If you’re working in the manufacturing business, you may hear of a “manufacturing order.” It is an essential part of the production process, and it’s key to understanding how all the individual steps involved with producing a product or service come together.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the concept of a manufacturing order and explore its components, like how to create it, its management, process, and benefits.
What is Manufacturing Order?
A manufacturing order is a formal document or group of documents detailing the production of a specific item or product.
It includes comprehensive information on the required materials, resources, and work centers necessary for its completion. This order can be planned or released.
How to Create Manufacturing Orders?
Both planned and released manufacturing orders can be created manually or automatically. The creation of a manufacturing order involves the precise identification of the product to be produced, the determination of the production quantity, and the allocation of work to specific machines or work centers.
A manufacturing order contains basic information like order type, order documents, start date, finish date, order quantity, status, priority, start and finish points, etc.
Importance of Manufacturing Order in Manufacturing Process
A manufacturing order is vital in the manufacturing process for several reasons. It serves as a detailed guide for producing a specific item, outlining the necessary materials, resources, and work centers. This clarity ensures the production team knows exactly what needs to be done and when, leading to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and minimized waste.
It also helps manage inventory levels by specifying the required materials for each production run. This prevents stockouts and delays, ensuring production runs smoothly and meets demand. Additionally, it enhances quality control by detailing the steps and resources needed, which helps maintain consistent quality and reduces defects and rework.
Types of Manufacturing Order
There are three common types of manufacturing orders, each with distinct characteristics and purposes. Manufacturers utilize these orders based on the specific manufacturing process and product type.
Production Order
This type is used for the manufacturing of assemblies and complete products. It includes comprehensive details such as the type of product to be produced, the quantity required, and the necessary materials and resources.
Work Order
This order is utilized for the production of individual parts or components. It specifies the particular work centers or machines to be used, as well as the required materials and resources. Work orders are typically employed in assembly line production processes.
Batch Order
This order is employed to produce a specific quantity of a product. It includes information regarding the quantity to be produced, as well as the necessary materials and resources.
Manufacturers select the appropriate type of order based on their production requirements and the nature of the product being manufactured.
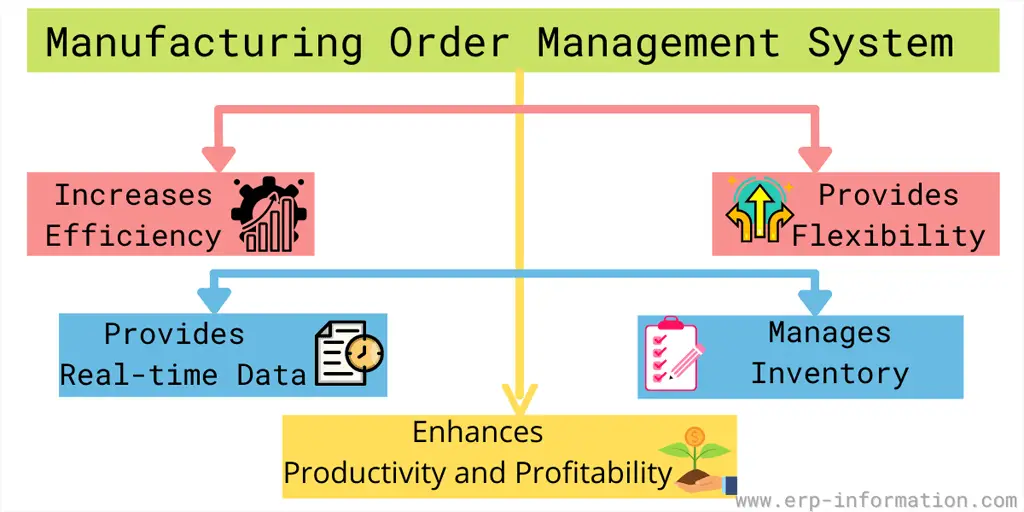
Manufacturing Order Management System
This system is crucial for every business to monitor and control sales and manufacturing order management.
What is manufacturing order management?
A manufacturing order management system is the software for coordinating production orders from product planning, purchasing or transportation scheduling, and inventory management at a project and enterprise level.
It automatically manages the entire process from order creation to GRN (Goods Receipt Note).
The manufacturing order process starts with BOM (bill of materials) and raw materials needed for the manufacturing. You will get all this information in the manufacturing order form.
(Manufacturers use MOM (Manufacturing Operations Management)systems to synchronize supply and demand forecasts with projected business selling rates and ultimately give more accurate quotes to customers on future costs. On top of maximizing efficiency by transmitting information quickly across many different departments, MOM also allows companies to maintain an unbroken chain of documentation that can be archived more rapidly than paper records.)
Benefits
Increases efficiency
Manual work leads to errors, and you must invest more in the workforce. But with an efficient order management system, you can avoid human mistakes and save money by investing less in human resources.
The system also helps to save time by giving attention to your business growth and customer satisfaction, increasing efficiency.
Provides flexibility
If you want to check your orders instantly, you can access the order details from anywhere, on any device, and at any time, with the help of cloud order management software.
Provides real-time data
The system provides real-time updates on sales and inventory that help you solve issues immediately. When you get real-time data, you can make better business decisions.
Manages inventory
The system enhances your inventory by providing real-time data about stock levels, stock-outs, billed items, and production items. That helps the manufacturer to avoid overstock and understock.
Enhances productivity and profitability
Your order process becomes automatic because of the management software, and you will become free to analyze your data.
That helps you to plan your business growth with the help of real-time data. In this way, the system helps to increase productivity and profitability.
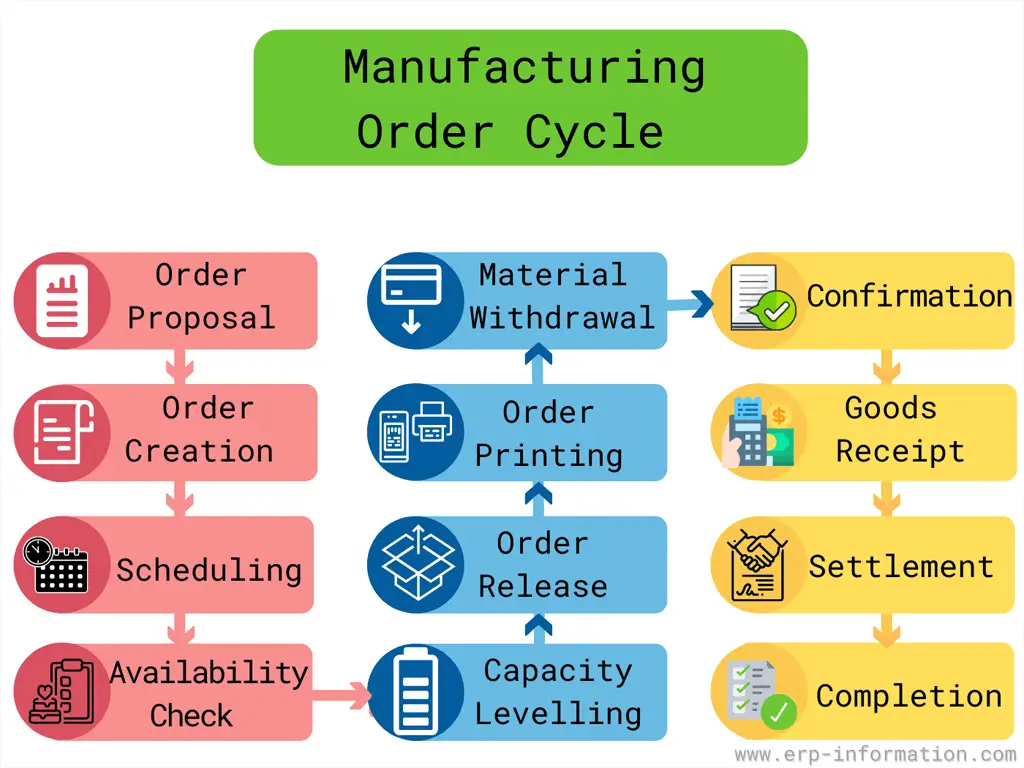
Manufacturing Order Process
Typically manufacturing order process includes the following steps.
- Order placement: The customer places an order online or via phone calls. The system automatically saves customers’ details.
- Order fulfillment: The corresponding department sends the sales details to the warehouse for an availability check. If ordered items are available in the warehouse, picking and packing the items begins. Otherwise, the production department manufactures the requested item, and then picking and packing starts.
- Creation of GRN: When items are ready to deliver, GRN creation will be done.
- Shipment: Finally, the order is dispatched to the customer, and sales items are recorded in the software as delivered orders.
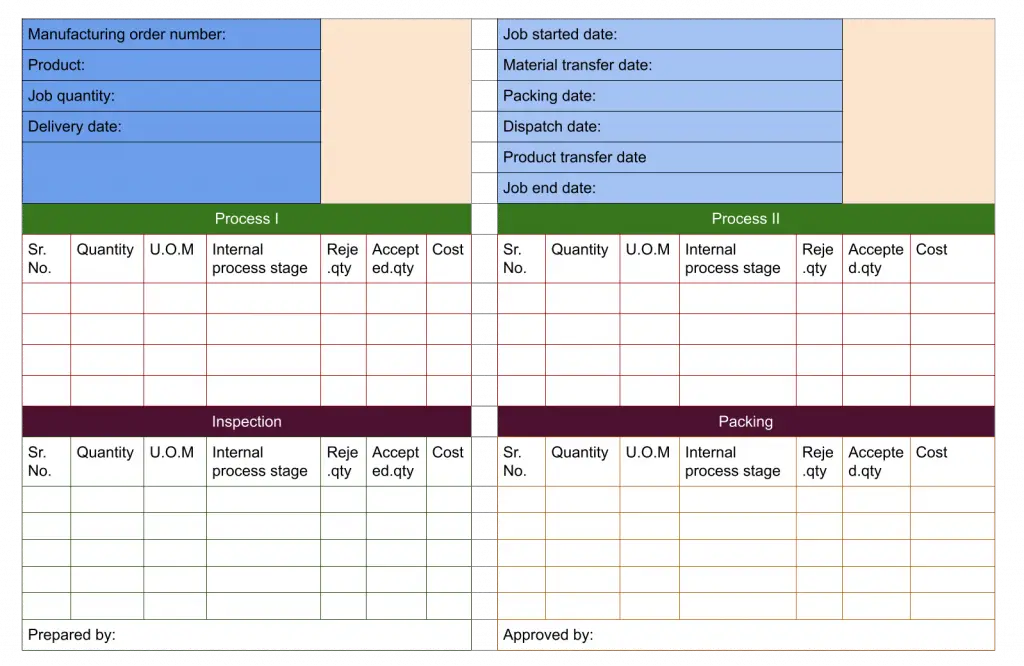
Manufacturing Order Form
It contains the following details.
- Manufacturing order number and date: The order number and date must be mentioned in this field.
- Product name: Name of the product that you are going to manufacture.
- Job quantity: The complete quantity of the order has to be specified in this field. For that, you can refer to the customer order.
- Delivery date: Here, you need to mention the date you will deliver the product on that date. In the customer purchase order, the expected date of the product will be noted. The exact date you can mention in the customer delivery date.
- Job start date: Here, specify the start date of the process.
- Material transfer / raw material location date: Mentioned the date on which raw material should be transferred.
- Packing date: Mention the target date of packing
- Finished product location/ material transfer date: Specify the date until the product is stored temporarily to complete all the documentation.
- Dispatch date: Target date of dispatching the product
- Job end date: Mention when the finished product reaches the customer location.
- Manufacturing process: Process I and II AND inspection & packing contain the following fields.
- Quantity
- Unit of measurement
- Internal process stage
- Rejection quantity
- Accepted quantity
- Cost of the process
Best Practices
Creating a manufacturing order form is an essential task in the production process. A well-structured order form is like a blueprint that guides the entire manufacturing journey.
Adhering to best practices is crucial for the precise and streamlined creation of manufacturing orders. By embracing these guidelines, manufacturers can enhance the efficiency of their production procedures and reduce the occurrence of mistakes.
Thorough product analysis
Before creating manufacturing orders, delve deep into the specifics of your product. Understand its components, specifications, and any unique requirements.
This step not only ensures you have a comprehensive understanding of your product but also aids in determining the quantity and type of materials required.
Demand forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is the bedrock of manufacturing order creation. Use historical data, market trends, and seasonality patterns to predict future demand.
Up-to-date Bill of Materials (BOM)
A well-structured Bill of Materials is indispensable. Organize it meticulously, and consider using software tools to manage and update it efficiently. Ensure it’s always up to date to avoid discrepancies and production delays.
Choose the right software
Leverage cutting-edge Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software to streamline manufacturing order creation. These systems can automate the process, reduce human error, and provide real-time insights into your manufacturing operations.
Work order synchronization
Align your manufacturing orders with the work orders effectively. Ensure that the tasks and processes outlined in the work orders are synchronized with the production schedule.
Capacity and resource planning
Understanding your production capacity and resource constraints is vital. Always create manufacturing orders with these factors in mind to ensure a realistic and feasible production schedule.
Lean manufacturing principles
Implement lean manufacturing principles like Just-in-Time (JIT), Kanban, and Six Sigma to minimize waste, reduce lead times, and enhance the overall efficiency of your operations.
Common Mistakes to be avoided in Manufacturing Order Form Creation
Ambiguous product specifications
One of the most frequent errors is providing incomplete product specifications. The manufacturing order form should contain detailed information about the product, including materials, dimensions, quality standards, and any unique requirements.
Failing to provide this data can lead to confusion, subpar production, or even costly rework.
Neglecting quantity accuracy
Another pitfall is inaccuracies in the quantity of items ordered. Precision is key; overestimating or underestimating the quantity needed can lead to wastage or production shortfalls. Always double-check and verify the quantities to avoid these costly mistakes.
Outdated Bill of Materials
Relying on an outdated Bill of Materials (BOM) is a recipe for disaster. Ensure your BoM is up to date, with all components and materials accurately listed. Changes in product design or new suppliers should promptly be reflected in the BOM to prevent costly mix-ups.
Inadequate material sourcing
Ordering materials from unreliable or unqualified suppliers is a significant pitfall. These materials might not meet quality standards, leading to production delays, defects, and unhappy customers. Always conduct thorough research on your material sources and verify their quality and reliability.
Ignoring work instructions
Failure to provide comprehensive work instructions to accompany the order form is another common mistake. Clear and precise instructions are essential to ensure that the manufacturing team understands the production process, including sequence, machinery settings, and quality control measures.
Communication gaps
It is crucial to establish transparent and effective communication channels among the production team, management, and other stakeholders to ensure shared understanding and minimize errors resulting from miscommunication.
Lack of standardization
Implementing a standardized format for the manufacturing order form can promote consistency and clarity, reducing errors and enhancing overall efficiency.
FAQs
What is manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process of transforming tangible materials into a final product. In other words, it is converting raw materials into finished goods.
It typically involves machinery, tools, and labor to produce a finished product. The manufacturing process can be divided into several steps: design, production planning, scheduling, fabrication, assembly, and testing.
When is the manufacturing order created?
A manufacturing order is a document that carries the authority to manufacture specific parts or products in quantities.
This planning is done before an authorized person immediately releases it for implementation at your factory floor level. Then, after some initial sampling has been taken and verified, the quantity can be good enough.
What is the difference between a manufacturing order and a work order?
A manufacturing order is created when a customer requests a product that has not yet been manufactured. A work order is made when a customer requests a product already manufactured and in stock.
A manufacturing order will include the specifications for the product that needs to be manufactured. A work order will consist of the required quantities and the delivery date.
Manufacturing orders must be processed in the order that they are received. However, work orders can be processed in any order.
What is manufacturing order processing software?
Manufacturing order processing software is a type of software that helps manufacturers manage the orders they receive from customers.
The software can help manage everything from the initial order to the final shipment and track inventory levels and shipping schedules to ensure that orders are fulfilled on time. In addition, the software can help create purchase orders and invoices and provide reports on how well the manufacturing process is performing.
Various manufacturing order processing software options are available depending on the business’s specific needs. Some popular options include:
• Microsoft Dynamics NAV
• Sage 100 ERP
• Epicor ERP
These software programs offer different features and benefits, so it’s important to research which option would be best for your business.
What is the production order definition?
A production order is a document that lists the specific materials, parts, and tools required to produce a product. It also defines the sequence of operations to create the product.
A production order can be used as a guide for manufacturing personnel to ensure that all necessary materials and components are gathered before beginning production and that the steps required to produce the product are followed correctly.
What’s the role of technology in modern manufacturing order management?
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing orders, enabling real-time tracking, automation of order generation, and improving data accuracy. With the right software, you can streamline your entire order management process, reducing errors and delays.
What are the types of manufacturing production processes?
Make-to-order (MTO), Make to Stock (MTS), and Make to Assemble (MTA) are three types of manufacturing production processes.
Conclusion
Manufacturing orders are a cornerstone of the manufacturing process, providing a structured and detailed guide for production. By clearly outlining the necessary materials, resources, and steps, they ensure efficient and effective operations, helping to reduce downtime, manage inventory, and maintain quality control.
Utilizing different types of manufacturing orders—production, work, and batch—manufacturers can tailor their processes to meet specific product requirements. With the integration of advanced order management systems, businesses can further enhance productivity, flexibility, and real-time decision-making.