You need to be able to quickly and easily deploy new applications, but you want to avoid the hassle or expense of setting up your server infrastructure.
Getting a new server set up and ready for use can take weeks or even months. Not only is this process time-consuming, but it can also be expensive.
Cloud service architecture provides a way to quickly and easily deploy new applications without worrying about setting up your server infrastructure. With cloud services, you can have a new application up and running in minutes, and you only pay for the resources you use.
This blog post will discuss cloud architecture layers, types of clouds, and types of cloud services, along with their drawbacks and benefits. We will also discuss the steps to choose the right cloud service provider.
What is Cloud Service Architecture?
Cloud Service Architecture is a process that defines how cloud services should be delivered and managed. It includes the design of the service, the selection of the appropriate delivery model, and the definition of operational processes and procedures.
The goal of cloud service architecture is to ensure that cloud services are reliable, secure, and meet the needs of the business. It also helps to ensure that costs are controlled and that service levels are met.
Cloud architecture requires close collaboration between IT and business units to ensure that the business requirements are properly captured and that the service meets their needs.
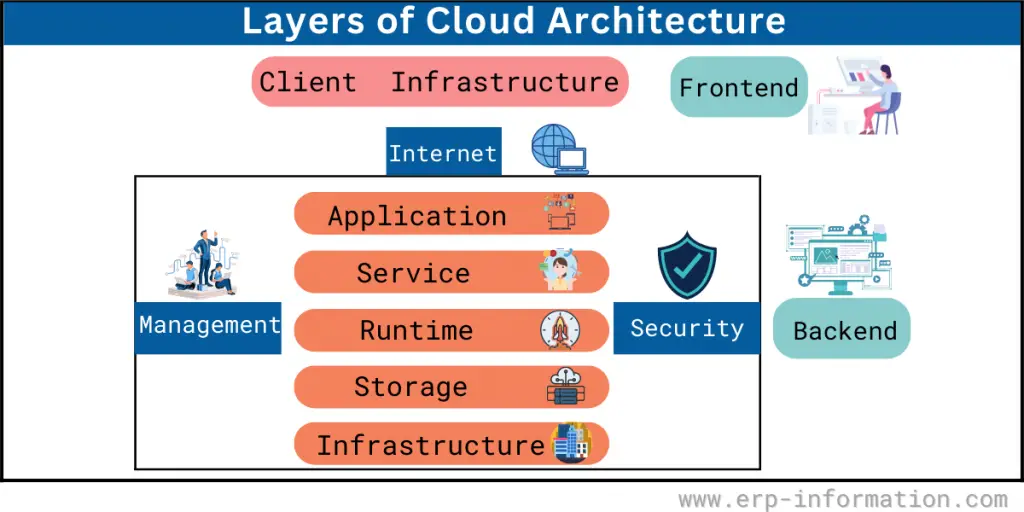
Cloud Architecture Layers
The layers of a cloud architecture include,
Application layer
Developers create and manage end users’ cloud-based applications at the application layer.
Services layer
The services layer includes various services that are utilized by applications to power their functionality.
Runtime layer
This layer provides a virtual machine’s runtime and execution
Storage layer
The storage layer is responsible for storing and managing data, including structured and unstructured information.
Infrastructure layer
The infrastructure layer manages the underlying hardware infrastructure of the cloud, including compute, network, and storage resources.
Security and management layer
The security and management layer ensures that data is protected from unauthorized access and that the cloud environment is properly monitored and managed.
Other key components of a cloud architecture include,
Client layer
The client layer, which enables users to access applications and services from any location,
Front-end layer
The front-end layer provides the user interface for accessing cloud services.
Back-end layer
The back-end layer of a cloud architecture handles all the behind-the-scenes work, including managing data storage, network communication, and server resources. It also includes the cloud controller, ensuring the entire system operates efficiently and securely.
Types of Clouds
There are four types of clouds, including,
Public clouds
They are open to anyone and provide on-demand access to computing resources, often through a self-service portal.
Private clouds
Businesses typically use private clouds and offer greater control over security and privacy.
Hybrid clouds
They combine the benefits of both public and private cloud services, enabling flexibility in how resources are deployed.
Community clouds
They are shared by a group of organizations with similar needs and may be hosted by a third party or the cloud’s owner.
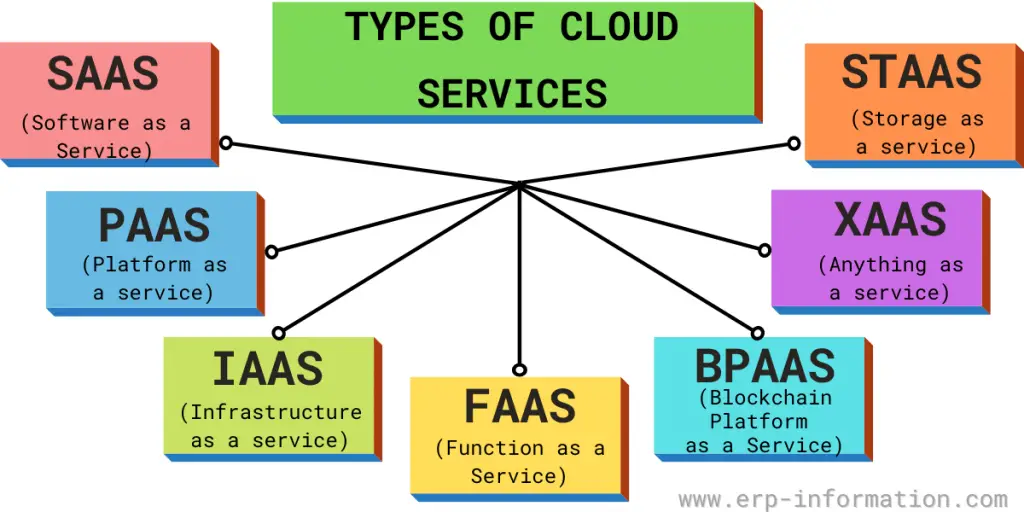
Types of Cloud Services
The main types of cloud services include
1. SaaS
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is one of the most popular cloud service models and allows users to access software applications hosted in the cloud.
Benefits
- Since the software is hosted in the cloud, users can access it from anywhere without worrying about setting up or maintaining their infrastructure.
- SaaS solutions are often scalable, allowing businesses of all sizes to access the same level of functionality.
- By eliminating the need for on-premise software and associated hardware, SaaS can help businesses save money on their IT expenses.
Drawbacks
One potential issue is vendor lock-in, which can make it difficult to switch services or move data if a business needs to change providers.
Additionally, SaaS solutions may only sometimes be optimized for specific business needs and can require customizations or integrations to work well for a particular organization.
2. PaaS
PaaS, or platform as a service, is a type of cloud computing that enables users to develop and run applications without needing dedicated hardware.
Benefits
- Compared to traditional hosting models, there is enhanced scalability, flexibility, and lower costs.
- It offers powerful development tools and support for various programming languages, making it relatively easy for developers to build and deploy their applications.
Drawbacks
- These platforms often require users to pay monthly fees to access their resources or services.
- Many Paas platforms offer limited levels of control over certain aspects of the environment. As a result, it can be frustrating for more experienced developers who want greater control over their applications and environments.
3. IaaS
IaaS, or Infrastructure as a service, is a type of cloud computing that enables users to access virtualized computing resources such as networks, servers, and storage.
Benefit
- IaaS providers typically offer a wide range of configuration options, allowing users to choose the level of control they need.
Drawbacks
- IaaS solutions may require users to pay for resources they do not use, leading to higher costs than expected.
Some other Cloud service architectures include
FaaS
FaaS, or Function as a Service, is a type of cloud computing that enables users to run and manage functions in the cloud.
One of the key benefits of Faas is that it allows developers to quickly and easily create and deploy functions without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure.
BpaaS
BpaaS, or Blockchain Platform as a Service, is a type of cloud computing that enables users to develop and deploy decentralized applications on top of a blockchain platform.
XaaS
XaaS, or anything as a service, refers to a model where users can access a range of services via the cloud, including storage, software, network infrastructure, and more.
STaaS
Storage as a service is a type of XaaS that enables users to store and manage data in the cloud.
How to Choose a Cloud Service Provider?
When choosing a cloud service, there are several factors to consider.
- Security – The cloud service provider should have a robust security protocol to protect your data.
- Reliability – They should have a proven track record of reliability and uptime.
- Scalability – They should be able to scale up or down as needed to accommodate your changing needs.
- Cost-effective – The provider should offer competitive rates without sacrificing quality or security.
- Ease of use – They should make it easy to access your data and manage your account from any device, anywhere, anytime.
- Customer support – The service provider should offer superior customer support and be available.
It is also important to evaluate different providers and compare their offerings.
FAQs
Can businesses of all sizes benefit from Cloud Service Architecture?
Yes, Cloud Service Architecture is scalable and adaptable, making it beneficial for businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises.
Conclusion
Cloud services are becoming increasingly common and popular, as they offer many benefits for organizations and individual users alike.
Whether you need access to powerful computing resources, flexible storage options, or support for a particular software platform or programming language, the cloud has something to offer.
Whether looking for cost-effective, easy-to-use, or highly secure solutions, a cloud service can meet your needs.