Enter the world of manufacturing, where the Master Production Schedule (MPS) plays a crucial role in guiding the production of finished goods.
It carefully outlines what needs to be produced, how much is needed, and when it should be made. It acts as a synchronizer, ensuring that production capacity, inventory levels, and customer demand are well-aligned.
MPS is a tool for manufacturers to ensure the right products are made at the right time and in the right quantities. This post will answer questions on MPS, the steps involved, its functions, examples, and its benefits. You can also download different MPS templates at the end of this post.
Evaluate Production capacity using our Online Production Capacity Calculator.
Definition
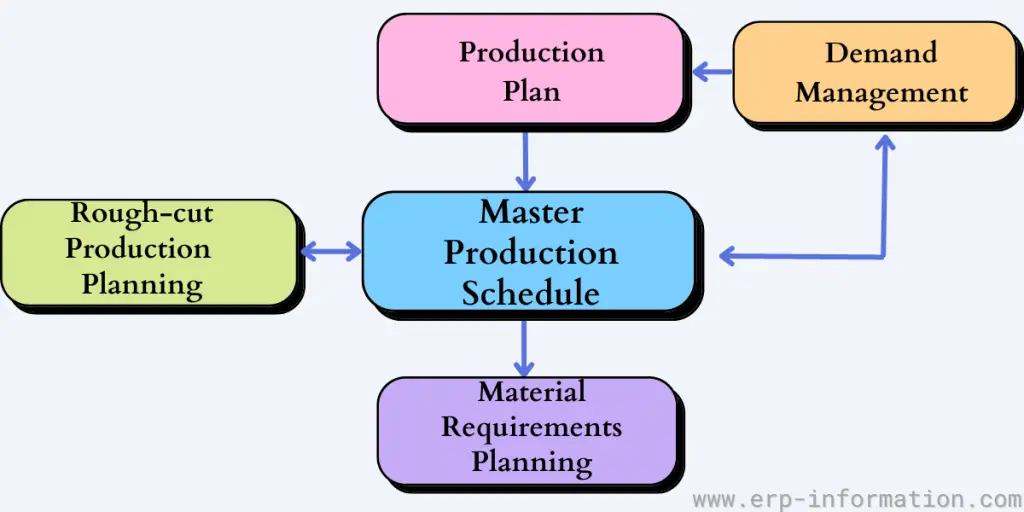
Master Production Schedule is a way of planning what products need to be made and when they need to be made. This is used in any industry where production is necessary, like manufacturing, construction, and logistics.
There are many different versions of this plan, but they all have the same goal: ensuring products are delivered on time and at the lowest possible cost.
It is a production planning tool that helps companies manage their resources to produce products efficiently while reducing waste. As a result, companies using it report improved customer satisfaction due to on-time delivery and fewer errors.
The essential parts of MPS are the Bill of Materials (BOM) and Material Requirements Planning (MRP I).
Components
You can enhance your MPS and make it more effective by including essential components. Here are the four main components.
1. Product List
The product list is the foundation of your MPS. It includes all the items that your company plans to manufacture over a specified period. Each product on this list should have detailed descriptions, including:
- Product Name: The name of the item to be produced.
- SKU (Stock Keeping Unit): A unique identifier for each product.
- Description: Brief details about the product, including its features and intended use.
- ABC analysis: Identify the popular products by ABC analysis and keep them at the top of the list.
By clearly outlining the products, you ensure that everyone in the production process knows exactly what needs to be made.
Use our ABC Analysis Calculator to classify your products.
2. Variations of Sublists for Each Product
Within the main product list, you may have variations or sublists. These sublists account for different versions or models of each product. For example, if you manufacture smartphones, sublists might include different models, colors, storage capacities, and any other specifications.
- Model Variations: Different designs or versions of the same product.
- Specifications: Details like size, color, or additional features.
- Customization Options: Any customizable elements available for the product.
These sublists help in managing and planning for the production of multiple variants, ensuring that specific requirements for each variant are met without confusion.
3. Time Periods (Months, Weeks)
The time period component of an MPS breaks down the production schedule into manageable intervals. This can be organized into months, weeks, or even days, depending on the manufacturing cycle and business needs.
- Monthly Schedule: Long-term planning, useful for products with longer production cycles.
- Weekly Schedule: More detailed planning, allowing for adjustments based on demand and production capacity.
- Daily Schedule: For operations that require precise, day-to-day planning.
By defining clear time periods, you can better allocate resources, manage workloads, and ensure timely completion of production goals.
4. Production Quantities
The production quantities specify the number of units to be produced for each product or variant within a given time period. This component ensures that you meet customer demand without overproducing or underproducing.
- Demand Forecasting: Estimating the number of units needed based on market demand and historical data.
- Capacity Planning: Ensuring that the manufacturing facilities can handle the production volume.
- Inventory Levels: Balancing production to maintain optimal inventory levels, avoiding both shortages and excess stock.
Accurate production quantities help maintain a smooth workflow, optimize resource use, and meet customer expectations efficiently.
Importance of Master Production Schedule
MPS is an integral part of an Enterprise Resource Planning system. It provides the most effective planning functionality by extracting the actual demand and supply data to deliver precise production plans.
These plans assist manufacturers in quickly achieving their production goals and minimizing the cost incurred on the procurement.
While performing calculations of operating expenses, it pays special heed to the manufacturing capacity of the production plant.
Automatic initiation of the Material Requirements Planning management process and generation of the purchase order take place soon after the production orders’ analysis and approval.
Aside from all these implications, it acts as a protective barrier against shortages, unexpected scheduling snafus, and inefficient allocation of resources.
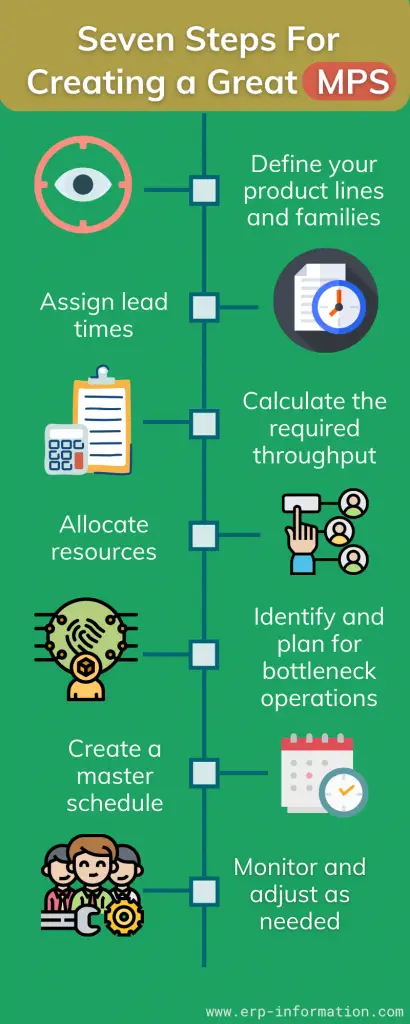
Seven Proven Steps for Creating Great MPS
1. Define your product lines and families
Product lines represent different categories of products, while product families represent similar products within a line. You’ll need to define both to create an accurate MPS.
2. Assign lead times
Lead times are the time it takes from when you place an order until you receive the product. You’ll need to know this information to calculate your required throughputs (more on that later).
3. Calculate the required throughput
The required throughput is the number of products you must produce daily to meet customer demand. This figure can vary depending on your business and production needs, so it’s important to calculate it accurately.
4. Allocate resources
Once you know the throughputs needed for each product line/family, you’ll need to allocate the necessary resources (staff, equipment, etc.) to meet those demands.
5. Identify and plan for bottleneck operations
A bottleneck operation is an area of your production process that’s unable to meet customer demand. You’ll need to identify these areas and determine how much additional capacity you need to meet demand.
6. Create a master schedule
This is where the real work of creating an MPS begins. Using steps one through five information, create a master schedule that shows when the company will produce each product line/family.
7. Monitor and adjust as needed
As with any plan, your schedule will require regular monitoring and adjustment to meet your business needs. So make sure to revisit the previous step regularly to ensure that your master schedule is up-to-date.
Following these seven steps, you can create a master production schedule to help your business run more smoothly and efficiently.
Three Tips for Creating MPS
Create a realistic schedule
One of the most important things to remember when creating your master production schedule is to be realistic about the amount of product. Don’t try to cram too many items into your schedule, or you’ll overschedule yourself and run into problems.
Start with your high-priority items
When creating your master production plan, start by listing the most necessary items for your business. These items should be at the top of your list and given priority treatment.
Break down each task into smaller steps
When creating a master production schedule, it’s important to break each task down into smaller steps to estimate better how much time it will take to complete. This will help you ensure that each job is completed on time.
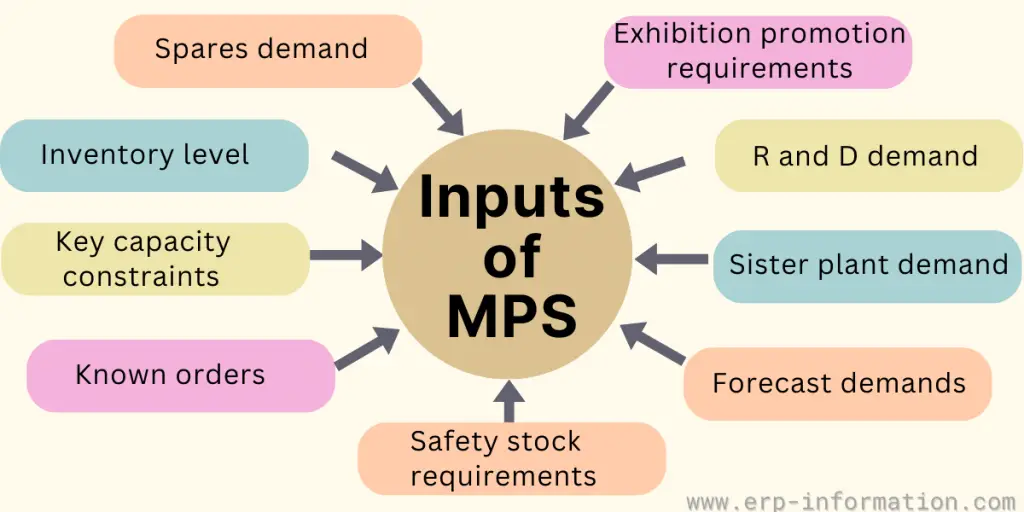
Inputs to MPS
Following is the list of inputs,
- Forecast demands
- Known orders
- Key capacity constraints
- Inventory level
- Spares demand
- Safety stock requirements
- Exhibition promotion requirements
- R & D demands
- Sister plant demand
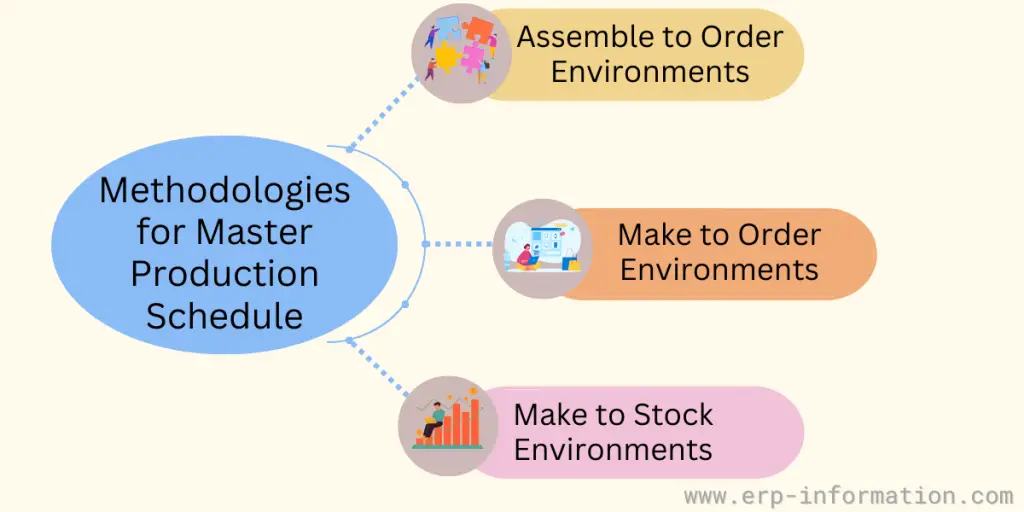
Different Methodologies for Master Production Scheduling
We call it master production schedule techniques also. The production schedule decides how to make things using all the resources that are currently available. Therefore, if too many items are in the MPS, it won’t work for those who make things.
Another problem is that if the MPS doesn’t have enough details, then there might not be enough things made. Usually, you can only use a Master Production Schedule if there aren’t too many product choices.
Make-to-Stock Environments
In this specialized scenario, a minimal quantity of items is assembled to form a more significant number of components. The Master Production schedule would finish valuable items.
Make-to-Order or Build-to-Order Environments
In this case, various finishing goods are made from minimal raw materials. One of the great examples of this case is the manufacturing process of automobile vehicles.
The main aim of the Master Production Schedule in the Make-to-Order environment would be the periodic arrangement of the actual customer orders.
Assemble-to-Order Environments
Assemble-to-order environments utilize raw materials to produce subassemblies and essential components effectively. These components and sub-assemblies work in harmony to form various finishing goods. The Master Production schedule should emphasize the subassembly level in this technological environment.
MPS in each of these scenarios emphasizes the specific area.
Common Reports of MPS
Master production schedules are typically reported on to track and optimize goods manufacturing. These reports provide visibility into the current state of production and help identify issues or opportunities to better plan for the future.
Common master production schedule reports include Available-to-Promise, Demand Tracking Reports, Forecast Data Reports, Schedule vs. Actual Output Reports, and Build Schedule Reports.
- Available-to-Promise – The report provides a picture of available-to-promise quantities for every MPS item.
- Demand Tracking Report – Gives historical information on actual shipment and order bookings compared with management forecast.
- Forecast Data Report – It summarizes the difference between forecast and actual demand.
- Schedule vs. Actual Output – Compares actual output with the scheduled output of a specific work center.
- Build Schedule Report – Provides a report of the build schedule for all assemblies.
Benefits of Master Production Schedule
- It provides an effective and reliable communication skills conduit with the sales team to facilitate the planning process.
- Effectively reduce the time incurred in the manufacturing process throughout the year.
- It acts as an effective barrier against the shortage of raw materials and any unexpected mishap.
- Make necessary adjustments to address the demand fluctuation while reducing the waste properly.
- It managed the cost incurred on manufacturing on behalf of the business owner and made the most precise calculation about the raw material requirements.
- It enhances the overall efficiency in the location of production resources.
- It is a foundation to construct, improve, and track the sales forecast.
- It helps the organization’s account department reach income and expenses by providing account statements like profit & loss statements and balance sheets.
- It helps in the calculation of inventory levels.
Functions of MPS
The software system of Master Production Scheduling possesses too many attributes. Before implementing the system of Master Production Scheduling, it is generally regarded as a good practice to analyze the critical aspects of this computerized system that facilitate production.
Here are the critical functionalities of the Master Production Scheduling software system.
Transforming Plans
This portion of the software speculates the amount of material, labor, and specialized equipment required to meet the manufacturing goal.
Provide Alternative Production Routes
The Master Production Scheduling system produces a trial-and-error schedule that gives an alternative route to accomplish the production.
That would tackle any unexpected mishap that would arise during production completion.
Utilization of Available Resources
Master Production Scheduling solution establishes the relationship between the load and utilization of the machinery and equipment deployed in the manufacturing process.
That allows for the best utilization of all the available resources and a more efficient production flow.
Establish Capacity Requirement
The Master Production Scheduling facilitates capacity planning by establishing formal capacity requirements.
Master Production Scheduling facilitates the manufacturers to obtain the proper knowledge about the requirement of capacity.
Aid in Information Processing
MPS determines the most appropriate time for delivery. It consistently coordinates with the various management information systems.
Master Production Schedule Example
Master Production Schedule (MPS) transforms the business plans into the intelligent management of the impact of seasonality, promotion, and fluctuating demand.
Here is a typical real-life example,
The pump manufacturer wants to be able to sell ready-made products within 48 hours of orders. It takes one day to make a pump, but it would take two months if they didn’t have all the necessary components.
So to make pumps within 48 hours, the pump manufacturer must have access to all the components.
Another example is the production schedule for an automobile assembly plant. The schedule begins with the arrival of raw materials and ends with the finished product rolling off the assembly line.
In between, there are dozens of steps, including cutting and welding metal. Again, the MPS makes it possible to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement.
Difference Between MPS and Production Planning & Scheduling
| Master Production Schedule | Production Planning & Scheduling |
| Provides a high-level plan focused on what to produce, when, and in what quantities. It’s more strategic and long-term. | Offers a detailed plan of how to produce, covering the allocation of resources and the specific timing of tasks. It’s more tactical and short-term. |
| Focuses on fulfilling customer orders and balancing supply and demand at a macro level. | Focuses on the efficient use of resources and the smooth operation of the production process at a micro level. |
| Typically looks at weeks to months, providing a broad timeline for production activities. | Often looks at days to weeks, offering a more immediate and detailed timeline for manufacturing tasks. |
| More rigid, as it’s based on forecasted demand and customer orders which are less likely to change frequently. | More flexible, and capable of adapting to real-time changes and disruptions on the production floor. |
FAQs
What is the production schedule?
The production schedule is the sequence of steps or operations necessary to produce a product.
The production schedule for a chocolate bar, for example, might involve the following steps:
1. Obtaining cocoa beans
2. Roasting the beans
3. Grinding the beans into a powder
4. Adding sugar and other ingredients
5. Shaping the chocolate bars and
6. Packaging the chocolate bars.
What is meant by master scheduling?
Master scheduling is creating a master production schedule, a plan that outlines the organization’s production tasks and their associated timeframes.
A master schedule is created in manufacturing and production to plan how much of each product will be produced. The plan considers future demand, the availability of resources, and the organization’s production capacity.
Master scheduling is also sometimes called aggregate planning or horizon planning. This is because it serves as a “framework” against which you can create shorter-term plans (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly production plans). It also helps ensure that the organization produces only what it can sell without excess inventory.
How is production planning different from the master production schedule?
Production planning is the phase that comes before the master production schedule. Production planning defines the higher production level and tiny details.
Production planning determines how many products should be produced. But MPS defines and decides the number of products made in a given time.
Download MPS Templates
Simple Inventory Template
General Inventory Template
Annual Template
Work Assignment Template
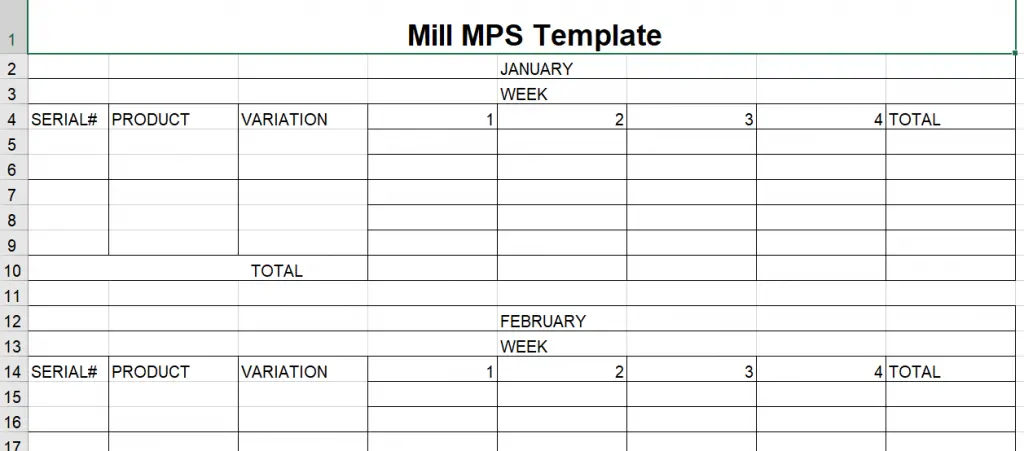
Mill Template
Conclusion
The Master Production Schedule is vital to manufacturing because it helps to plan and organize production. It also calculates the resources needed for each production goal.
It helps identify problems that may occur with production. It can help forecast demand, predict future growth, manage inventory, and ensure orders are fulfilled on time.
Having an MPS makes it easier for a company to predict customer demand, leading to fewer stock shortages and improved customer service.
References: