Creating a product that resonates with your customers is only half the battle in the dynamic business world.
The other half lies in ensuring your product meets their needs and expectations. That is called the ‘product acceptance.‘
Several elements contribute to effective product acceptance strategies, from setting clear and concise acceptance criteria to crafting compelling user stories.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into product acceptance, its challenges, and tips to overcome them. We’ll explore product acceptance criteria and their importance. We will also provide practical tips for drafting robust criteria and illuminate the concept of user stories and their 3C’s – Card, Conversation, and Confirmation.
What is Product Acceptance?
It is the process of ensuring that a product meets all requirements for delivery to the customer. It verifies that a given purchased or manufactured item meets specifications and is usable for its intended purpose.
It is typically conducted during or after development by verifying and validating that the product meets performance criteria and other standards such as safety and usability.
The acceptance involves testing, inspecting, and reviewing the product to ensure it meets all specifications before being released for sale or use.
Once a product has been accepted, it can be released to the market, fully deployed onsite, or used in production environments.
Factors that Affect Product Acceptance
Product characteristics
The product itself is an essential factor in finding whether or not customers will accept it. Factors such as the product’s quality, features, benefits, and price can all influence product acceptance.
For example, a product that is well-designed, high-quality, and offers unique features is more likely to be accepted by consumers than a poorly designed, low-quality product with no unique features.
Target market
The target market is also a major factor in product acceptance. Factors such as the target market’s needs, wants, and preferences can all play a role in product acceptance.
For example, a product targeted at a specific niche market is more likely to be accepted by consumers in that niche market than a product targeted at a general market.
Competitive landscape
The competitive landscape is another factor that can influence product acceptance. Factors such as the number of competitors, the quality of competing products, and competitors’ marketing strategies can all play a role in product acceptance.
For example, a product with many competitors is more likely to face challenges with product acceptance than a product with few competitors.
Challenges
Several challenges can hinder product acceptance, including:
- Competition from existing products: If already established products are in the market, it can be difficult for a new product to gain traction.
- Product-market fit: If the product does not solve a real problem for users or is not targeted to the right market, it is less likely to be accepted.
- Lack of awareness: Potential users may not know the product or understand its benefits. That is a common challenge for new and innovative products.
- Resistance to change: People are often reluctant to change their habits and adopt new products, especially if they are complex or require a learning curve.
- Technical challenges: If the product is difficult to use or has technical problems, users are less likely to adopt it.
- Cost and budget constraints: Users may not be willing to pay for the product or have the budget to do so.
- Trust: Users need to trust the product and the company behind it before they are willing to adopt it. That is especially important for products that collect personal data or that are used for sensitive tasks.
Tips to Overcome Challenges
To overcome challenges, product teams need to focus on developing products that are user-friendly, solve real problems, and offer a clear value proposition.
They must also invest in marketing and sales efforts to reach and educate potential users about the product’s benefits.
Here are some specific tips for overcoming the challenges of product acceptance:
- Educate potential users: Create clear and concise messaging highlighting your product’s benefits and how it can solve users’ problems. Use different platforms to reach potential users, including your website, social media, and email marketing.
- Offer a free trial or demo: A free trial allows potential users to test your product before they commit to buying it.
- Make it easy to use: Your product should be easy to learn and use, even for non-technical users. Provide clear documentation and support resources.
- Get feedback from users: Feedback will help you identify usability issues or areas where the product can be improved.
- Build trust: Be transparent about how your product works and how you collect and use user data. Make it easy for users to contact you with questions or concerns.
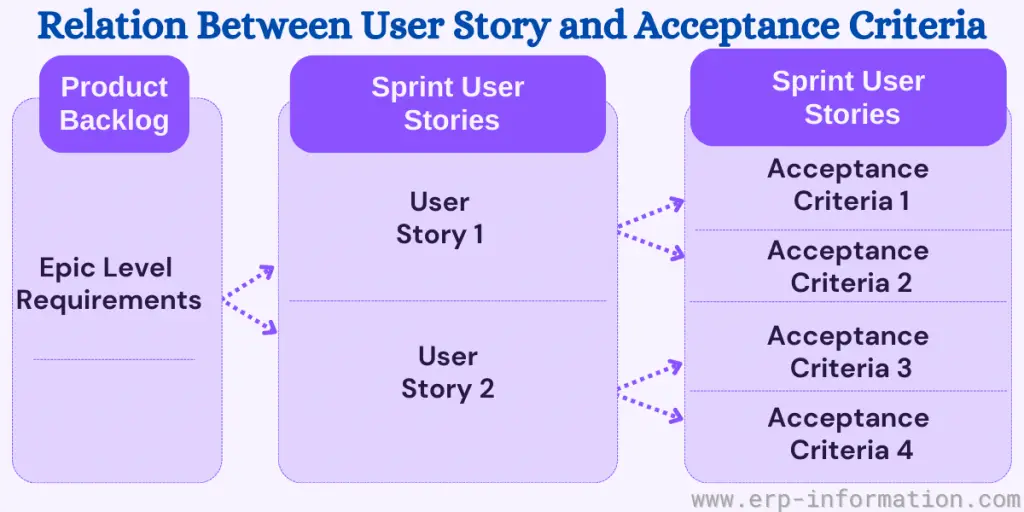
Product Acceptance Criteria
Product acceptance criteria are a set of business rules that a product or service must meet to be accepted by the user. They are distinctive for each user.
Good and realistic acceptance criteria help to avoid unwanted results in the end.
How to Set Product Acceptance Criteria?
To set acceptance criteria, you need to follow some rules. Initially, the product manufacturer sets these criteria based on the customer’s needs.
After that, the business analyst, requirement analyst, or development team member reviews these criteria with user stories. Then, the whole team discusses the user stories and acceptance criteria.
Features of Acceptance Criteria
- It should be capable of being proven right or wrong: The criteria should be able to define the result, yes or no.
- It should be short and clear: There is no need to write complete documentation. However, the criteria must be as transparent and straightforward as possible.
- It should be easily understandable: Set clear criteria, so your developers can understand it without much effort.
- It should serve the user viewpoint: Write the criteria for actual user experience.
What is a User Story?
A user story is an informal, detailed description of the product or software feature from the end-user’s point of view.
It contains the type of user, what they want, and why they want it. Usually, the client, end-user, manager, or development team member writes a user story.
It helps to describe the requirement of the product feature in a simplified manner.
You must concentrate on the necessary elements to write a compelling user story. They are who, what, and why.
Here,
- “Who” describes the type of user
- “What” means action
- “Why” describes the benefits
What does the User Story Template Look Like?
User story follows a simple template like as a < type of user>, I want <action>, so that <benefit>.
- Type of user means a person or a system who interacts with the implemented system to reach the goal.
- Action means an assurance that the user can be skilled by interacting with the system.
- Benefit means the user gets value because of the system’s interaction.
For example, As <Astha>, I want <to clean my workplace> so that<I can feel more comfortable>.
User stories may be written on an index card or small sticky notes and arranged on the table for discussion.
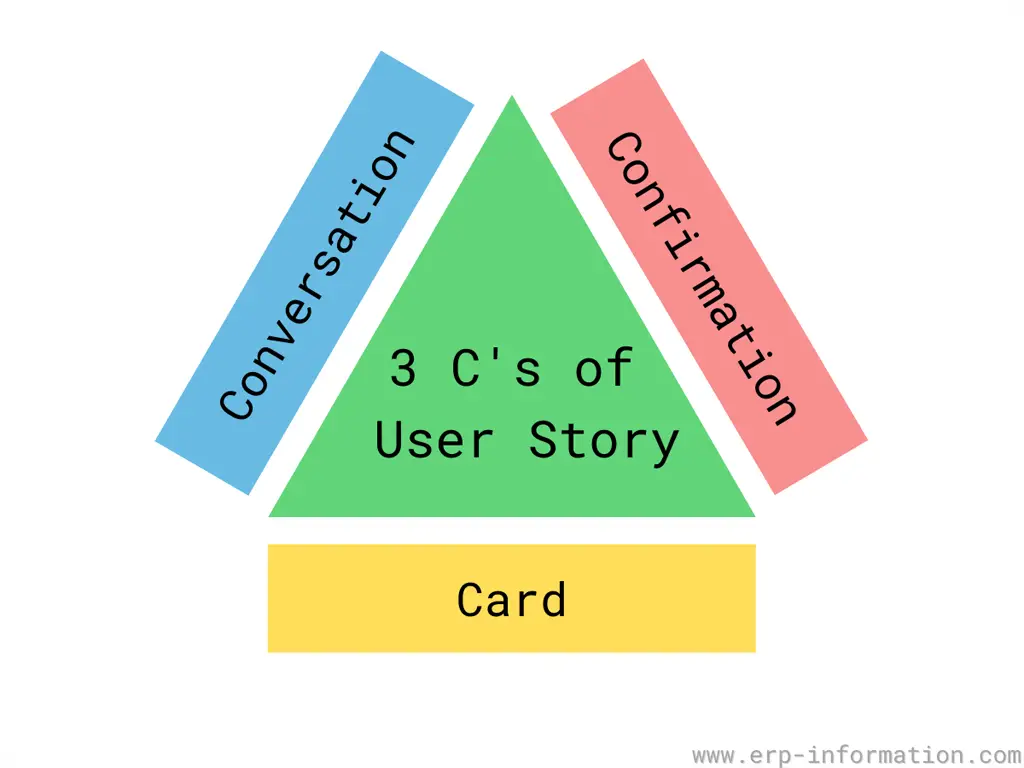
3C’s of User Story
3C’s are very important in user stories. They are card, conversation, and confirmation.
- The card contains the user story format. It must address ‘who,’ ‘what,’ and ‘why.’
- Conversation means the conference between the product owner, the end-user, team members, and other stakeholders. Most of the time, the conversation will be verbal and supported by documents.
- The product owner or end-user confirms that the story has been successfully implemented and attained the requirements.
User story plays a vital role in setting acceptance criteria for product acceptance.
Essential Tips for Writing Good Acceptance Criteria
- Before development, record the criteria: Documentation of acceptance criteria is necessary before actual development. Collect all customer needs before setting the criteria. Ensure that the specified criteria are acceptable to both parties ( vendors and buyers).
- Don’t create too short acceptance criteria: Set the AC to fetch the input but not the final solution.
- Set realistic and achievable acceptance criteria: Realistic criteria help you deliver efficiently.
- Don’t create too broad acceptance criteria: It leads to an indefinite user story.
- Don’t use technical words: Write AC in simple English so your stakeholders, team members, and managers can easily understand.
- Get consent from everyone: Communicate with your stakeholders & team members and make sure that everyone reviews AC because everyone has their point of view on solving problems.
- Create testable AC: Write AC such that the testers can easily confirm that all the requirements are met.
Importance
- It allows you to define the boundaries of a user story.
- Because of acceptance criteria, employees of a software company’s production company or development team come to know what they must do to meet customer requirements.
- It helps you to plan and estimate the project accurately.
- It acts as the basis for tests.
FAQs
How to create effective acceptance criteria?
Creating effective acceptance criteria is crucial for ensuring a successful project outcome. Here we suggest some points to craft compelling and original acceptance criteria.
1. Empathize with the End User
Begin by understanding the needs, pain points, and goals of the end users. Develop user personas to visualize different types of users who will interact with the product. This approach ensures that the acceptance criteria are user-centric and aligned with real-world scenarios.
2. Define specific and measurable criteria
Acceptance Criteria should be precise and clear, ensuring all stakeholders understand the exact expectations. Whenever possible, incorporate measurable criteria like response time, error rates, or user satisfaction to provide clear benchmarks for success.
3. Anticipate unusual scenarios
Identify and document edge cases that might not be common but are critical to the product’s reliability and robustness. This proactive approach ensures that the product performs well under various conditions.
4. Communicate with simple language
Write acceptance criteria in a straightforward manner, avoiding technical jargon. This makes the criteria accessible to all stakeholders, including non-technical team members, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Conclusion
To write good acceptance criteria, you should ensure they are realistic and achievable. Lastly, ensuring that all stakeholders review the acceptance criteria before development begins is vital.
User stories are a vital part of product development and can be extremely helpful in ensuring that all requirements are met. In addition, the 3C’s of the user story (card, conversation, and confirmation) are essential for good communication between stakeholders.
We hope this article helps you understand the importance of user stories and acceptance criteria.