The edge network is responsible for routing data to and from edge devices and ensuring that it’s processed quickly and securely.
On-premise infrastructure
On-premise infrastructure is an essential component. This hardware and software power edge device and keeps them connected to the network. On-premise infrastructure can include servers, routers, containers, hubs, bridges, storage arrays, and gateways.
Edge computing vs Cloud computing
| Edge computing | Cloud computing |
| More localized | More centralized |
| Better equipped to handle real-time data | Better for bulk data storage |
| Requires less bandwidth and power | Requires more bandwidth and power |
| Can process and act on data as it is generated | Processing data as it is generated is not possible |
| Short-distance data transmission | Long-distance data transmission |
Edge computing with other technologies
Edge computing is when you use other technologies together to get better results.
5G
5G technology makes it easy for devices to make decisions. It helps them connect to the internet and ensures they have the right software installed to do what needs to be done.
IoT
IoT and connected devices are special kinds of data. They need to be made safe and stored in the cloud. Edge will be close to these data sources.
Containers
Containers are like a box that helps developers build and package applications. This same container can be used on any computer, phone, or other device, no matter what type of hardware it has or what settings have been changed.
Digital twin
A digital twin connects physical and digital things. It helps data and applications be set up in a way everyone can understand instead of using complicated words like database tables or message streams. Digital twins let people who are experts in their field (not just experts in software) control how computers sense think, and act.
Software-defined networking
Software-defined networking makes it possible to set up networks. It also helps you decide how quickly information should move between devices and the cloud.
Service and data mesh
Service and data mesh help to set up and ask questions about information stored in containers and other places. It is like one big machine that helps us get our answers easily. Instead of asking each device the same question, we can now just ask once and get the answer for everyone at the edge.
Some Real-world Examples
Retail
A retailer may use edge computing technology to quickly identify and respond to inventory shortages and pricing changes.
For example, if a retailer notices an increase in demand for a product, they can use edge computing to place an order for more of that product from their supplier.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies can use edge computing to improve production efficiency and quality. For example, a manufacturer might use it to monitor the performance of machines on the factory floor in real-time.
This would allow them to identify and fix problems before they cause a stoppage in production.
Healthcare
Healthcare providers can use edge computing to reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to centralized data centers.
For example, a healthcare provider might use this to store patient data on local devices instead of sending data to the main data center. This would allow patients to access their data easily.
Transportation
Transportation companies can use it to improve the safety and efficiency of their operations. For example, a transportation company might use edge computing to track the location of vehicles and passengers in real-time.
This will allow them to respond quickly if there is an emergency.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Increased performance and reduced latency
It enables devices to process data and execute tasks near the information source, reducing the need for transmission over a network. That results in increased performance and faster response times.
Reduced infrastructure costs
Allows businesses to deploy computer resources at the network’s edge instead of investing in expensive infrastructure to handle traffic at centralized data centers. Edge computing is very helpful in avoiding unwanted costs.
Enhanced security
Processing data closer to the source can help reduce the risk of security breaches and protect sensitive information.
Improved efficiency
It can help optimize workflows by reducing the time spent transmitting data over a network.
Greater flexibility
Allows businesses to quickly adapt to changing needs and demands by deploying resources where they are needed most.
Enhanced scalability
This makes it easy for businesses to scale their operations without investing in additional infrastructure or personnel.
More efficient use of bandwidth
Businesses can better manage their bandwidth usage, ensuring that critical tasks receive priority treatment. At the same time, non-essential activities are delayed or eliminated.
Faster decision-making
Data processing at the network’s edge allows businesses to make decisions more quickly and efficiently without waiting for data to be transmitted from a central location.
Limitations
- Limited scalability: You can connect only a limited number of devices at any time.
- Limited capability: It is not as powerful as cloud computing in processing power and storage.
- Lack of standardization: There is no one-size-fits-all definition for edge computing, which makes it challenging to develop and deploy standardized applications and services.
- Fragmented infrastructure: Its deployments are often fragmented, which hampers interoperability and slows down innovation.
- Varying performance levels: The performance of edge computing systems depends heavily on the network topology and the proximity of devices to the edge node.
- Security and privacy concerns: Edge devices are often exposed to more security risks than centralized cloud systems, as they are more challenging to secure and manage effectively.
Despite these limitations, this is a promising technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with data and devices.
As the world becomes increasingly connected, providing low-latency, high-performance access to data and services will become more important.
What are the security risks of edge computing?
Edge computing is a worry because the device isn’t safe. It needs to manage data, which is often important and private. If the systems need to be more secure, someone could get access to them without permission.
Why is edge computing decentralized?
Decentralized IoT edge computing can make tasks faster and more flexible. However, it works best when tasks must be done quickly, and much data must be worked on.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a new path of handling data that is becoming increasingly popular. Managing data sources and moving data processing and storage closer to the network can provide many benefits.
These benefits include lower latency, higher security, and improved scalability. However, while it has many advantages, there are also some limitations.
These limitations include the need for specialized hardware and the lack of standardization.
Overall, this promising new technology can revolutionize how data is handled.
Reference