Production scheduling is an integral part of any business. It determines when and how products will be made, ensuring the company can meet customer demand while making a profit.
In production scheduling, there’s a special time known as the ‘frozen zone.’ Think of it as a protective shield around the master production schedule, where no changes are allowed. Read on to get a better idea.
Let’s dive into this unique concept and discover how it brings stability and order to the world of manufacturing. This blog post will explore what Frozen Zone is and how you can manage it effectively with examples.
Definition
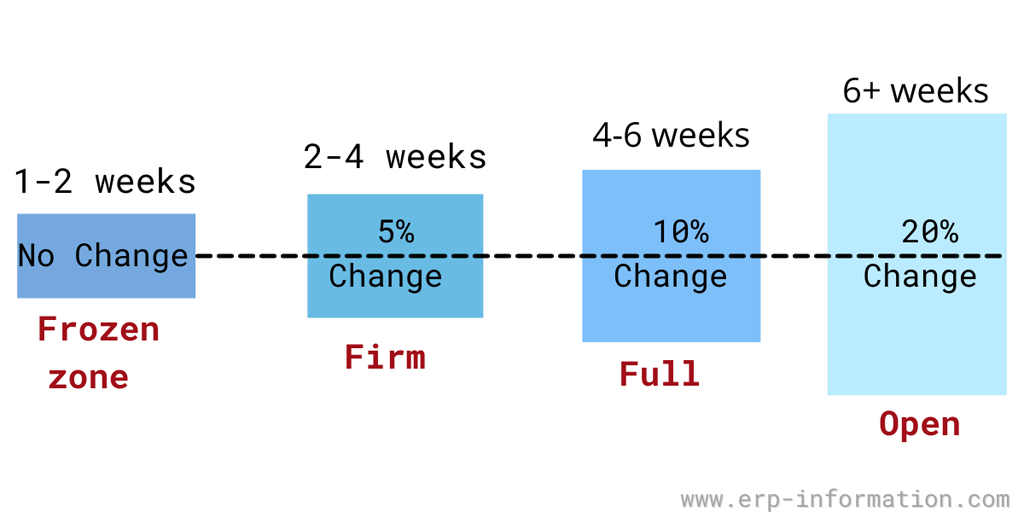
A frozen zone is the scheduling time horizon during which no alterations to the master production schedule are allowed. That provides more balance and control to the master production schedule.
According to Gartner (Global research and advisory firm), all organizations face one critical problem. That is the planning and execution of sales orders. Organizations make sales and operations planning in the unfrozen zone (liquid zone) and execute sales and processes in the frozen zone.
A time fence separates these two zones. Outside the fence, that means in the liquid zone. You can change the purchase order and production plans.
But you can not change the purchase orders and production plans inside the fence. You have to work in the real world.
Click here for the Online Purchase Order Financing Calculator
How do you unfreeze the frozen zone in the supply chain?
It is challenging to deal with unexpected orders and shipping delays even if you carefully plan and forecast. Unfortunately, dealing with this problem is not possible with a planning tool.
To manage your supply chain within set timelines, utilize an automation tool within a supply and operations execution (S&OE) platform. This tool effectively unfreezes operations, ensuring smooth control and support.
- This tool provides a clear vision of shortages and alerts you with early warnings.
- It allows you to take preventive actions by discovering issues immediately.
- It helps the people in the supply chain to interact with each other.
- It centralizes communication and keeps track of discussions and decisions.
- It allows you to boost your operations with the help of analytics of previous data available to you.
Frozen zone examples
Here, the production order is fixed for a set period. So after updating the production order, the first calendar month is generally considered a ‘frozen zone.’
You can not change or cancel the number of products in the production order at this period. You can change it only when both vendors and buyers agree on it.
For example, suppose a factory produces widgets and has a frozen time from midnight to 6 a.m. In that case, it will not make any widgets during that period, regardless of customer demand.
Click here for the Online Production capacity calculator
Frozen planning period
A frozen planning period is when the organization does not alter its product supply plan. The frozen planning period is crucial to avoid short-term alterations in the plan.
Usually, the frozen planning period will include review time and lead time for products. The recommended period is 1-2 weeks.
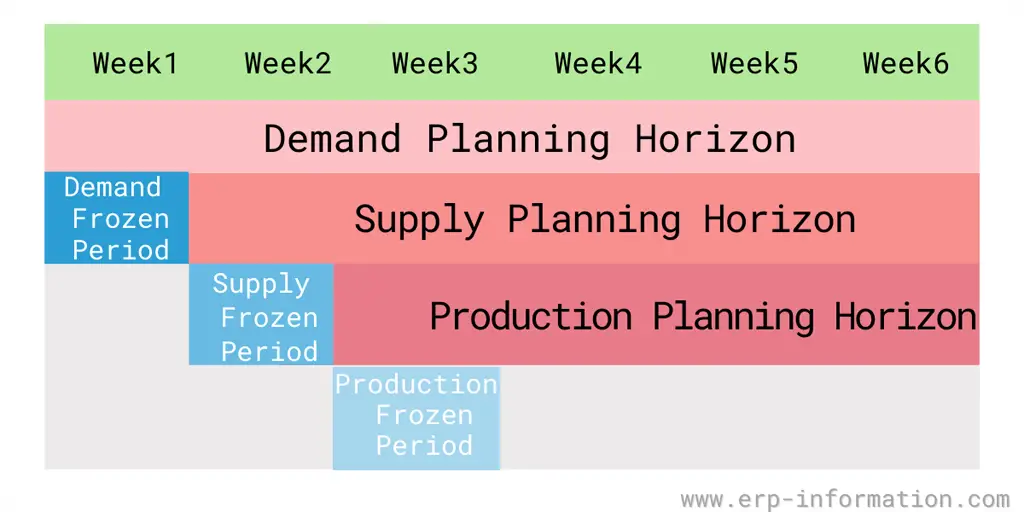
A frozen planning period helps bifurcate the different domains like demand planning, supply planning, and execution.
FAQs
What is a frozen period?
The frozen period is when a company cannot change its production schedule. This term is usually used in manufacturing, where it’s crucial to maintain a consistent flow of products.
In case of problems with the production process that need to be fixed, the frozen time prevents workers from making changes that disrupt that flow.
How to identify the frozen zone in your production schedule?
To identify frozen zones within your production schedule, scan for timeframes designated as fixed or immovable.
These may result from contracts, raw material constraints, or various other factors. Once these fixed periods are pinpointed, everything else falls into what we call the “frozen zone.”
During this phase, any alterations to the schedule demand proactive communication and coordination well ahead of time to prevent disruptions.
Conclusion
In summary, the frozen zone stands as the unchanging heart of the production schedule, crucial for maintaining a stable workflow. Although rigid, it’s vital for keeping production running smoothly.
As supply chains evolve, understanding their significance remains key for effective production planning and control. Thank you for your readership!