Giving a boost to warehouse zone operations is crucial for businesses. Understanding warehouse zoning and taking initial steps are important factors in enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
This article serves as a guide to elevate your operations in warehouse zoning, providing the necessary information and guidance.
Reading this article gives you a clear idea of the warehouse zone, its types, tips to improve each warehouse zone, types of zones in the warehouse’s storage area, and types of warehouses.
Evaluate warehouse capacity using our Warehouse Capacity Calculator
Evaluate warehouse storage costs using our Warehouse Storage Costs Calculator
Evaluate Storage costs using our Storage Cost of Inventory Calculator
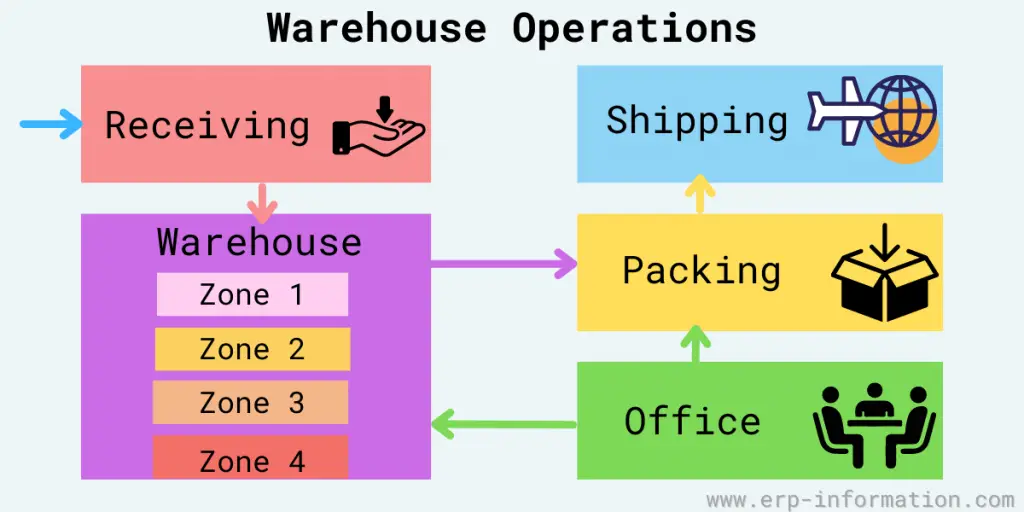
Definition of Warehouse Zone
A warehouse zone is a physically or logically segregated area within a warehouse defined by the type of material it contains (bulk or rack storage, hazardous material, etc.) or the division of equipment and personnel used to put away, move, and pick.
This warehouse zone system allows you to always store the items in the exact locations so that employees can know where the items are stored.
Depending on the type of products, we have to allocate the zone in the warehouse because some products must be stored in the refrigerator, some products are stored in racks, and some products are stored in bins.
Hence warehouses should have different types of zones.
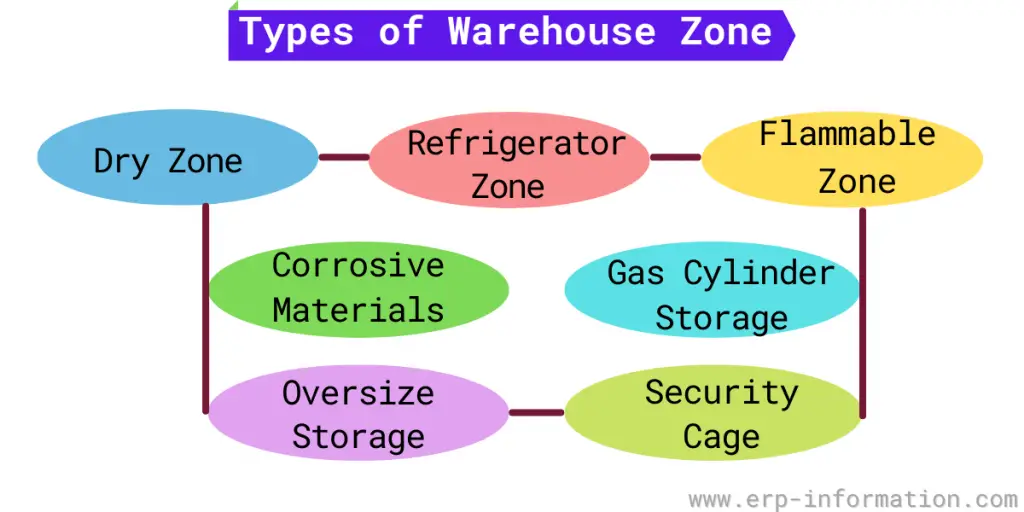
Different Types of Warehouse Zones in a Storage Area
Dry zone
In this zone, you can store products required to keep away from moisture.
It is the most common zone in a warehouse. In this zone, the temperature will be maintained between 50 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit.
Refrigerated zone
It is necessary to be there in the warehouse zone storage area. In this zone, you can keep the products required to be stored at low temperatures, such as food products, vaccines, etc.
The temperature of this zone will vary from zero to 38 degrees Fahrenheit.
Flammable zone
Some manufacturing companies require chemicals for their manufacturing process. An approved storage cabinet should store these chemicals.
Corrosive materials
In this zone, you can store acids. This zone should be located separately because corrosive materials like acids will not contact other items.
Gas cylinder storage
Gas cylinders must be stored separately in the warehouse. Therefore, it is necessary to follow safety measures like carts and safety chains while transporting the gas cylinders in the warehouse.
Oversize storage
Some products need more space because they will not fit on regular shelves. For those products, this zone is valuable.
Security cage
In this zone, you can store valuable items such as brand-name pharmaceuticals.
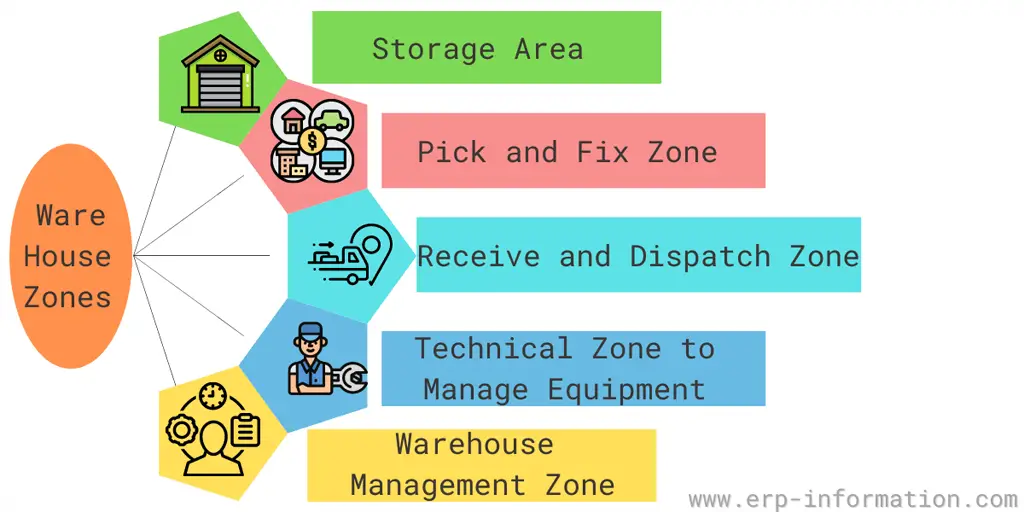
Tips for Developing Each Warehouse Zone
Following are the few warehouse zones you should have in your warehouse and some points to develop each warehouse zone.
Storage area
- Set dust-free surfaces in the product storage area.
- Have good quality, rust-free shelves so that rust will not affect stored products.
- When your storage area is completely occupied, they have added storage overhead so that you can expand your storage area.
- You can also use compact storage and mobile storage shelves to increase your storage capacity.
- Have shelves and racks that are suitable to your product dimension.
Pick and fix the zone
- Set a good outline for the picking zone. While developing the picking zone, consider the product size and product rotation.
- Improve the connection between the zones by having an automated system like a box conveyor.
- You can also have automated picking equipment.
The product receives and dispatch zone
- Have a sound warehouse management system to control the goods receiving and dispatching area traffic.
- Assign a proper place to the trucks while loading and unloading the goods. It helps the smooth flow of goods inside the warehouse.
Technical zone to manage equipment
- A technical zone is assigned to maintain equipment, like charging the batteries for equipment.
- Make sure that this zone is in proper environmental condition. That means some instrument needs AC.
Warehouse management zone
- Have an admin zone in your warehouse so that the supervisor can always keep in touch with the day-to-day activities of the warehouse.
- Have a good computer connection with your company server
Strategic Warehouse Zoning
The following factors influence the performance of your warehouse and hold the potential to redefine the entire logistics landscape:
Optimizing storage space to the fullest
The foremost priority is the maximization of available storage real estate. Use vertical space and ensure every square inch serves a purpose.
Facilitating swift and effortless access to stored goods
The efficiency of your warehouse hinges on the ease with which stored items can be accessed, speeding up handling and retrieval processes.
Ensuring optimal visibility and logical goods placement
Creating an environment where goods are visible and logically positioned reduces errors and enhances overall inventory management.
Trimming storage-related costs
Every decision made in zoning should lead to cost reduction, making the most of available resources and minimizing unnecessary expenses.
Minimizing travel distances for handling equipment
Efficiency translates to shorter distances traveled, which not only saves time but also diminishes wear and tear on handling equipment.
Prioritizing safety and navigability
Safety is paramount, and a well-zoned warehouse ensures unimpeded transit while maintaining a secure environment for all personnel.
Clearly defining and marking designated areas
The demarcation and marking of each zone serve as a visual roadmap for efficient operations, minimizing confusion and errors.
Classifying hazardous materials
Products classified as hazardous require distinct zoning with safety features, including fire-resistant materials and controlled access. Compliance with safety regulations is non-negotiable.
Considering shelf life and expiry dates
Perishable goods, like food or pharmaceuticals, should be zoned according to their shelf life and expiration dates. This practice reduces waste and ensures compliance with quality standards.
Stackability
Some products are stackable, while others are not. Effective zoning takes this into account to maximize space utilization while maintaining accessibility.
Special handling requirements
Products with unique handling needs, such as those requiring vertical storage, hanging, or specialized racks, must be appropriately zoned to accommodate these requirements.
FIFO or LIFO Method
Depending on your inventory strategy (e.g., First-In, First-Out or Last-In, First-Out), products must be zoned accordingly to maintain proper rotation and minimize waste.
Adopting technology
Equip your zones with technology such as barcode scanners, RFID systems, and inventory management software. These tools streamline processes, enhance tracking, and reduce errors.
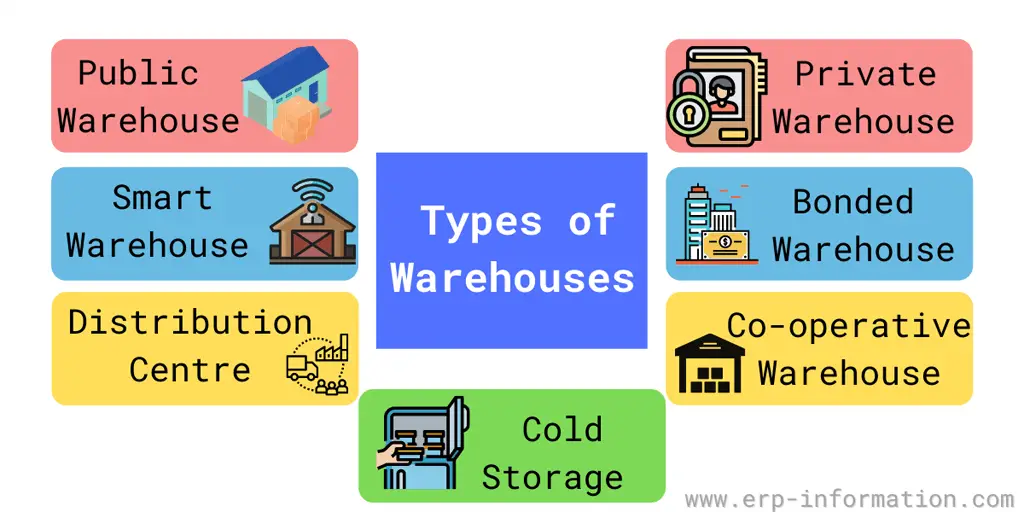
Types of Warehouse
Below is the list of different types of warehouses used for various purposes.
Public warehouse
It is a storage area owned by governmental bodies. A person or an organization can use this warehouse-type by paying rent.
A public warehouse is most suitable for startups and small-scale industries to store their goods temporarily.
Private warehouse
It is a storage area owned privately by manufacturers, distributors, wholesale dealers, etc. Therefore, it is a little expensive compared to public warehouses.
However, it is still affordable for startups and small-scale industries.
Distribution center
It is a storage area, especially for temporary storage goods. Unlike other warehouses, distribution centers might hold materials temporarily or for a short period.
When many materials are received, and you might distribute them to different resellers, the distribution center helps a lot.
Compared to other warehouse types, it is well equipped with advanced technologies and provides some value-added services like pick and pack services, docking, etc.
Bonded warehouse
It is a particular storage area used to store imported items before paying customs duties. You can keep the imported goods for an extended period also.
This warehouse’s most crucial advantage is that you need not pay duties until your items are released and sold because duties for imported items will be very high.
Smart warehouse
It is an advanced type of warehouse in that you can store and manage the items automatically with the help of Artificial Intelligence.
That includes managing software and performing tasks such as picking, weighing, packing, transporting, and storing goods using drones.
So this type of warehouse makes the work easy and increases sales and productivity by decreasing human errors. Hence, online vendors like Amazon and Alibaba use this type of warehouse.
Cooperative warehouse
This type of warehouse is most suitable for cooperative organizations. It is a storage area owned by cooperative organizations such as farmers, weavers, etc.
In this warehouse, both members of the cooperative organization and outsiders can store their goods. However, members will get some reduction in rent.
Cold storage
It is a storage area used to store items stored at low temperatures, such as some types of medicines, cosmetics, food items, and beverages.
FAQs
What is a Warehouse?
A warehouse is a planned storage area for products, materials, and equipment. It is usually an ample, unobstructed space with a high ceiling that stock can be moved around easily.
Businesses that need to store large amounts of inventory, such as manufacturers, retailers, and distributors, use warehouses. They are usually located near transportation hubs so that goods can be quickly shipped in and out.
Some warehouses are also used for other purposes, such as assembly or packaging. Proper planning is essential for a successful warehouse operation as it can help improve efficiency and reduce costs.
What is the primary goal of warehouse zoning?
Warehouse zoning’s primary goal is to optimize the use of space and resources within a warehouse. By strategically dividing the warehouse into different zones based on product characteristics and needs, it ensures that every inch of space is used efficiently, leading to smoother operations, reduced costs, and improved overall productivity.
How can the ideal zoning be determined for a warehouse?
Determining the ideal zoning for your warehouse involves a careful analysis of your product inventory, customer demand, and operational requirements. It’s like composing a symphony where each section (zone) is perfectly tuned to meet specific needs.
Start with a thorough assessment of your products and their characteristics to create zones that enhance accessibility, minimize handling, and streamline workflow.
What types of products benefit the most from specialized zoning?
Products with distinct characteristics, such as perishable items, hazardous materials, or high-value goods, greatly benefit from specialized zoning. Perishables need controlled environments, while hazardous materials require strict safety measures.
High-value items need secure zones. The key is to tailor each zone to meet the unique demands of the products it houses, ensuring their integrity and safety.
How does technology play a role in warehousing?
Technology plays a part in warehouse zoning. It operates with tools like barcode scanners, RFID systems, and inventory management software.
These digital instruments harmonize processes, enhance tracking, and minimize errors, resulting in a well-orchestrated and highly efficient warehouse.
Is it necessary to adapt zoning as a business evolves?
Absolutely, your zoning strategy should adapt as your business evolves. New products, changing customer demands, and technological advancements may require adjustments.
Staying flexible and open to changes in your zoning can help your warehouse remain in perfect harmony with your business’s needs.
What safety measures should be implemented within each zone?
Safety is the keynote in every zone. This includes providing personal protective equipment, fire safety measures like sprinklers and extinguishers, and clear emergency exit routes.
Think of it as ensuring that every performer in your symphony plays their part without missing a beat when it comes to safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, warehouse zones are essential for the effective storage of products. It will help you maximize your space’s use, improve production accuracy and accuracy, increase efficiency and safety in operations, and lead to cost savings.
Properly defining each zone’s functions helps all warehouse processes run smoothly, leading to higher productivity, fewer errors, and better-organized staff.
This guide covered the definition of warehouse zones, types of zones, tips to improve each zone, and types of warehouses. Hope it helps you.