The selection criteria for an ideal ERP system is crucial. With several options available, it can be overwhelming to determine the right one.
Suppose you are searching for the perfect ERP system for your business, identifying the key factors that align with your business goals and requirements to ensure seamless integration and maximize efficiency is required.
In this blog post, we will discuss some of the key selection criteria for ERP systems. By understanding what to look for, you can make a more informed decision about which solution is best for your company.
First, let us see what an ERP system is.
What is ERP?
ERP is an abbreviation for Enterprise Resource Planning. Different industries use ERP software to manage and automate many core business processes, such as accounting, finance, HR, and operations.
As a result, ERP software can help businesses streamline their operations and improve efficiency by integrating these various business functions into a single system.
To learn more about ERP, check our blog post “What is ERP“.
Selection Criteria for ERP System
Following is the ERP selection criteria checklist with checkpoints.
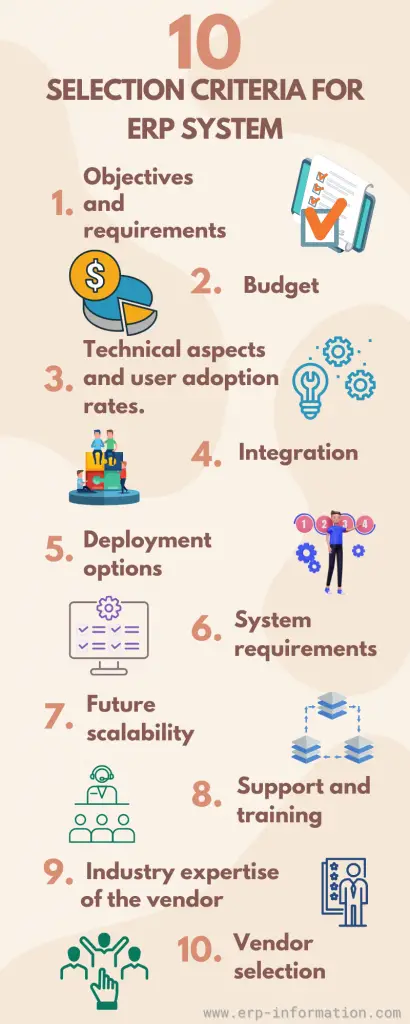
1. Objectives and requirements
The first step in ERP system selection criteria is requirements. Understand what you want to achieve with an ERP system and what specific features and functionality you need.
For example, what are your business objectives? What processes do you want to automate? What information do you need to track? Answering these questions will help you narrow down the field of options and choose a solution best suited to your needs.
For example, if you want to improve customer service, you will need a system that provides visibility into customer orders’ status and easy access to customer information.
Likewise, if you want to reduce inventory levels, you will need a system that can help you track inventory levels and reorder points.
2. Budget
What is your budget for an ERP system? That will likely be one of the most critical factors in your decision.
The budget for an ERP system depends on the size of your company, the complexity of your business processes, and the features and functionality you need.
It would help if you also considered the system’s total cost of ownership (TCO). The TCO includes the initial purchase price, Licensing, ongoing maintenance, support, upgrades, and training costs.
3. Technical aspects and user adoption rates
Technical aspects include the system architecture, platform, customization, and implementation requirements.
- Architecture: The system architecture is how the system is designed, for example, client-server or web-based.
- Platform: The platform is the type of computer system, for example, Windows or Linux.
- Customization: Customization requirements mean how much the system can adapt to your business needs.
- Implementation: This means how long and complex the installation process is.
- User adoption rates: These refer to how quickly and easily users can learn and use the system.
You should also consider things like the system’s usability and training requirements.
4. Integration
You must check how well the ERP system integrates with your existing systems. Integrating an ERP system is a critical component for the success of any business.
It allows different parts of the organization to share information and coordinate activities, improving the accuracy and timeliness of data transferred between systems.
The ERP system must be able to interface with the other systems in the organization, including the accounting system, the production system, and the human resources system.
The ERP system must also be able to interface with the outside world, including the suppliers and the customers.
5. Deployment options
On-premise systems are installed and run on your company’s servers. This option gives you more control over the system but requires a significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Cloud-based systems are hosted by the ERP vendor and accessed through a web browser. This option is typically more affordable and easier to implement, but you will have less control over the system.
6. System requirements
The system requirements will depend on your company’s infrastructure and IT capabilities. You can support an on-premise ERP system if you have a robust IT infrastructure.
However, a cloud-based solution may be better if you don’t have the internal resources to support an on-premise system.
7. Future scalability
A company’s ERP system should be scalable to grow with the company. The provider of the ERP should have a good track record of keeping up with technological advances and be willing to continue developing the system to meet the company’s needs.
8. Support and training
Ensure that the vendor provides proper support for the initial implementation and training of employees.
Find out what kind of supports are available and whether they’re appropriate to meet those requirements to prevent costly problems later on down the road.
9. Industry expertise of the vendor
Industry expertise is one of the most critical factors when selecting an ERP. A vendor familiar with your industry can provide a system tailored to your needs.
In addition, they can offer you advice and support that can help you make the most of your ERP system. However, it is essential to remember that industry expertise can also be a double-edged sword.
If a vendor is too specialized, they may be unable to provide you with a system that truly fits your purpose. As a result, it is crucial to strike a balance between specialization and versatility when assessing the industry expertise of your potential ERP vendor.
10. Vendor selection
Once you have determined your selection criteria, you can begin the vendor selection process. There are many ERP vendors to choose from, so it’s essential to research and select a vendor that is a good fit for your company.
ERP Vendor Selection Process
The selection process of an ERP vendor typically involves the following steps:
1. Evaluation of business requirements
The first step is evaluating the business requirements and determining the organization’s needs. That will help to focus the search for potential ERP vendors.
2. Shortlisting of vendors
Once the needs have been identified, a shortlist of potential ERP vendors is created based on factors such as reputation, experience, product features, and pricing.
3. Request for proposal (RFP)
Once the shortlist has been created, a request for proposal (RFP) is sent to all of the vendors on the list. This document outlines the specific needs of the organization and how the potential vendor can meet these needs.
4. Evaluation of proposals
Once the proposals have been received, they are evaluated by the evaluation team to determine which vendor best meets the organization’s needs.
5. Negotiation and selection
Once a vendor has been chosen, negotiations determine final pricing and contract terms. The selection process is finalized when both parties have agreed to the contract terms.
Importance of Selection Criteria For ERP System
Well-defined selection criteria can help businesses to:
- Reduce risk due to a wrong decision: By carefully considering their needs and requirements, businesses can choose an ERP system that is well-suited for their business. That prevents costly mistakes and ensures the ERP system is a valuable investment.
- Improve the probability of selecting a system that aligns with the requirements of the business: Businesses can determine an ERP system with the necessary features and functionality by clearly understanding their needs. That helps ensure the system can support the business’s operations and growth.
- Improve communication and collaboration between stakeholders. The ERP selection process can be complex and involve several stakeholders. By having a well-defined selection criterion, businesses can enhance communication and collaboration between stakeholders and ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the ERP selection process: By having a clear set of criteria, businesses can streamline the ERP selection process and make it more efficient.
- Maximize returns on investment: By carefully considering their needs and requirements, businesses can choose an ERP system that meets their needs without overpaying.
- Increase satisfaction with the ERP system: By choosing an ERP system that is well-suited for their business, businesses are more likely to be satisfied with the system.
Real-Life Example
How Selection Criteria for ERP Systems Impact Business?
Businesses can choose and successfully implement an ERP system tailored to their specific needs by carefully assessing selection criteria.
Company: A large retail company with over 1,000 stores worldwide.
Requirements: The company sought an ERP system to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. Key requirements included:
- Seamless integration with existing systems: The ERP system must integrate with point-of-sale, inventory management, and CRM systems.
- Scalability: The system should support future expansion plans into new markets.
- User-friendly interface: All employees, irrespective of technical skills, should find the ERP system easy to use.
- Vendor expertise: The ERP vendor must have a proven retail industry track record.
Framing of Selection Criteria by Company: The company devises the selection criteria aligned with its needs:
- Functional requirements: The ERP system must possess essential features and capabilities for efficient operations.
- Integration capabilities: Seamless integration with existing systems is a non-negotiable requirement.
- Scalability: The ERP system must be flexible enough to accommodate future growth.
- Usability: The UI should be user-friendly and easily usable by employees of varying skill levels.
- Vendor experience: The selected ERP vendor must demonstrate expertise and success in the retail industry.
Implementation: Following the selection criteria, the company evaluated various ERP systems. Eventually, they chose an ERP system that met all their needs within their budget.
FAQs
What are ERP vendor selection criteria?
ERP vendor selection criteria include the following factors.
* The vendor’s reputation and experience
* The vendor’s financial stability
* The quality of the vendor’s products and services
* The vendor’s customer references
* The vendor’s support and maintenance offerings
* The vendor’s implementation and training services.
* The vendor’s pricing plan and cost of the ERP
* You should also read online reviews and talk to other companies implementing an ERP system to get their feedback.
Conclusion
The process of selecting an ERP system is not to be underestimated – it carries the potential to shape your business for years to come.
This post has delved into the crucial selection criteria for ERP systems and provided a step-by-step guide to choosing the perfect vendor.
By adhering to these steps and utilizing the comprehensive ERP Selection Checklist, you can confidently approach this decision-making process and make the best choice for your company’s success.