Do you remember the last time you ordered something online? Unfortunately, getting that item to your door requires incredible coordination, whether it is a pair of shoes, a refrigerator, or even your groceries. To make this possible, we must look at outbound logistics and their role in any supply chain.
Outbound logistics refers to the processes necessary to move products from their source to their eventual destination.
This could include scheduling deliveries, complying with government regulations, ensuring accurate documentation, and more – all while ensuring quality control and fast delivery.
Our blog post will discuss the outbound logistics topic in-depth with its process steps and challenges. The post will also inform about the difference between outbound and inbound logistics.
What is outbound logistics?
It is the process of planning, executing, and controlling all activities associated with transporting and storing goods from their origin to the end customer.
This includes inventory management, order fulfillment, packaging, pickup, delivery coordination, freight forwarding, and tracking.
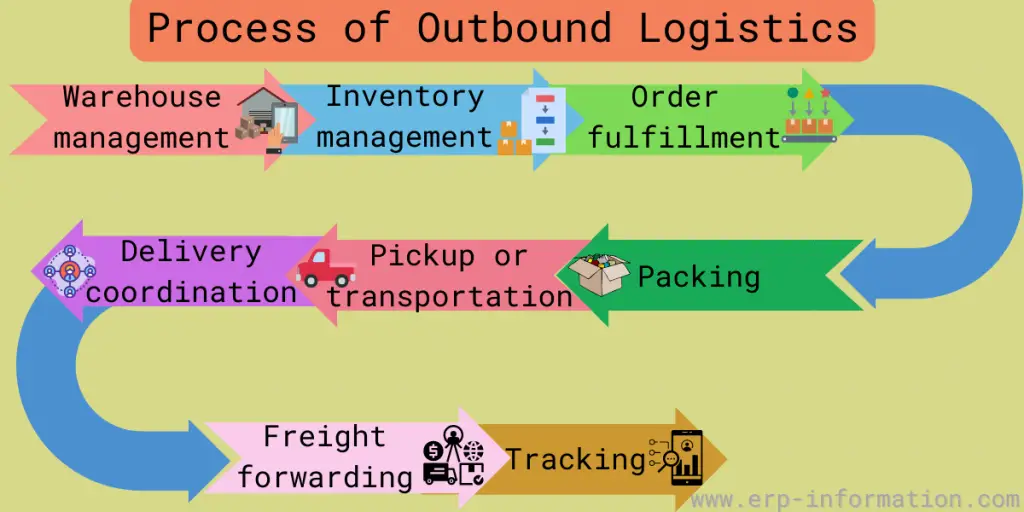
Process of outbound logistics
Warehouse management
Warehouse management is essential to the outbound logistics process. The purpose of warehouse management is to ensure that goods are stored in an organized and safe manner while they wait to be transported.
This includes activities such as
- Inventory tracking,
- Updating stock levels,
- Stocking shelves,
- Arranging pickup and delivery schedules,
- Monitoring storage conditions. Businesses can reduce delays in the outbound logistics process by having a clear warehouse management system and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Inventory management
Inventory management is an important part of the process. It involves tracking and analyzing records to ensure that all products are in stock and available to be shipped.
This includes activities such as
- Ordering stock
- Organizing storage areas
- Monitoring lead times and delivery dates
- Checking product quality
- Updating inventory levels
Proper inventory management helps businesses keep costs down by ensuring no product overstocking or understocking. Ultimately, this leads to more efficient outbound logistics processes and better customer satisfaction.
Order fulfillment
Order fulfillment is a key process in outbound logistics that involves picking, packing, and accurately distributing orders.
- The goal of order fulfillment is to have orders arrive at their destination on time, with the correct products and in good condition.
- This includes tracking inventory levels, verifying shipping information, correctly labeling packages, and ensuring products are packaged properly for transport.
- By having an efficient order fulfillment system in place, businesses can reduce delays in delivery times and ensure customer satisfaction.
Packing
Packaging plays an important role in this process. It involves preparing items for transport to their destination safely and securely. This can include activities such as
- Selecting the most suitable packaging materials, labeling packages correctly, and packing items to protect them from damage during transit.
- Good packaging practices are essential for businesses as they help reduce the risk of lost or damaged goods during shipment, resulting in smoother delivery processes and happier customers.
Pickup or transportation
Outbound transportation often requires special consideration and care, especially when transporting goods that require extra protection, such as frozen or perishable items.
Finding the most effective modes of transport, assigning drivers, and deciding the routes are crucial to getting finished products to their desired destination in one piece.
The pickup process involves collecting items from the warehouse and transporting them to their destination.
- This process usually begins with verifying that the order is complete and accurate and loading the items into the delivery vehicle.
- The pickup process should be properly organized and efficient to ensure that orders are delivered on time and in good condition.
- Good communication between staff responsible for pickup, inventory management, and shipping is essential to ensure smooth outbound logistics.
Delivery coordination
Delivery coordination is an essential part of the process. It involves
- Coordinating all activities throughout the delivery process, such as scheduling pickups, tracking shipments, and preparing documents for customs clearance.
- Ensure the orders get delivered on time and in good condition; it is important to have effective communication between staff responsible for delivery coordination and other stakeholders, such as the warehouse manager and the shipping company.
- Delivery coordination also involves providing customers with updates on delivery progress, tracking items while in transit, and managing any unexpected delays or changes.
Freight forwarding
The freight forwarding process is a key part of the process. It involves coordinating all aspects of moving goods from the point of origin to their destination. This includes
- Arranging for shipments
- Obtaining the necessary documents and permits
- Negotiating rates with carriers
- Complying with customs regulations
- Resolving any issues that may arise during transit
- Ensuring timely delivery
The freight forwarder also plays an important role in providing customer service by responding to inquiries and helping customers track and trace their shipments.
A freight forwarder must have extensive knowledge of local laws and regulations to coordinate the movement of goods efficiently and effectively.
Tracking
Tracking involves monitoring the movement of goods from their origin to their destination. This includes
- Tracking orders throughout the entire supply chain,
- Updating customers on delivery status, and
- Providing visibility into any potential delays that may occur.
Tracking also helps identify potential opportunities for cost savings or efficiency improvements.
In addition, the ability to track goods ensures that they are delivered on time and in good condition while providing an added layer of security and peace of mind for shippers and customers.
Challenges
It can present several challenges.
- Logistical complexities are associated with organizing and coordinating the various components of the shipment process. This includes selecting transportation routes, securing carriers and services, obtaining necessary permits and documents, and ensuring compliance with local laws and regulations.
- Controlling the cost of transportation by identifying the inefficiencies
- Maintaining a sufficient inventory level for requirements or demand.
- Managing risk is a key challenge for outbound logistics providers. This includes protecting against natural disasters, political unrest, theft or damage to goods in transit, customs issues, and other unforeseen events.
- Ensuring timely delivery is also a major challenge for outbound logistics providers in this ever-changing global market.
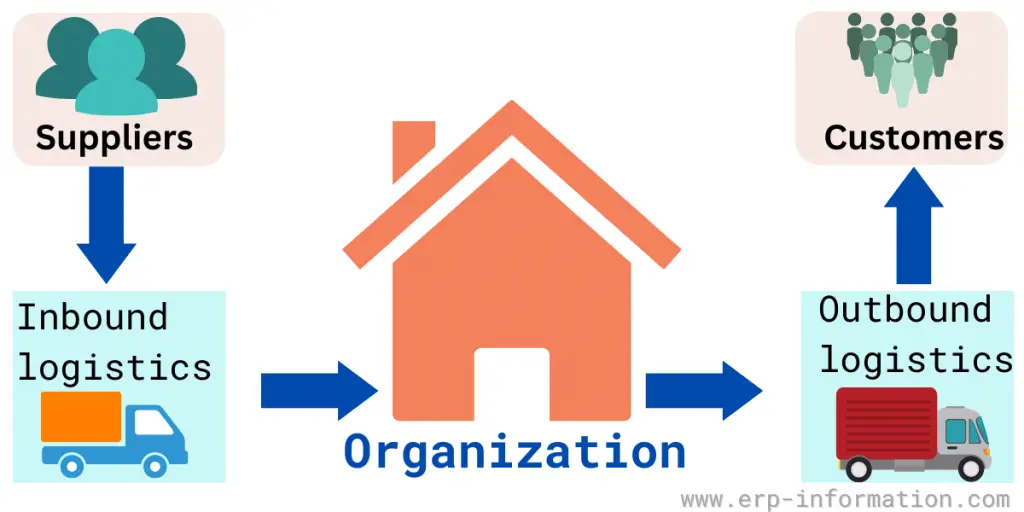
Difference between inbound logistics and outbound logistics
The main difference is the direction of goods movement.
| Inbound logistics | Outbound logistics |
| It is the process of receiving and storing materials or products that are being brought into an organization. | It is the transportation and delivery of finished goods from the origin to the customer’s destination. |
| Inbound primarily deals with incoming raw materials | Outbound requires managing a more complex supply chain, tracking orders, monitoring shipment progress, and delivering goods on time |
| It typically involves a one-way flow from suppliers to a company | It involves overseeing multiple sending points throughout an entire supply chain |
| Materials are transported from suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors | Materials transported from a company, retailer, brand, third-party logistics, etc |
FAQs
What are the three types of logistics?
Inbound, Outbound and reverse logistics are the three main types of logistics.
Conclusion
Outbound logistics involves managing the shipment and delivery of goods from their origin to the customer’s destination. It requires effective coordination of transportation and services, risk management, and timely delivery to ensure a successful result.
Outbound and inbound logistics may share some commonalities but differ primarily in directionality, focus, and complexity.