Have you ever set a budget for a shopping trip, only to find out at the register that the prices were different from what you expected? In the business world, there’s a similar scenario that purchasing departments face regularly, known as Purchase Price Variance (PPV).
It is a crucial financial metric that helps companies measure how well they stick to their procurement budgets. This tool helps in benchmarking and keeping an eye on prices, which are essential for successful procurement.
It can significantly impact your bottom line, so it’s essential to understand how to calculate it and what factors affect it.
This blog post will discuss what PPV is and how to calculate it. We’ll also look at some factors influencing it and tips to minimize it.
What is PPV (Purchase Price Variance)?
It is the difference between the budgeted or standard price of an item and the actual amount paid to acquire that item. Think of it as a financial reflection of how a company’s purchasing strategies perform against market price fluctuations.
- Positive PPV: Occurs when you spend less than expected. Imagine you are planning to buy a laptop for $800, but the price drops to $750 by the time you purchase. This variance indicates that you’ve saved money against your expectations, which is a positive outcome for your finances.
- Negative PPV: This happens when you spend more than planned. Using the same example, if the laptop’s price has jumped to $850 by the time you purchase. This variance indicates that you’ve paid more, which could affect your budget if not monitored.
Why is PPV Important?
It allows businesses to:
- Monitor price fluctuations: Understanding how prices change helps businesses adapt their purchasing strategies, potentially securing better deals or avoiding overpayments.
- Evaluate procurement performance: PPV helps assess whether the purchasing team is achieving cost savings and staying within budget.
- Refine budgeting and forecasting: Regular analysis of PPV can refine future budgets, making them more accurate and realistic.
Monthly, Quarterly, and Yearly Tracking
By monitoring PPV over different periods (monthly, quarterly, yearly), businesses can identify trends, seasonal changes, and the impact of external economic factors on their purchasing costs. This ongoing tracking provides invaluable insights that help businesses optimize their spending strategies and improve financial performance.
Purchase Price Variance Formula and Calculation
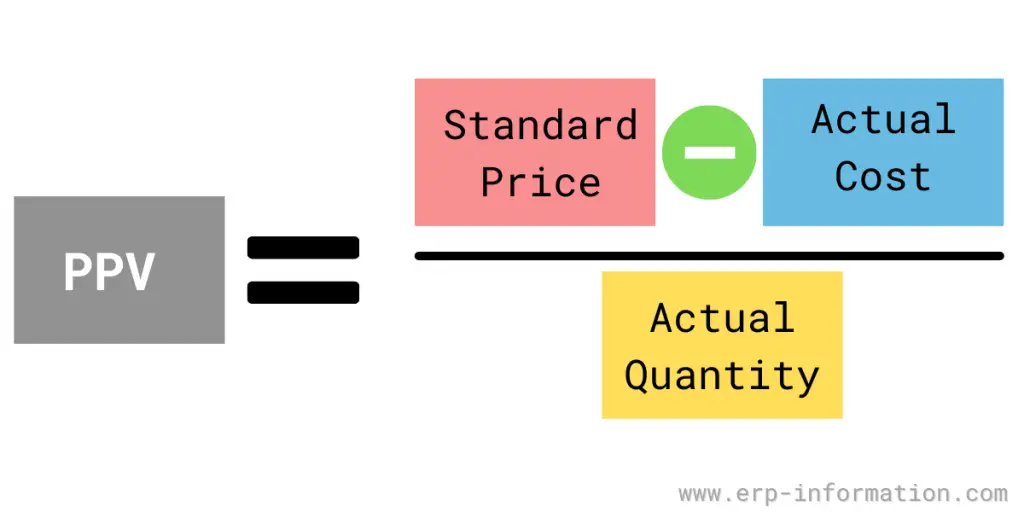
To calculate purchase price variance, you need to know the standard price, the actual paid cost, and the quantity purchased. The formula is
PPV = ( Standard price – Actual paid cost ) / Actual quantity
You can use our Purchase Price Variance Online Calculator for calculation.
The general model for calculating a quantity variance is:
Quantity Variance = (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity)
This calculation tells you how much the actual quantity of products differs from the standard quantity. The result is expressed in terms of dollars or percentages.
This information can be helpful when trying to identify reasons for discrepancies. For example, if the purchase order stated that 500 widgets were ordered, but only 450 were received, the quantity variance would be (-50).
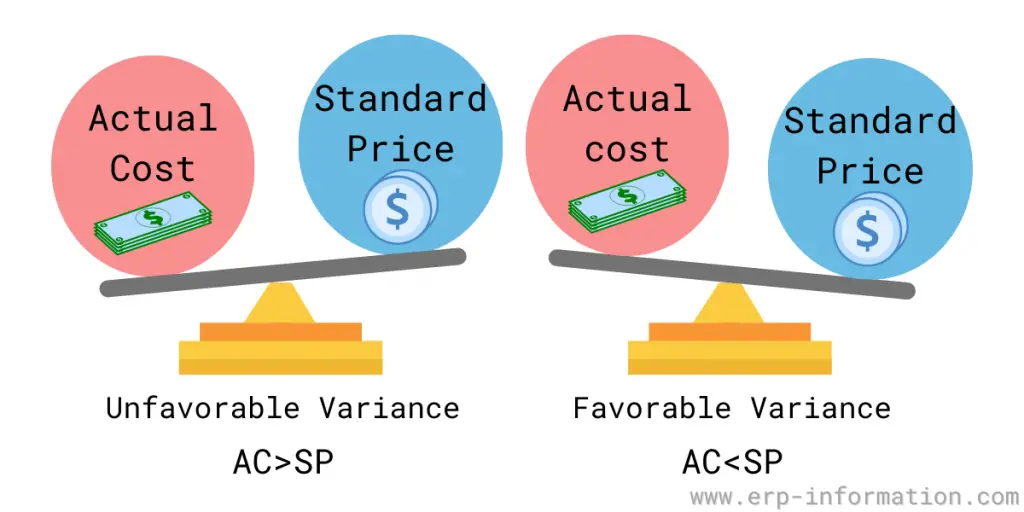
Favorable Variance
Favorable variance occurs when the actual unit price of an item purchased is lower than its standard purchase price. That results in saving the organization money on purchases.
For example,
An organization planned to purchase 10 mobile handsets to gift its employees. The purchase price of each handset is $500. However, after negotiation with the supplier, the organization gets a handset for $400 each.
Now Purchase price is = $500 X 10 handsets = $5000
Actual cost is = $400 X 10 handsets = $4000
Let us calculate cost variance. Variance is $5000-$4000 = $1000
PPV on the purchase is positive and is a favorable variance of $1000 for 10 handsets
Reasons for it
Negotiation with suppliers
Achieving a positive purchase price variance can result from effective negotiations between the purchasing team and suppliers. While cost savings are important, successful negotiations consider other factors like delivery speed and contract terms that may affect overall cost efficiency.
Strategic supplier management
Effective supplier management can positively impact purchase price variance by improving procurement processes and enabling better price negotiations with suppliers. Standardizing procurement practices leads to consistent pricing and enhanced cost control.
Multi-year contract with the supplier
Opting for long-term contracts spanning multiple years can reduce costs per unit and mitigate variance caused by inflation or potential price increases. Accurate capacity planning and forecasting are essential in committing to multi-year agreements.
Unfavorable Variance
Unfavorable variance occurs when the actual unit price of an item purchased is higher than its standard purchase price. This results in an unfavorable PPV.
Let us take the same example. The purchase price of each handset is $500. But, because of the increase in raw materials price, the supplier supplies each handset for $600.
Hence Purchase price is = $500 X 10 handsets = $5000
Actual cost is = $600 X 10 handsets = $6000
PPV on the purchase is negative and is an unfavorable variance of $1000 for 10 handsets.
Reasons for it
Uncontrolled spending
It refers to unauthorized purchases made by employees outside of proper procurement procedures. This can lead to higher prices as employees may not have access to the best deals or negotiated contracts.
Item quantity variations
Companies often receive discounted prices when they purchase goods and services in large quantities. If a company’s purchase volume decreases, they may lose the benefit of these volume-based discounts, which can negatively impact NPV.
Increase in raw material pricing
Rising inflation can result in increased costs for raw materials and components, making it challenging for companies to maintain their standard prices.
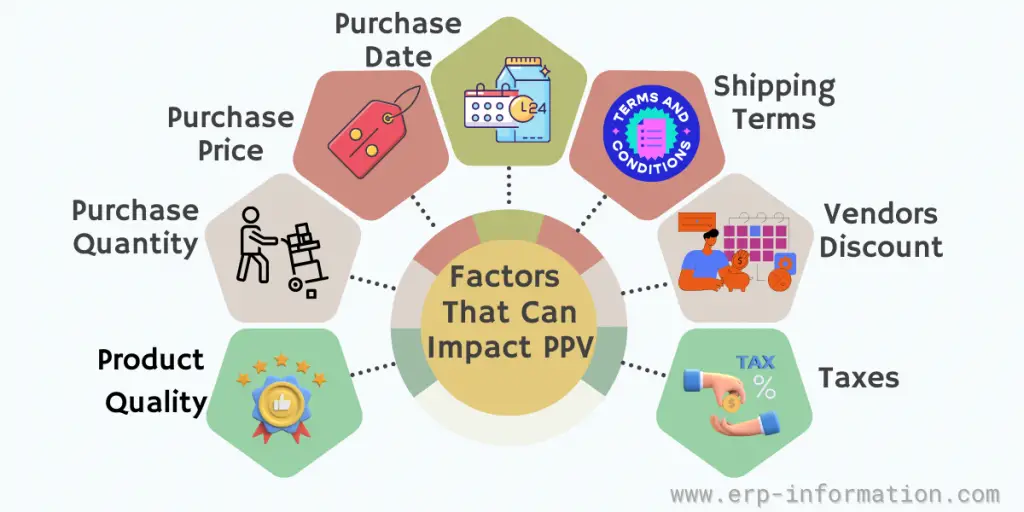
Factors That Can Impact PPV
Factors that can impact it include:
- Purchase quantity – If the buyer orders more products than expected.
- Purchase price – If the purchase price is higher or lower than expected.
- Purchase date – If it is earlier or later than expected.
- Shipping Terms – FOB (free on board) or CIF (cost, insurance, and freight) can affect which party is responsible for any variation in cost.
- Vendor discounts – If the buyer negotiates a deal with the vendor, that causes variance.
- Taxes – Different tax rates in other states can cause it to vary.
- Product quality – If the product is of a lower or higher rate than expected, this will also affect it.
It’s essential to be aware of these factors to make informed decisions about your spending.
Examples of PPV in action
Example 1
For example, if a company orders 100 gadgets at a purchase price of $10 per widget, but the actual cost is $11 per widget, the variance would be ($10 – $11) / 100 = -$0.1 or -10%.
The company spent 10% more than it should have on the widgets.
Example 2
If a company orders 100 gadgets at a purchase price of $10 per widget, but the actual cost is $9 per widget, the variance would be ($10 – $9) / 100 = $0.1 or 10%.
The company saved 10% on the purchase price by ordering the gadgets lower than expected.
Tips for Minimizing Purchase Price Variance
- Compare prices before making a purchase
- Negotiate prices with suppliers
- Order smaller quantities to avoid overbuying
- Use purchase order forms to track orders and ensure accuracy
- Make sure you understand the shipping terms of your purchase
- Check for supplier discounts
- Stay up-to-date on market prices
- Keep track of purchase prices over time
FAQs
What is the price variance?
The price variance is the difference between the price at which a good or service is expected to be sold and the price at which it is sold.
Many factors influence price variance, including availability, demand, seasonality, and weather. In addition, in some cases, price variance can be caused by market manipulation or fraud.
How do you calculate purchase price variance in SAP?
To calculate PPV in SAP, you need to follow these steps:
1. Firstly, you need to identify the price variances for each purchase order.
2. To do this, compare the purchase order price with the standard purchase price.
3. Then, calculate the difference between the two amounts.
4. Finally, multiply this difference by the purchase order quantity.
When does the favorable cost variance occur?
The favorable cost variance usually occurs when the standard purchase price is more than the actual paid cost.
What are direct materials price variances?
Direct materials price variance (DMPV) is the variance between the actual purchase price of materials and the standard cost. This variance can be positive or negative, depending on whether the purchase price was higher or lower than the standard cost.
It is calculated by subtracting the standard cost of material from the actual purchase price.
DMPV = (actual purchase price – standard cost)
This calculation will help you understand how much money was saved (or lost) due to purchase price fluctuations. It’s important to note that the DMPV includes only the direct materials in a product, not indirect materials.
What causes Purchase Price Variance?
It can be attributed to several key factors, including:
1. Inflation: When prices rise across the board due to economic factors.
2. Fluctuations in Supplier Prices: Changes in the rates charged by suppliers.
3. Alterations in Product Quality or Specifications: Shifting standards can impact costs.
4. Freight and Transportation Expenses: The cost of getting goods from supplier to company.
5. Unforeseen Events: External factors like natural disasters or political instability can disrupt supply chains.
How does PPV affect company profitability?
PPV’s impact on profitability is profound. A negative PPV signifies that a company is spending more on goods and services than initially anticipated. This can significantly reduce profits and erode profit margins.
How can companies mitigate PPV risks?
Companies can minimize risks through:
1. Effective Procurement Policies: Crafting and implementing policies that optimize procurement practices.
2. Supplier Contract Negotiations: Negotiating favorable terms with suppliers to secure consistent pricing.
3. Close Spending Oversight: Monitoring spending patterns to identify and address areas of potential PPV risk.
How can companies harness PPV for performance improvements?
Ways PPV can be used to bring about improvements:
1. Tracking Trends: Monitoring PPV trends over time to detect areas of concern.
2. Root Cause Investigation: Delving into the reasons behind negative PPV to tackle issues at their source.
3. Proactive Resolution: Taking action to rectify the causes of negative PPV, such as adjusting procurement strategies or negotiating with suppliers.
What is the difference between purchase price variance and purchase quantity variance?
Purchase Price Variance relates to the price difference between the standard and actual costs, while Purchase Quantity Variance deals with differences in the expected and actual quantities purchased.
Conclusion
PPV is the difference between a product or service’s purchase and selling price. This calculation considers discounts, rebates, allowances, and other deductions from the purchase price.
Understanding purchase price variance is essential for making sound pricing and inventory management decisions.