Do you know about RPA?
It is a process automation technology that allows employees to automate repetitive tasks using software robots, or “bots.”
It helps your company save time and money by automating simple, routine tasks. For example, employees can use bots to perform tasks such as data entry, copying and pasting text, and filling out forms.
Read out our blog post to get detailed knowledge about it. The post discloses the definition of robotic process automation, its benefits, limits, applications, and examples.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
It is the application of technology to automate tasks normally done by human beings. This software is used to create ‘bots’ that mimic human actions, and in this application, solutions allow organizations to automate various tasks.
It is often used to streamline business processes and save time and money. As a result, RPA is growing in popularity, and many businesses are now using it to improve their operations and better business outcomes.
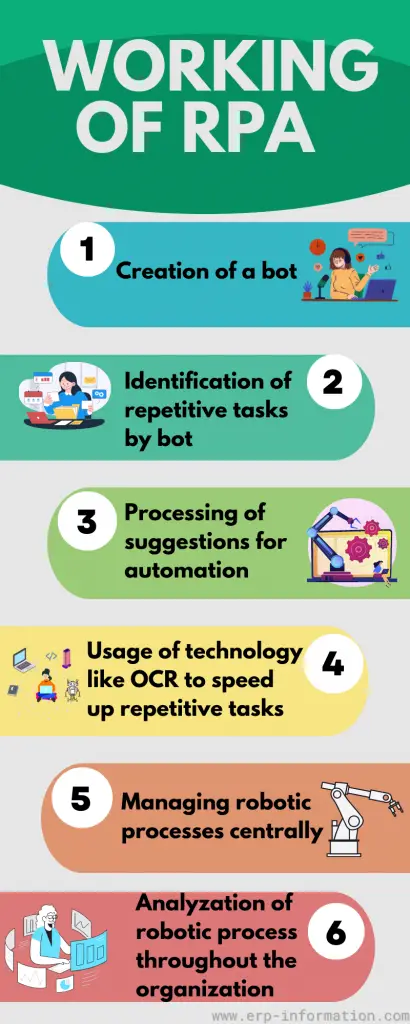
How does it work?
RPA is a form of business process automation (BPA).
It uses software applications with AI and machine learning abilities to drive high-volume, repetitive tasks that previously required humans to perform.
This software controls robots, which are digital workers programmed to do specific tasks. When an employee completes a task that can be automated, they create a “bot” or “robot” using the software.
The bot then completes the task for them according to the instructions. For example, if an employee has to copy and paste information from one document into another, they might create a bot that can do this automatically. That saves time and reduces the risk of human error.
Benefits
- Increased efficiency: When a process is automated, it can be completed faster and with fewer errors.
- Cost savings: Workflow automation reduces manual tasks and also can reduce the cost of a process by reducing the need for manual labor.
- Improved accuracy: Automating a process can improve accuracy by eliminating human error.
- Increased compliance: Process automation can help ensure that it is completed in compliance with regulations.
- Increased productivity: It helps to free up employees to work on other essential, valuable tasks.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Automated process helps to complete the task faster with no errors, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
- Increased flexibility: Automating a process can make it easier to adapt to changing conditions.
- Improved scalability: Automating a process can make it easier to scale up or down as needed.
Challenges
Understanding the business process and requirements
One of the biggest challenges is understanding the actual business process and mapping it to the robot. This is where a lot of time and effort must be put in to ensure that there isn’t any misinterpretation of what needs to be automated.
Choosing the right tool
Another big challenge is deciding which tool will work best for automating a particular process. Unfortunately, many software options are available in the market, and it can often be difficult to decide which one will fit like a glove.
Developing or finding reusable scripts
A big part of successfully implementing RPA has ready-made scripts that can be reused across processes. If these are not readily available, developing them can be a daunting task – especially if you’re unfamiliar with coding languages.
Dealing with data integration challenges
Robotic processes often need to interface with various legacy systems and databases to get all required information for automation purposes. That can lead to data integration challenges that must be overcome before anything else can happen.
Lack of skilled resources
The final challenge businesses face regarding RPA implementation is finding skilled resources to help manage and operate robots. Unfortunately, that is often a difficult and costly task, as there is currently a global shortage of these resources.
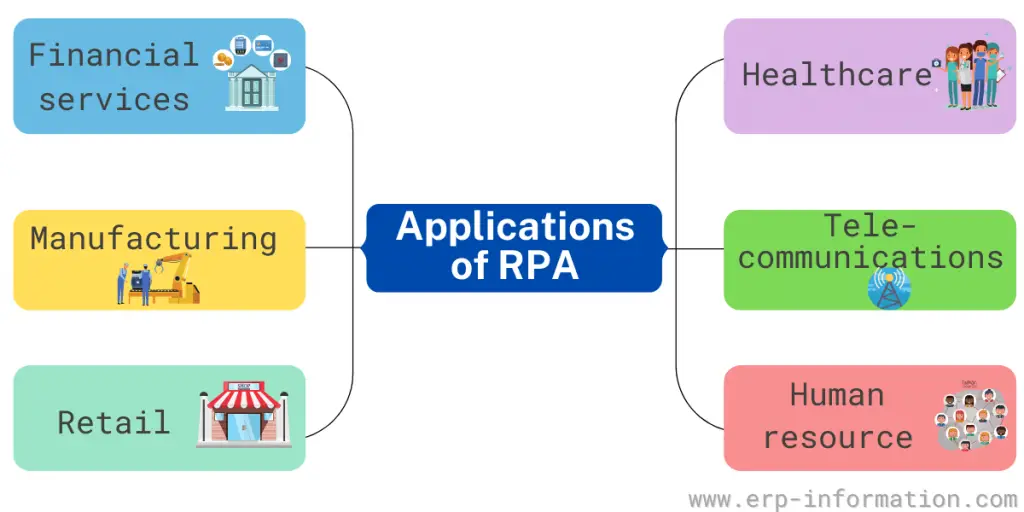
Applications
Financial services
It can help with foreign exchange payments, automating account openings and closings, managing audit requests, and processing insurance claims.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry uses this application to automate processes and repetitive tasks such as prior authorizations, patient record management, and billing.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry uses it to automate tasks in the manufacturing process, such as quality control, material handling, and assembly line tasks.
Retail
It can be used in retail for price checking, shelf stocking, and customer order processing.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications can use for customer service, fraud detection, and order processing tasks.
Human resource
This application can help with data entry, tracking employee attendance, and managing employee files.
Robotic Process Automation Examples
- Receiving customer orders and entering them into the company’s order management system
- Auditing invoices for compliance with company policy
- Processing insurance claims
- Checking inventory levels and placing orders for new stock
- Updating customer account information
- Sorting and routing incoming mail
- Responding to customer emails
- Generating reports
- Filling out online forms
- Submitting expense reports
Robotic Process Automation tools
Below are the RPA Software tools available in the market.
- IBM Robotic Process Automation
- Akabot
- SS & C Blue Prism Intelligent Automation Platform
- RocketBot
- Aiwozo
- Robocorp-Open source Gen 2 RPA
- Laiye RPA
- Appian
FAQs
What are the factors that need to be considered while choosing RPA tools?
When choosing these RPA tools, it is important to consider the following factors:
Handling capability: The tool should handle the volume of processes that need to be automated.
Integrating capability: The tool should integrate with the organization’s existing systems.
Easy to use: The tool should be easy to use and require minimal employee training.
Flexibility: The tool should be flexible to accommodate changes in business operations.
Cost: The tool should offer a reasonable price.
Are specialized skills required to automate the tasks?
RPA programming uses Low-code or No-Code to build bots. Low/No code makes designing applications easier for people of all skill levels. Instead of typing on the computer, you can drag and drop pieces of code into a workflow to create the bots.
Conclusion
Robotic process automation is an exciting and growing field with many potential applications. As we have seen, this software can be used to automate monotonous tasks, freeing up employees from other work.
In addition, These tools can help businesses improve efficiency and accuracy while reducing costs. While there are many benefits to implementing robotic process automation, it is equally important to consider the impact on jobs.
Some positions may be eliminated due to increased automation; others may be created to support the new technology.
However, with proper planning and execution, RPA software can help businesses achieve organizational goals while minimizing negative impacts on employees.