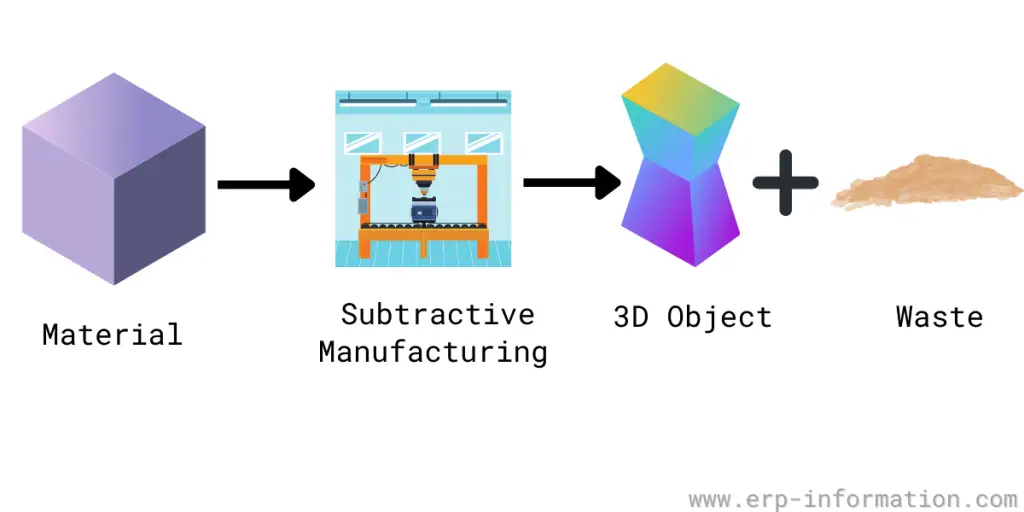
Subtractive manufacturing, also commonly known as machining or material removal process, is a widely used technique in the manufacturing sector.
This traditional method involves starting with a solid block of material and removing or ‘subtracting’ unwanted portions to create a desired shape or product.
This blog post will help you explore subtractive manufacturing- what it is, how it works, its types, and some examples of its applications.
You can calculate 3D print time using our free online 3D print time calculators.
What is Subtractive Manufacturing?
Subtractive manufacturing is a technology that’s been around for centuries and is still in use today. It’s sometimes called subtractive machining, traditional machining, or material removal.
This is a process where the material is removed from a workpiece using tools such as milling cutters, lathes, grinders, and drilling machines to create the desired shape. You can use the process to create parts with exact dimensions and shapes.
Features
Essential features of subtractive manufacturing are,
- This process is more suitable for mass production with simple geometry parts.
- The components built have accurate structure and excellent heat resistance.
- Finishing is not mandatory for parts created using this approach, as the process gives a smooth surface finish.
- High tolerance and better finishing can be achieved using fully automated machines and robotics technology.
Example
One typical example of subtractive manufacturing is CNC machining.
It uses computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece. A virtual model created in CAD software is used as an input to the fabrication equipment in CNC machining.
The user’s commands, combined with the program simulation, start tool paths that enable the cutting tools to perform the required removals and cuts to create the desired shape.
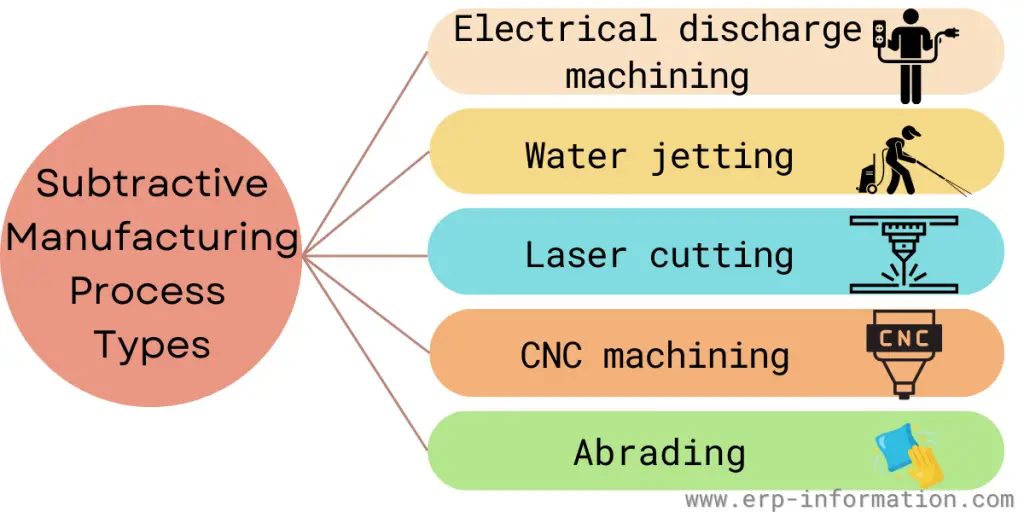
Types of Subtractive Manufacturing Processes
These processes help to get exact structures and can be used to cut complex shapes.
The most common processes are
| PROCESS NAME | DEFINITION | MATERIALS |
| Water jetting | Water jetting is the process of cutting the material using high-pressure water jets. | Metals, plastics, glass, composites, and stone |
| Laser cutting | Laser cutting uses a high-powered laser to cut material. | Acrylic, Thermoplastics metals, wood, and fabrics |
| CNC machining (grinding, milling, rolling, turning, drilling) | CNC machining uses computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece. | Hard thermoplastics, soft or hard metals, thermoset plastics, and glass |
| Abrading | Abrading is using an abrasive material to remove material from a workpiece. | Sandpaper, grinding wheels, and abrasive belts |
| Electrical discharge machining | Electrical discharge machining uses electrical sparks to remove material from a workpiece. | Hard metals and plastics |
When to Use Subtractive Manufacturing?
- This is most often the best choice for fabricating finished parts.
- Subtractive metal processes for higher volumes or parts subject to more extreme mechanical stress and strain.
- Subtraction is often preferable when dealing with metals and other materials that are difficult to work with using an additive approach.
How to Choose the Proper Subtractive Process?
When choosing a subtractive process for your project, it is vital to consider the following factors:
- The type of material you are machining
- The shape and size of the part you need to create
- The tolerance requirements for the finished part
- The surface finish requirements for the finished part
- The number of parts you need to create
- The lead time you have for your project
- The budget you have for your project
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
There are five main benefits of subtractive manufacturing:
- First, it’s versatile: The subtractive process can be used on various materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics.
- It’s precise: When done correctly, the subtractive method can create particular parts and products. Tolerances of plus or minus 0.001 inches (0.0254 millimeters) are not unusual.
- It’s fast: In many cases, the subtractive process is shorter than the additive process. That is because you don’t have to build an object from scratch.
- It uses less material: Since the subtractive process involves removing material from a workpiece, it often uses less material overall. That can save on costs.
- It’s easy to automate: Subtractive manufacturing processes can be easily automated, further improving efficiency and accuracy.
Disadvantages
- It can be expensive: The equipment needed for subtractive manufacturing can be costly.
- It can be messy: Removing material from a workpiece can create a lot of dust and debris.
- It can be dangerous: The tools and equipment used in subtractive manufacturing can be dangerous if not used properly.
Applications
- Textured surfaces fabrication
- Cutting features for household items
- In industries like Aerospace, Automotive, Medical, Electronics, and Consumer products
FAQs
What is the similarity between Additive and Subtractive Manufacturing?
Both subtractive and additive manufacturing involve the use of computer-controlled machines.
What is Hybrid Manufacturing?
Hybrid manufacturing is a process that combines both subtractive and additive manufacturing techniques. That allows for the creation of parts and products with complex and simple geometries.
Is 3d printing used in the Subtractive Manufacturing process?
No, 3D printing is not used in the subtractive manufacturing process.
What are the primary advantages of Subtractive Manufacturing over Additive Manufacturing?
Subtractive Manufacturing offers high precision, superior surface finishes, and is well-suited for mass production. It’s particularly favored for materials like metals, ceramics, and other traditional materials.
Which industries commonly use Subtractive Manufacturing, and what are some typical applications?
It is widely employed in the aerospace, automotive, electronics, and tooling industries. Common applications include producing engine components, circuit boards, molds, and precise mechanical parts.
What are the main challenges in Subtractive Manufacturing, and how can they be addressed?
Challenges include material waste from cutting, longer setup times, and limitations in creating complex internal structures. These challenges can be mitigated by optimizing machining processes and investing in efficient equipment.
How does technology, such as CNC machining, impact Subtractive Manufacturing, and what are the benefits of automation in this process?
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a pivotal technology in Subtractive Manufacturing, offering precise control over tool movements. Automation enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and enables cost-effective production.
Conclusion
In short, subtractive manufacturing is the process of removing material from a workpiece to create finished parts. It’s versatile, precise, fast, and uses less material than additive manufacturing.
While there are some disadvantages to it, the pros often outweigh them. It is used in a variety of industries and can be applied to a variety of materials.
If you’re considering using this process for your next project, consult a professional to ensure that it’s the best option for you.